Abstract
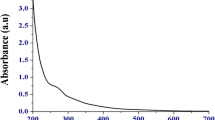
A bioreductive capacity of a plant, Terminalia arjuna leaf extract, was utilized for preparation of selenium nanoparticles. The leaf extract worked as good capping as well as stabilizing agent and facilitated the formation of stable colloidal nanoparticles. Resulting nanoparticles were characterized using UV–Vis spectrophotometer, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), respectively. The colloidal solution showed the absorption maximum at 390 nm while TEM and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) indicated the formation of polydispersed, crystalline selenium nanoparticles of size raging from 10 to 80 nm. FT-IR analysis suggested the involvement of O–H, N–H, C=O, and C–O functional group of the leaf extract in particle formation while EDAX analysis indicated the presence of selenium in synthesized nanoparticles. The effect of nanoparticles on human lymphocytes treated with arsenite, As(III), has been studied. Studies on cell viability using MTT assay and DNA damage using comet assay revealed that synthesized selenium nanoparticles showed protective effect against As(III)-induced cell death and DNA damage. Chronic ingestion of arsenic infested groundwater, and prevalence of arsenicosis is a serious public health issue. The synthesized benign nanoselenium can be a promising agent to check the chronic toxicity caused due to arsenic exposure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matthew AA, Cameron WE, Colin LR (2006) Green chemistry and the health implications of nanoparticles. Green Chem 8:417–432
Prabha S, Dubey M, Sillanpää LM (2010) Tansy fruit mediated greener synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. Process Biochem 45:1065–1071
Kumar KP, Paul W, Sharma CP (2011) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles with Zingiber officinale extract: characterization and blood compatibility. Process Biochem 46:2007–2013
Ip C, Hayes C, Budnick RM, Ganther HE (1991) Chemical form of selenium, critical metabolites, and cancer prevention. Cancer Res 51:595–600
Dhanjal S, Singh C (2010) Aerobic biogenesis of selenium nanospheres by Bacillus cereus isolated from coalmine soil. Microb Cell Fact 52:1–11
Benko I, Nagy G, Tanczos B, Ungvari E, Sztrik A, Eszenyi P, Prokisch J, Banfalvi G (2012) Subacute toxicity of nano-selenium compared to other selenium species in mice. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:2812–2820
Zhang JS, Wang HL, Yan XX, Zhang LD (2005) Comparison of short-term toxicity between nano-Se and selenite in mice. Life Sci 76:1099–1109
Wang H, Zhang J, Yu H (2007) Elemental selenium at nano size possesses lower toxicity without compromising the fundamental effect on selenoenzymes: comparison with selenomethionine in mice. Free Radic Biol Med 42:1524–1533
Zhang J, Wang X, Xu T (2008) Elemental selenium at nano size (Nano-Se) as a potential chemopreventive agent with reduced risk of selenium toxicity: comparison with se-methylselenocysteine in mice. Toxicol Sci 101:22–31
Gunter SA, Beck PA, Hallford DM (2013) Effects of supplementary selenium source on the blood parameters in beef cows and their nursing calves. Biol Trace Elem Res 152:204–211
Wang Y, Fu L (2012) Forms of selenium affect its transport, uptake and glutathione peroxidase activity in the Caco-2 cell model. Biol Trace Elem Res 149:110–116
Zheng S, Li X, Zhang Y, Xie Q, Wong YS, Zheng W Chen T (2012) PEG-nanolized ultrasmall selenium nanoparticles overcome drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells through induction of mitochondria dysfunction. Int J Nanomedicine 7:3939–3949
Ramamurthy CH, Sampath KS, Arunkumar P, Suresh KM, Sujatha V, Premkumar K, Thirunavukkarasu C (2013) Green synthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles and its augmented cytotoxicity with doxorubicin on cancer cells. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36:1131–1139
Chen T, Wong YS, Zheng W, Bai Y, Huang L (2008) Selenium nanoparticles fabricated in Undaria pinnatifida polysaccharide solutions induce mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in A375 human melanoma cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 67:26–31
Yang F, Tang Q, Zhong X, Bai Y, Chen T, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zheng W (2012) Surface decoration by Spirulina polysaccharide enhances the cellular uptake and anticancer efficacy of selenium nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 7:835–844
Luo H, Wang F, Bai Y, Chen T, Zheng W (2012) Selenium nanoparticles inhibit the growth of HeLa and MDA-MB-231 cells through induction of S phase arrest. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 94:304–308
Yu B, Zhang Y, Zheng W, Fan C, Chen T (2012) Positive surface charge enhances selective cellular uptake and anticancer efficacy of selenium nanoparticles. Inorg Chem 51:8956–8963
Wu H, Li X, Liu W, Chen T, Li Y, Zheng W, Man CWY, Wong MK, Wong KH (2012) Surface decoration of selenium nanoparticles by mushroom polysaccharides–protein complexes to achieve enhanced cellular uptake and antiproliferative activity. J Mater Chem 22:9602–9610
Bai Y, Qin B, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang Z, Zheng W (2011) Preparation and antioxidant capacity of element selenium nanoparticles sol–gel compounds. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:5012–5017
Ren Y, Zhao T, Mao G, Zhang M, Li F, Zou Y, Yang L, Wu X (2013) Antitumor activity of hyaluronic acid–selenium nanoparticles in Heps tumor mice models. Int J Biol Macromol 57:57–62
Hassanin KMA, El-Kawi SA, Khalid SH (2013) The prospective protective effect of selenium nanoparticles against chromium-induced oxidative and cellular damage in rat thyroid. Int J Nanomedicine 8:1713–1720
Sadeghian S, Kojouri GA, Mohebbi A (2012) Nanoparticles of selenium as species with stronger physiological effects in sheep in comparison with sodium selenite. Biol Trace Elem Res 146:302–308
Bao-hua X, Zi-rong X, Mei-sheng X, Cai-hong H, Yue-song D, Li X (2003) Effect of Nano red elemental selenium on GPx activity of broiler chick kidney cells in vitro. Wuhan Univ J Nat Sci 8:1161–1166
Gao X, Zhang J, Zhang L (2002) Hollow sphere selenium nanoparticles: their in-vitro anti-hydroxyl radical effect. Adv Mater 14:290–293
Peng D, Zhang J, Liu Q, Taylor EW (2007) Size effect of elemental selenium nanoparticles (Nano-Se) at supranutritional levels on selenium accumulation and glutathione S-transferase activity. J Inorg Biochem 101:1457–1463
Shi L, Xun W, Yue W, Zhang C, Ren Y, Shi L, Wang Q, Yang R, Lei F (2011) Effect of sodium selenite, Se-yeast and nano-elemental selenium on growth performance, Se concentration and antioxidant status in growing male goats. Small Rumin Res 96:49–52
Li Q, Yam VWW (2006) High-yield synthesis of selenium nanowires in water at room temperature. Chem Commun 9:1006–1008
Zhu Y, Qian Y, Huang H, Zhang M (1996) Preparation of nanometer-size selenium powders of uniform particle size by γ- irradiation. Mater Lett 28:119–122
Shah CP, Kumar M, Pushpa KK, Bajaj PN (2008) Acrylonitrile-induced synthesis of polyvinyl alcohol stabilized selenium nanoparticles. Cryst Growth Des 8:4159–4164
Li X, Li Y, Li S, Zhou W, Chu H, Chen W, Li IL, Tang Z (2005) Single crystalline trigonal selenium nanotubes and nanowires synthesized by sonochemical process. Cryst Growth Des 5:911–916
Chen Y, Zhang W, Fan Y, Xu X, Zhang Z (2006) Hydrothermal preparation of selenium nanorods. Mater Chem Phys 9:191–194
Prasad KS, Vyas P, Prajapati V, Patel P, Selvaraj K (2012) Biomimetic synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using cell-free extract of Microbacterium sp. ARB05. Micro Nano Lett 17:1–4
Li S, Shen Y, Xie A, Yu X, Zhang X, Yang L, Li C (2007) Rapid, room-temperature synthesis of amorphous selenium/protein composites using Capsicum annuum L extract. Nanotechnology 18: Article ID 405101
Shakibaie M, Khorramizadeh MR, Faramarzi MA, Sabzevari O, Shahverdi AR (2010) Biosynthesis and recovery of selenium nanoparticles and the effects on matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 58:7–15
Nriagu JO (2002) Arsenic poisoning through the ages. In: Frankenberger WT Jr (ed) Environmental chemistry of arsenic. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–26
Prasad KS, Subramanian V, Paul J (2011) Biosorption of As(III) ion on Rhodococcus sp.WB-12: Biomass characterization and kinetic studies. Separ Sci Technol 46:2517–2525
Prasad KS, Subramanian V, Paul J (2009) Purification and characterization of arsenite oxidase from Arthrobacter sp. Biometals 5:711–721
Milton AH, Hasan Z, Rahman A, Rahman M (2001) Chronic arsenic poisoning and respiratory effects in Bangladesh. J Occup Health 43:136–140
Biswas M, Biswas K, Karan TK, Bhattacharya S, Ghosh AK, Haldar PK (2011) Evaluation of analgesic and anti-inflamatory activities of Terminalia arjuna leaf. J Phytol 3:33–38
Bajpayee M, Dhawan A, Parmar D, Pandey AK, Mathur N, Seth PK (2002) Gender-related differences in basal DNA damage in lymphocytes of healthy Indian population as revealed by the alkaline comet assay. Mutat Res 520:83–91
Dhawan A, Mathur N, Seth PK (2001) The effect of smoking and eating habits on DNA damage in Indian population as measured in the comet assay. Mutat Res 474:121–128
Dhawan A, Anderson D, Pascual TS, Santos BC, Clifford MN, Ioannides C (2002) Evalution of the antigenotoxic potential of monomeric, dimeric and black tea polyphenolics against heterocyclic amine-induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes using the comet assay. Mutat Res 515:39–56
Fesharaki PJ, Nazari P, Shakibaie M, Rezaie S, Banoee M, Abdollahi M, Shahverdi AR (2010) Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Klebsiella pneumoniae and their recovery by a simple sterilization process. Braz J Microbiol 41:461–466
Lin ZH, Wang CRC (2005) Evidence on the size-dependent absorption spectral evolution of selenium nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 591–594
Shen Y, Xiufang W, Xie A, Huang L, Zhu J, Chen L (2008) Synthesis of dextran/Se nanocomposites for nanomedicine application. Mater Chem Phys 109:534–540
Chen H, Ji-Beom Y, Liu Y, Zhao G (2011) Green synthesis and characterization of se nanoparticles and nanorods. Electron Mater Lett 7:333–336
Ingole AR, Thakare SR, Khati NT, Wankhadea AV, Burghate DK (2010) Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles under ambient condition. Chalcogenide Lett 7:485–489
Mishra RR, Prajapati S, Das J, Dangar TK, Das N, Thatoi H (2011) Reduction of selenite to red elemental selenium by moderately halotolerant Bacillus megaterium strains isolated from Bhitarkanika mangrove soil and characterization of reduced product. Chemosphere 84:1231–1237
Prasad KS, Patel H, Patel T, Patel K, Selvaraj KP (2013) Biosynthesis of Se nanoparticles and its effect on UVB-induced DNA damage. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 103:261–266
Silverstein RM, Bassler GC (1962) Spectrometric identification of organic compounds. J Chem Educ 39:546–553
Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhang L (2010) Creation of highly stable selenium nanoparticles capped with hyperbranched polysaccharide in water. Langmuir 26:17617–17623
Kessel M, Liu SX, Xu A, Santella R, Hei TK (2002) Arsenic induces oxidative DNA damage in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biochem 235:301–308
Kitchin KT, Ahmad S (2003) Oxidative stress as a possible mode of action for arsenic carcinogenesis. Toxicol Lett 137:3–13
Shi H, Hudson LG, Ding W, Wang S, Cooper KL, Liu S, Chen Y, Shi X, Liu KJ (2004) Arsenite causes DNA damage in keratinocytes via generation of hydroxyl radicals. Chem Res Toxicol 17:871–878
Lantz RC, Hays AM (2006) Role of oxidative stress in arsenic-induced toxicity. Drug Metab Rev 38:791–804
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160:1–40
Andrew AS, Burgess JL, Meza MM, Demidenko E, Waugh MG, Hamilton JW, Karagas MR (2006) Arsenic exposure is associated with decreased DNA repair in vitro and in individuals exposed to drinking water arsenic. Environ Health Perspect 114:1193–1198
Witkiewicz-Kucharczyk A, Bal W (2006) Damage of zinc fingers in DNA repair proteins, a novel molecular mechanism in carcinogenesis. Toxicol Lett 162:29–42
DuMond JW Jr, Singh KP (2007) Gene expression changes and induction of cell proliferation by chronic exposure to arsenic of mouse testicular Leydig cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A 70:1150–1154
Lehmann GM, McCabe MJ Jr (2007) Arsenite slows S phase progression via inhibition of cdc25A dual specificity phosphatase gene transcription. Toxicol Sci 99:70–78
Biswas R, Poddar S, Mukherjee A (2007) Investigation on the genotoxic effects of long-term administration of sodium arsenite in bone marrow and testicular cells in vivo using the comet assay. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 26:29–37
Raisuddin S, Jha AN (2004) Relative sensitivity of fish and mammalian cells to sodium arsenate and arsenite as determined by alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis and cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay. Environ Mol Mutagen 44:83–9
Anderson D, Plewa MJ (1998) The International Comet Assay Workshop. Mutagenesis 13:67–73
Waters DJ, Shen S, Cooley DM, Bostwick DG, Qian J, Gerald F, Jr C, Glickman LT, Oteham C, Schlittler DJ, Steven M (2003) Effects of dietary selenium supplementation on DNA damage and Apoptosis in canine prostate. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:237–241
Acknowledgments
K.S.P. is grateful to Dr. C. L. Patel, Chairman, Charutar Vidyamandal, and Mr. Vipul J. Patel, senior scientific officer at DST (Department of Science and Technology) sponsored SICART (Sophisticated Instrumentation Center for Applied Research and Testing) Anand, Gujarat, India, for their help in analysis of samples. Authors would like to express their deepest gratitude to Prof. C. G. Joshi and Ms. Manisha Patel, Department of Veterinary Science, AAU, Anand, for their help in comet assay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, K.S., Selvaraj, K. Biogenic Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles and Their Effect on As(III)-Induced Toxicity on Human Lymphocytes. Biol Trace Elem Res 157, 275–283 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9891-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9891-0