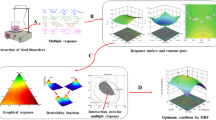
Abstract
Response surface methodology (RSM) is a technique widely used to optimize various processes. This review presents the state-of-the-art applications of RSM in the optimization of different food processes such as extraction, drying, blanching, enzymatic hydrolysis and clarification, production of microbial metabolites, and formulation. The principles of RSM, its implementation steps, and different designs (full factorial design (FFD), Box-Behnken design (BBD), and central composite design (CCD)) are described. Furthermore, this work presents a comprehensive study of RSM literature recently published about the various food process fields and evaluating their RSM elements summarized in tables. Finally, the challenges and future prospects of using this statistical technique in the food industry processes are discussed. It can be concluded that appropriate selection of RSM design, independent variables (screening), and levels of the factors significantly influences the successful application of RSM. In addition, validity evaluation of the optimum conditions predicted through RSM is crucial too.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Fattah, Y. R. (2002). Optimization of thermostable lipase production from a thermophilic Geobacillus sp. using Box-Behnken experimental design. Biotechnology Letters, 24(14), 1217–1222.
Abu-Izza, K. A., Garcia-Contreras, L., & Lu, D. R. (1996). Preparation and evaluation of sustained release AZT-loaded microspheres: optimization of the release characteristics using response surface methodology. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 85(2), 144–149.
Açıkel, Ü., Erşan, M., & Açıkel, Y. S. (2010). Optimization of critical medium components using response surface methodology for lipase production by Rhizopus delemar. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 88(1), 31–39.
Acosta, O., Víquez, F., & Cubero, E. (2008). Optimisation of low calorie mixed fruit jelly by response surface methodology. Food Quality and Preference, 19(1), 79–85.
Ade-Omowaye, B., Rastogi, N., Angersbach, A., & Knorr, D. (2002). Osmotic dehydration behavior of red paprika (Capsicum annuum L.). Journal of Food Science, 67(5), 1790–1796.
Agatonovic-Kustrin, S., Zecevic, M., Zivanovic, L., & Tucker, I. (1998). Application of neural networks for response surface modeling in HPLC optimization. Analytica Chimica Acta, 364(1), 265–273.
Ahn, J.-H., Kim, Y.-P., Lee, Y.-M., Seo, E.-M., Lee, K.-W., & Kim, H.-S. (2008). Optimization of microencapsulation of seed oil by response surface methodology. Food Chemistry, 107(1), 98–105.
Alam, M. S., Amarjit, S., & Sawhney, B. (2010). Response surface optimization of osmotic dehydration process for aonla slices. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 47(1), 47–54.
Aliakbarian, B., De Faveri, D., Converti, A., & Perego, P. (2008). Optimisation of olive oil extraction by means of enzyme processing aids using response surface methodology. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 42(1), 34–40.
Alizadeh, M., Hamedi, M., & Khosroshahi, A. (2005). Optimizing sensorial quality of Iranian white brine cheese using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Science, 70(4), S299–S303.
Alvarez, M. D., & Canet, W. (1999). Optimization of stepwise blanching of frozen-thawed potato tissues (cv. Monalisa). European Food Research and Technology, 210(2), 102–108.
Assadpour, E., Maghsoudlou, Y., Jafari, S.-M., Ghorbani, M., & Aalami, M. (2016). Optimization of folic acid nano-emulsification and encapsulation by maltodextrin-whey protein double emulsions. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 86, 197–207.
Bai, X. L., Yue, T. L., Yuan, Y. H., & Zhang, H. W. (2010). Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenols from apple pomace using response surface methodology and HPLC analysis. Journal of Separation Science, 33(23–24), 3751–3758.
Baş, D., & Boyacı, İ. H. (2007). Modeling and optimization I: usability of response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 78(3), 836–845.
Beg, Q. K., Sahai, V., & Gupta, R. (2003). Statistical media optimization and alkaline protease production from Bacillus mojavensis in a bioreactor. Process Biochemistry, 39(2), 203–209.
Bezerra, M. A., Santelli, R. E., Oliveira, E. P., Villar, L. S., & Escaleira, L. A. (2008). Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta, 76(5), 965–977.
Bimakr, M., Rahman, R. A., Ganjloo, A., Taip, F. S., Salleh, L. M., & Sarker, M. Z. I. (2012). Optimization of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of bioactive flavonoid compounds from spearmint (Mentha spicata L.) leaves by using response surface methodology. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(3), 912–920.
Bocchini, D., Alves-Prado, H., Baida, L., Roberto, I., Gomes, E., & Da Silva, R. (2002). Optimization of xylanase production by Bacillus circulans D1 in submerged fermentation using response surface methodology. Process Biochemistry, 38(5), 727–731.
Box, G. E., & Behnken, D. W. (1960). Some new three level designs for the study of quantitative variables. Technometrics, 2(4), 455–475.
Box, G. E., & Wilson, K. (1951). On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), 13(1), 1–45.
Baranda, A. B., Etxebarria, N., Jimenez, R. M., & Alonso, R. M. (2005). Development of a liquid–liquid extraction procedure for five 1, 4-dihydropyridines calcium channel antagonists from human plasma using experimental design. Talanta, 67(5), 933–941.
Bruns, R. E., Scarminio I. S., & de Barros Neto, B. (2006). Statistical design-chemometrics (vol. 25): Elsevier
Burande, R. R., Kumbhar, B. K., Ghosh, P. K., & Jayas, D. S. (2008). Optimization of fluidized bed drying process of green peas using response surface methodology. Drying Technology, 26(7), 920–930.
Cao, H., Zhang, M., Mujumdar, A. S., Du, W. H., & Sun, J. C. (2006). Optimization of osmotic dehydration of kiwifruit. Drying Technology, 24(1), 89–94.
Cheison, S. C., Wang, Z., & Xu, S.-Y. (2007). Use of response surface methodology to optimise the hydrolysis of whey protein isolate in a tangential flow filter membrane reactor. Journal of Food Engineering, 80(4), 1134–1145.
Chen, K.-N., Chen, M.-J., & Lin, C.-W. (2006). Optimal combination of the encapsulating materials for probiotic microcapsules and its experimental verification (R1). Journal of Food Engineering, 76(3), 313–320.
Chen, K. N., Chen, M. J., Liu, J. R., Lin, C. W., & Chiu, H. Y. (2005). Optimization of incorporated prebiotics as coating materials for probiotic microencapsulation. Journal of Food Science, 70(5), M260–M266.
Chen, Q., He, G., & Ali, M. A. (2002). Optimization of medium composition for the production of elastase by Bacillus sp. EL31410 with response surface methodology. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 30(5), 667–672.
Chen, X., Xu, F., Qin, W., Ma, L., & Zheng, Y. (2012). Optimization of enzymatic clarification of green asparagus juice using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Science, 77(6), C665–C670.
Cladera-Olivera, F., Caron, G., & Brandelli, A. (2004). Bacteriocin production by Bacillus licheniformis strain P40 in cheese whey using response surface methodology. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 21(1), 53–58.
Coman, G., & Bahrim, G. (2011). Optimization of xylanase production by Streptomyces sp. P12-137 using response surface methodology and central composite design. Annals of Microbiology, 61(4), 773–779.
Cubas, C., Lobo, M. G., & González, M. (2008). Optimization of the extraction of chlorophylls in green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by N, N-dimethylformamide using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 21(2), 125–133.
Deepak, V., Kalishwaralal, K., Ramkumarpandian, S., Babu, S. V., Senthilkumar, S., & Sangiliyandi, G. (2008). Optimization of media composition for Nattokinase production by Bacillus subtilis using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 99(17), 8170–8174.
Dutta, J. R., Dutta, P. K., & Banerjee, R. (2004). Optimization of culture parameters for extracellular protease production from a newly isolated Pseudomonas sp. using response surface and artificial neural network models. Process Biochemistry, 39(12), 2193–2198.
Erbay, Z., & Icier, F. (2009). Optimization of hot air drying of olive leaves using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 91(4), 533–541.
Eren, İ., & Kaymak-Ertekin, F. (2007). Optimization of osmotic dehydration of potato using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 79(1), 344–352.
Esmaeili, M., Yolmeh, M., Shakerardakani, A., & Golivari, H. (2015). A central composite design for the optimizing lipase and protease production from Bacillus subtilis PTCC 1720. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 4(3), 349–354.
Fan, G., Han, Y., Gu, Z., & Chen, D. (2008). Optimizing conditions for anthocyanins extraction from purple sweet potato using response surface methodology (RSM). LWT-Food Science and Technology, 41(1), 155–160.
Felberg, I., Deliza, R., Farah, A., Calado, E., & Donangelo, C. (2010). Formulation of a soy–coffee beverage by response surface methodology and internal preference mapping. Journal of Sensory Studies, 25(s1), 226–242.
Fernández, C., Dolores Alvarez, M., & Canet, W. (2006). The effect of low-temperature blanching on the quality of fresh and frozen/thawed mashed potatoes. International journal of food science & technology, 41(5), 577–595.
Francis, F., Sabu, A., Nampoothiri, K. M., Ramachandran, S., Ghosh, S., Szakacs, G., & Pandey, A. (2003). Use of response surface methodology for optimizing process parameters for the production of α-amylase by Aspergillus oryzae. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 15(2), 107–115.
Gallagher, E., O’Brien, C., Scannell, A., & Arendt, E. (2003). Use of response surface methodology to produce functional short dough biscuits. Journal of Food Engineering, 56(2), 269–271.
Gan, C.-Y., & Latiff, A. A. (2011). Optimisation of the solvent extraction of bioactive compounds from Parkia speciosa pod using response surface methodology. Food Chemistry, 124(3), 1277–1283.
Gan, C.-Y., Manaf, N. H. A., & Latiff, A. A. (2010). Optimization of alcohol insoluble polysaccharides (AIPS) extraction from the Parkia speciosa pod using response surface methodology (RSM). Carbohydrate Polymers, 79(4), 825–831.
Gangadharan, D., Sivaramakrishnan, S., Nampoothiri, K. M., Sukumaran, R. K., & Pandey, A. (2008). Response surface methodology for the optimization of alpha amylase production by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Bioresource Technology, 99(11), 4597–4602.
Gao, L., & Mazza, G. (1996). Extraction of anthocyanin pigments from purple sunflower hulls. Journal of Food Science, 61(3), 600–603.
Garrote, R. L., Silva, E. R., Bertone, R. A., & Roa, R. D. (2004). Predicting the end point of a blanching process. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 37(3), 309–315.
Ge, Y., Ni, Y., Yan, H., Chen, Y., & Cai, T. (2002). Optimization of the supercritical fluid extraction of natural vitamin E from wheat germ using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Science, 67(1), 239–243.
Gfrerer, M., & Lankmayr, E. (2005). Screening, optimization and validation of microwave-assisted extraction for the determination of persistent organochlorine pesticides. Analytica Chimica Acta, 533(2), 203–211.
Gharibzahedi, S. M. T., Mousavi, S. M., Hamedi, M., & Ghasemlou, M. (2012). Response surface modeling for optimization of formulation variables and physical stability assessment of walnut oil-in-water beverage emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids, 26(1), 293–301.
Ghorbannezhad, P., Bay, A., Yolmeh, M., Yadollahi, R., & Moghadam, J. Y. (2016). Optimization of coagulation–flocculation process for medium density fiberboard (MDF) wastewater through response surface methodology. Desalination and Water Treatment, 1–16. doi:10.1080/19443994.2016.1170636.
Gong, Y., Hou, Z., Gao, Y., Xue, Y., Liu, X., & Liu, G. (2012). Optimization of extraction parameters of bioactive components from defatted marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) residue using response surface methodology. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 90(1), 9–16.
Guo, W.-Q., Ren, N.-Q., Wang, X.-J., Xiang, W.-S., Ding, J., You, Y., & Liu, B.-F. (2009). Optimization of culture conditions for hydrogen production by Ethanoligenens harbinense B49 using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 100(3), 1192–1196.
Han, Q.-H., Yin, L.-J., Li, S.-J., Yang, B.-N., & Ma, J.-W. (2010). Optimization of process parameters for microwave vacuum drying of apple slices using response surface method. Drying Technology, 28(4), 523–532.
He, Y.-Q., & Tan, T.-W. (2006). Use of response surface methodology to optimize culture medium for production of lipase with Candida sp. 99-125. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 43(1), 9–14.
Huang, Y.-B., Tsai, Y.-H., Lee, S.-H., Chang, J.-S., & Wu, P.-C. (2005). Optimization of pH-independent release of nicardipine hydrochloride extended-release matrix tablets using response surface methodology. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 289(1), 87–95.
Huynh, T. V., Caffin, N., Dykes, G. A., & Bhandari, B. (2008). Optimization of the microencapsulation of lemon myrtle oil using response surface methodology. Drying Technology, 26(3), 357–368.
Ismail, N., & Revathi, R. (2006). Studies on the effects of blanching time, evaporation time, temperature and hydrocolloid on physical properties of chili (Capsicum annum var kulai) puree. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 39(1), 91–97.
Jackson, J. C., Bourne, M. C., & Barnard, J. (1996). Optimization of blanching for crispness of banana chips using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Science, 61(1), 165–166.
Jafari, S. M., Assadpoor, E., He, Y., & Bhandari, B. (2008). Encapsulation efficiency of food flavours and oils during spray drying. Drying Technology, 26(7), 816–835.
Juntachote, T., Berghofer, E., Bauer, F., & Siebenhandl, S. (2006). The application of response surface methodology to the production of phenolic extracts of lemon grass, galangal, holy basil and rosemary. International journal of food science & technology, 41(2), 121–133.
Karazhiyan, H., Razavi, S. M., & Phillips, G. O. (2011). Extraction optimization of a hydrocolloid extract from cress seed (Lepidium sativum) using response surface methodology. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(5), 915–920.
Kasankala, L. M., Xue, Y., Weilong, Y., Hong, S. D., & He, Q. (2007). Optimization of gelatine extraction from grass carp (Catenopharyngodon idella) fish skin by response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 98(17), 3338–3343.
Katapodis, P., Christakopoulou, V., Kekos, D., & Christakopoulos, P. (2007). Optimization of xylanase production by Chaetomium thermophilum in wheat straw using response surface methodology. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 35(2), 136–141.
Kaur, D., Wani, A. A., Oberoi, D., & Sogi, D. (2008). Effect of extraction conditions on lycopene extractions from tomato processing waste skin using response surface methodology. Food Chemistry, 108(2), 711–718.
Kaur, S., Sarkar, B., Sharma, H., & Singh, C. (2009). Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis pretreatment conditions for enhanced juice recovery from guava fruit using response surface methodology. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2(1), 96–100.
Kaushik, R., Saran, S., Isar, J., & Saxena, R. (2006). Statistical optimization of medium components and growth conditions by response surface methodology to enhance lipase production by Aspergillus carneus. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 40(3), 121–126.
Kha, T. C., Nguyen, M. H., Roach, P. D., & Stathopoulos, C. E. (2014). Microencapsulation of gac oil by spray drying: optimization of wall material concentration and oil load using response surface methodology. Drying Technology, 32(4), 385–397.
Khazaei, K. M., Jafari, S., Ghorbani, M., Kakhki, A. H., & Sarfarazi, M. (2016). Optimization of anthocyanin extraction from saffron petals with response surface methodology. Food Analytical Methods, 9(7), 1993–2001.
Kim, M.-S., Kim, J.-S., You, Y.-H., Park, H. J., Lee, S., Park, J.-S., & Hwang, S.-J. (2007). Development and optimization of a novel oral controlled delivery system for tamsulosin hydrochloride using response surface methodology. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 341(1), 97–104.
Ko, J., Park, H. J., Park, Y., Hwang, S., & Park, J. (2003). Chitosan microparticle preparation for controlled drug release by response surface methodology. Journal of Microencapsulation, 20(6), 791–797.
Kumar, D., Prasad, S., & Murthy, G. S. (2014). Optimization of microwave-assisted hot air drying conditions of okra using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 51(2), 221–232.
Kunamneni, A., & Singh, S. (2005). Response surface optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of maize starch for higher glucose production. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 27(2), 179–190.
Kurozawa, L., Park, K., & Hubinger, M. (2008). Optimization of the enzymatic hydrolysis of chicken meat using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Science, 73(5), C405–C412.
Lee, W., Yusof, S., Hamid, N. S. A., & Baharin, B. S. (2006). Optimizing conditions for enzymatic clarification of banana juice using response surface methodology (RSM). Journal of Food Engineering, 73(1), 55–63.
Li, X., Liu, Z., & Chi, Z. (2008). Production of phytase by a marine yeast Kodamaea ohmeri BG3 in an oats medium: optimization by response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 99(14), 6386–6390.
Liew, S. L., Ariff, A., Raha, A., & Ho, Y. (2005). Optimization of medium composition for the production of a probiotic microorganism, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, using response surface methodology. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 102(2), 137–142.
Lin, Y.-P., Lee, T.-Y., Tsen, J.-H., & King, V. A.-E. (2007). Dehydration of yam slices using FIR-assisted freeze drying. Journal of Food Engineering, 79(4), 1295–1301.
Liu, J.-Z., Weng, L.-P., Zhang, Q.-L., Xu, H., & Ji, L.-N. (2003). Optimization of glucose oxidase production by Aspergillus niger in a benchtop bioreactor using response surface methodology. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19(3), 317–323.
Lundstedt, T., Seifert, E., Abramo, L., Thelin, B., Nyström, Å., Pettersen, J., & Bergman, R. (1998). Experimental design and optimization. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 42(1), 3–40.
Madamba, P. S. (2002). The response surface methodology: an application to optimize dehydration operations of selected agricultural crops. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 35(7), 584–592.
Maran, J. P., & Manikandan, S. (2012). Response surface modeling and optimization of process parameters for aqueous extraction of pigments from prickly pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) fruit. Dyes and Pigments, 95(3), 465–472.
Martinez, B., Rincón, F., Ibáñez, M., & BELLÁN, P. (2004). Improving the nutritive value of homogenized infant foods using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Science, 69(1), SNQ38–SNQ43.
Masmoudi, M., Besbes, S., Chaabouni, M., Robert, C., Paquot, M., Blecker, C., & Attia, H. (2008). Optimization of pectin extraction from lemon by-product with acidified date juice using response surface methodology. Carbohydrate Polymers, 74(2), 185–192.
McCarthy, D., Gallagher, E., Gormley, T., Schober, T., & Arendt, E. (2005). Application of response surface methodology in the development of gluten-free bread. Cereal Chemistry, 82(5), 609–615.
Mestdagh, F., De Wilde, T., Fraselle, S., Govaert, Y., Ooghe, W., Degroodt, J.-M., & De Meulenaer, B. (2008). Optimization of the blanching process to reduce acrylamide in fried potatoes. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 41(9), 1648–1654.
Mirmoghtadaie, L., Ensafi, A. A., Kadivar, M., & Norouzi, P. (2013). Highly selective electrochemical biosensor for the determination of folic acid based on DNA modified-pencil graphite electrode using response surface methodology. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 33(3), 1753–1758.
Montgomery, D. C. (2008). Design and analysis of experiments: John Wiley & Sons.
Moulai Mostefa, N., Hadj Sadok, A., Sabri, N., & Hadji, A. (2006). Determination of optimal cream formulation from long-term stability investigation using a surface response modelling. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 28(3), 211–218.
Moyo, S., Gashe, B., Collison, E., & Mpuchane, S. (2003). Optimising growth conditions for the pectinolytic activity of Kluyveromyces wickerhamii by using response surface methodology. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 85(1), 87–100.
Muralidhar, R., Chirumamila, R., Marchant, R., & Nigam, P. (2001). A response surface approach for the comparison of lipase production by Candida cylindracea using two different carbon sources. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 9(1), 17–23.
Myers, R. H., Montgomery, D. C., & Anderson-Cook, C. M. (2016). Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments: John Wiley & Sons.
Mylonaki, S., Kiassos, E., Makris, D. P., & Kefalas, P. (2008). Optimisation of the extraction of olive (Olea europaea) leaf phenolics using water/ethanol-based solvent systems and response surface methodology. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 392(5), 977–985.
Neifar, M., ELLOUZE-GHORBEL, R., Kamoun, A., Baklouti, S., Mokni, A., Jaouani, A., & ELLOUZE-CHAABOUNI, S. (2011). Effective clarification of pomegranate juice using laccase treatment optimized by response surface methodology followed by ultrafiltration. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 34(4), 1199–1219.
Nikerel, İ. E., Öner, E., Kirdar, B., & Yildirim, R. (2006). Optimization of medium composition for biomass production of recombinant Escherichia coli cells using response surface methodology. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 32(1), 1–6.
Novotná, K., Havliš, J., & Havel, J. (2005). Optimisation of high performance liquid chromatography separation of neuroprotective peptides: fractional experimental designs combined with artificial neural networks. Journal of Chromatography A, 1096(1), 50–57.
Nur’Aliaa, A., Siti Mazlina, M., Taip, F. S., & Liew Abdullah, A. (2010). Response surface optimization for clarification of white pitaya juice using a commercial enzyme. Journal of Food Process Engineering, 33(2), 333–347.
Ozdemir, M., Ozen, B. F., Dock, L. L., & Floros, J. D. (2008). Optimization of osmotic dehydration of diced green peppers by response surface methodology. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 41(10), 2044–2050.
Pappa, I., Bloukas, J., & Arvanitoyannis, I. (2000). Optimization of salt, olive oil and pectin level for low-fat frankfurters produced by replacing pork backfat with olive oil. Meat Science, 56(1), 81–88.
Peričin, D., Radulović-Popović, L., Vaštag, Ž., Mađarev-Popović, S., & Trivić, S. (2009). Enzymatic hydrolysis of protein isolate from hull-less pumpkin oil cake: application of response surface methodology. Food Chemistry, 115(2), 753–757.
Pompeu, D., Silva, E., & Rogez, H. (2009). Optimisation of the solvent extraction of phenolic antioxidants from fruits of Euterpe oleracea using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 100(23), 6076–6082.
Puri, S., Beg, Q. K., & Gupta, R. (2002). Optimization of alkaline protease production from Bacillus sp. by response surface methodology. Current Microbiology, 44(4), 286–290.
Quintero-Ramos, A., Bourne, M., Barnard, J., & ANZALDÚA-MORALES, A. (1998). Optimization of low temperature blanching of frozen jalapeño pepper (Capsicum annuum) using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Science, 63(3), 519–522.
Rai, P., Majumdar, G., Dasgupta, S., & De, S. (2004). Optimizing pectinase usage in pretreatment of mosambi juice for clarification by response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 64(3), 397–403.
Ratnam, B., Rao, M. N., Rao, M. D., Rao, S. S., & Ayyanna, C. (2003). Optimization of fermentation conditions for the production of ethanol from sago starch using response surface methodology. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19(5), 523–526.
Reyes-Moreno, C., Parra-Inzunza, M. A., Milán-Carrillo, J., & Zazueta-Niebla, J. A. (2002). A response surface methodology approach to optimise pretreatments to prevent enzymatic browning in potato (Solanum tuberosum L) cubes. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 82(1), 69–79.
Rezzoug, S.-A., Boutekedjiret, C., & Allaf, K. (2005). Optimization of operating conditions of rosemary essential oil extraction by a fast controlled pressure drop process using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 71(1), 9–17.
Rodrigues, L., Teixeira, J., Oliveira, R., & Van Der Mei, H. C. (2006). Response surface optimization of the medium components for the production of biosurfactants by probiotic bacteria. Process Biochemistry, 41(1), 1–10.
Rodrigues, S., Pinto, G. A., & Fernandes, F. A. (2008). Optimization of ultrasound extraction of phenolic compounds from coconut (Cocos nucifera) shell powder by response surface methodology. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 15(1), 95–100.
Rodríguez-Nogales, J. M., Ortega, N., Perez-Mateos, M., & Busto, M. D. (2007). Experimental design and response surface modeling applied for the optimisation of pectin hydrolysis by enzymes from A. niger CECT 2088. Food Chemistry, 101(2), 634–642.
Rosa, P. A., Azevedo, A. M., & Aires-Barros, M. R. (2007). Application of central composite design to the optimisation of aqueous two-phase extraction of human antibodies. Journal of Chromatography A, 1141(1), 50–60.
Saccani, G., Tanzi, E., Mallozzi, S., & Cavalli, S. (2005). Determination of niacin in fresh and dry cured pork products by ion chromatography: experimental design approach for the optimisation of nicotinic acid separation. Food Chemistry, 92(2), 373–379.
Salimi, A., Maghsoudlou, Y., Jafari, S. M., Mahoonak, A. S., Kashaninejad, M., & Ziaiifar, A. M. (2015). Preparation of lycopene emulsions by whey protein concentrate and maltodextrin and optimization by response surface methodology. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 36(2), 274–283.
Sanchez, H., Osella, C., & De La Torre, M. (2004). Use of response surface methodology to optimize gluten-free bread fortified with soy flour and dry milk. Food Science and Technology International, 10(1), 5–9.
Sarfarazi, M., Jafari, S. M., & Rajabzadeh, G. (2015). Extraction optimization of saffron nutraceuticals through response surface methodology. Food Analytical Methods, 8(9), 2273–2285.
Schwabe, C., & Büllesbach, E. (2013). Relaxin and the fine structure of proteins: Springer Science & Business Media.
Servais, A. C., Fillet, M., Chiap, P., Abushoffa, A. M., Hubert, P., & Crommen, J. (2002). Optimization of the separation of β-blockers by ion-pair capillary electrophoresis in non-aqueous media using univariate and multivariate approaches. Journal of Separation Science, 25(15–17), 1087–1095.
Shahraki, M. H., Jafari, S. M., Mashkour, M., & Esmaeilzadeh, E. (2013). Optimization of closed-cycle fluidized bed drying of sesame seeds using response surface methodology and genetic algorithms. International Journal of Food Engineering, 10(1), 167–181.
Sin, H., Yusof, S., Hamid, N. S. A., & Rahman, R. A. (2006a). Optimization of hot water extraction for sapodilla juice using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 74(3), 352–358.
Sin, H. N., Yusof, S., Hamid, N. S. A., & Rahman, R. A. (2006b). Optimization of enzymatic clarification of sapodilla juice using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 73(4), 313–319.
Singh, B., Chakkal, S. K., & Ahuja, N. (2006). Formulation and optimization of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of atenolol using response surface methodology. AAPS PharmSciTech, 7(1), E19–E28.
Singh, B., Panesar, P. S., Gupta, A., & Kennedy, J. F. (2007). Optimisation of osmotic dehydration of carrot cubes in sucrose-salt solutions using response surface methodology. European Food Research and Technology, 225(2), 157–165.
Singh, S., Raina, C. S., Bawa, A. S., & Saxena, D. C. (2004). Sweet potato-based pasta product: optimization of ingredient levels using response surface methodology. International journal of food science & technology, 39(2), 191–200.
Sinha, K., Chowdhury, S., Saha, P. D., & Datta, S. (2013). Modeling of microwave-assisted extraction of natural dye from seeds of Bixa orellana (Annatto) using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN). Industrial Crops and Products, 41, 165–171.
Sinha, K., Saha, P. D., & Datta, S. (2012). Extraction of natural dye from petals of flame of forest (Butea monosperma) flower: process optimization using response surface methodology (RSM). Dyes and Pigments, 94(2), 212–216.
Souza, A. S., dos Santos, W. N., & Ferreira, S. L. (2005). Application of Box–Behnken design in the optimisation of an on-line pre-concentration system using knotted reactor for cadmium determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 60(5), 737–742.
Spanilá, M., Pazourek, J., Farková, M., & Havel, J. (2005). Optimization of solid-phase extraction using artificial neural networks in combination with experimental design for determination of resveratrol by capillary zone electrophoresis in wines. Journal of Chromatography A, 1084(1), 180–185.
Stamatopoulos, K., Katsoyannos, E., Chatzilazarou, A., & Konteles, S. J. (2012). Improvement of oleuropein extractability by optimising steam blanching process as pre-treatment of olive leaf extraction via response surface methodology. Food Chemistry, 133(2), 344–351.
Suh, M.-H., Yoo, S.-H., & Lee, H. G. (2007). Antioxidative activity and structural stability of microencapsulated γ-oryzanol in heat-treated lards. Food Chemistry, 100(3), 1065–1070.
Sunitha, K., Lee, J.-K., & Oh, T.-K. (1999). Optimization of medium components for phytase production by E. coli using response surface methodology. Bioprocess Engineering, 21(6), 477–481.
Suresh Babu, C. V., Chung, B. C., & Yoo, Y. S. (2004). Experimental design to investigate factors affecting capillary zone electrophoresis. Analytical Letters, 37(12), 2485–2499.
Tabaraki, R., & Nateghi, A. (2011). Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of natural antioxidants from rice bran using response surface methodology. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 18(6), 1279–1286.
Tang, X.-J., He, G.-Q., Chen, Q.-H., Zhang, X.-Y., & Ali, M. A. (2004). Medium optimization for the production of thermal stable β-glucanase by Bacillus subtilis ZJF-1A5 using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 93(2), 175–181.
Tanyildizi, M. S., Özer, D., & Elibol, M. (2005). Optimization of α-amylase production by Bacillus sp. using response surface methodology. Process Biochemistry, 40(7), 2291–2296.
Thakur, S., & Saxena, D. (2000). Formulation of extruded snack food (gum based cereal–pulse blend): optimization of ingredients levels using response surface methodology. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 33(5), 354–361.
Tonon, R. V., Grosso, C. R., & Hubinger, M. D. (2011). Influence of emulsion composition and inlet air temperature on the microencapsulation of flaxseed oil by spray drying. Food Research International, 44(1), 282–289.
Tran, A. T., Hyne, R. V., Pablo, F., Day, W. R., & Doble, P. (2007). Optimisation of the separation of herbicides by linear gradient high performance liquid chromatography utilising artificial neural networks. Talanta, 71(3), 1268–1275.
Vohra, A., & Satyanarayana, T. (2002). Statistical optimization of the medium components by response surface methodology to enhance phytase production by Pichia anomala. Process Biochemistry, 37(9), 999–1004.
Wang, H., Liu, Y., Wei, S., & Yan, Z. (2012). Application of response surface methodology to optimise supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of essential oil from Cyperus rotundus Linn. Food Chemistry, 132(1), 582–587.
Wang, L., Yang, B., Du, X., Yang, Y., & Liu, J. (2008). Optimization of conditions for extraction of acid-soluble collagen from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) by response surface methodology. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 9(4), 604–607.
Wijngaard, H. H., & Brunton, N. (2010). The optimisation of solid–liquid extraction of antioxidants from apple pomace by response surface methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 96(1), 134–140.
Xie, J.-H., Shen, M.-Y., Xie, M.-Y., Nie, S.-P., Chen, Y., Li, C., & Wang, Y.-X. (2012). Ultrasonic-assisted extraction, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja polysaccharides. Carbohydrate Polymers, 89(1), 177–184.
Xie, J. H., Xie, M. Y., Shen, M. Y., Nie, S. P., Li, C., & Wang, Y. X. (2010). Optimisation of microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja using response surface methodology. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 90(8), 1353–1360.
Xiong, C., Jinhua, W., & Dongsheng, L. (2007). Optimization of solid-state medium for the production of inulinase by Kluyveromyces S120 using response surface methodology. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 34(2), 179–184.
Yang, L., Jiang, J. G., Li, W. F., Chen, J., Wang, D. Y., & Zhu, L. (2009). Optimum extraction process of polyphenols from the bark of Phyllanthus emblica L. based on the response surface methodology. Journal of Separation Science, 32(9), 1437–1444.
Yolmeh, M., Najafi, M. B. H., & Farhoosh, R. (2014). Optimisation of ultrasound-assisted extraction of natural pigment from annatto seeds by response surface methodology (RSM). Food Chemistry, 155, 319–324.
Yolmeh, M., & Najafzadeh, M. (2014). Optimisation and modelling green bean’s ultrasound blanching. International journal of food science & technology, 49(12), 2678–2684.
Yoshida, T., Tsubaki, S., Teramoto, Y., & Azuma, J. I. (2010). Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of carbohydrates from industrial waste of corn starch production using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 101(20), 7820–7826.
Zhang, Q., Qu, Y., Zhou, J., Zhang, X., Zhou, H., Ma, Q., & Li, X. (2011). Optimization of 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl 1,2-dioxygenase expression and its application for biosensor. Bioresource Technology, 102, 10553–10560.
Zhong, K., & Wang, Q. (2010). Optimization of ultrasonic extraction of polysaccharides from dried longan pulp using response surface methodology. Carbohydrate Polymers, 80(1), 19–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yolmeh, M., Jafari, S.M. Applications of Response Surface Methodology in the Food Industry Processes. Food Bioprocess Technol 10, 413–433 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1855-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1855-2