Opinion statement
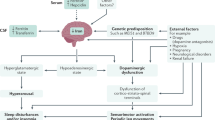
Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is a complicated sensory-motor syndrome. The pathology is increasingly understood, but a clear physiologic understanding still remains elusive. The most robust findings remain reduced central nervous system (CNS) iron and some perturbation in dopaminergic systems. Other neurotransmitter systems are also like involved, and the phenotype may result from distinct pathophysiologic processes. Treatment of RLS is often very successful, and treatment goals should be high. Dopamine agonists may most robustly improve pure urge to move and certainly periodic limb movements. They do not directly improve sleep, and long-term use is limited by augmentation. Alpha-2-delta ligand drugs such as gabapentin enacarbil and pregabalin improve RLS, presumably in a less specific manner. These drugs increase slow wave sleep and improve pain, but have less impact on leg movements. Mu specific opioids also robustly improve RLS and are probably underutilized in severe cases. Intravenous iron inconsistently but sometimes considerably improves RLS and can be considered in refractory cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Allen RP, Picchietti D, Hening WA, Trenkwalder C, Walters AS, Montplaisi J. Restless legs syndrome: diagnostic criteria, special considerations, and epidemiology. A report from the restless legs syndrome diagnosis and epidemiology workshop at the national institutes of health. Sleep Med. 2003;4(2):101–19. Most accepted definition of RLS.
Montplaisir J, Boucher S, Poirier G, Lavigne G, Lapierre O, Lesperance P. Clinical, polysomnographic, and genetic characteristics of restless legs syndrome: a study of 133 patients diagnosed with new standard criteria. Mov Disord. 1997;12(1):61–5.
Giannaki CD, Zigoulis P, Karatzaferi C, Hadjigeorgiou GM, George KP, Gourgoulianis K, et al. Periodic limb movements in sleep contribute to further cardiac structure abnormalities in hemodialysis patients with restless legs syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2013;9(2):147–53.
Li Y, Walters AS, Chiuve SE, Rimm EB, Winkelman JW, Gao X. Prospective study of restless legs syndrome and coronary heart disease among women. Circulation. 2012;126(14):1689–94.
Walters AS, Moussouttas M, Siddiqui F, Silveira DC, Fuentes K, Wang L, et al. Prevalence of stroke in restless legs syndrome: initial results point to the need for more sophisticated studies. Open Neurol J. 2010;4:73–7.
Winkelman JW, Shahar E, Sharief I, Gottlieb DJ. Association of restless legs syndrome and cardiovascular disease in the sleep heart health study. Neurology. 2008;70(1):35–42.
Winter AC, Schurks M, Glynn RJ, Buring JE, Gaziano JM, Berger K, et al. Vascular risk factors, cardiovascular disease, and restless legs syndrome in women. Am J Med. 2013;126(3):220–7. 227 e221-222.
Szentkiralyi A, Volzke H, Hoffmann W, Happe S, Berger K. A time sequence analysis of the relationship between cardiovascular risk factors, vascular diseases and restless legs syndrome in the general population. J Sleep Res. 2013;22(4):434–42.
Manconi M, Ferri R, Zucconi M, Clemens S, Rundo F, Oldani A, et al. Effects of acute dopamine-agonist treatment in restless legs syndrome on heart rate variability during sleep. Sleep Med. 2011;12(1):47–55.
Manconi M, Ferri R, Zucconi M, Bassetti CL, Fulda S, Arico D, et al. Dissociation of periodic leg movements from arousals in restless legs syndrome. Ann Neurol. 2012;71(6):834–44.
Ekbom KA. Growing pains and restless legs. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1975;64(2):264–6.
Rajaram SS, Walters AS, England SJ, Mehta D, Nizam F. Some children with growing pains may actually have restless legs syndrome. Sleep. 2004;27(4):767–73.
Picchietti DL, Bruni O, de Weerd A, Durmer JS, Kotagal S, Owens JA, et al. Pediatric restless legs syndrome diagnostic criteria: an update by the international restless legs syndrome study group. Sleep Med. 2013;14(12):1253–9.
Yeh P, Walters AS, Tsuang JW. Restless legs syndrome: a comprehensive overview on its epidemiology, risk factors, and treatment. Sleep Breath. 2012;16(4):987–1007.
Berger K, Luedemann J, Trenkwalder C, John U, Kessler C. Sex and the risk of restless legs syndrome in the general population. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164(2):196–202.
Pantaleo NP, Hening WA, Allen RP, Earley CJ. Pregnancy accounts for most of the gender difference in prevalence of familial RLS. Sleep Med. 2010;11(3):310–3.
Earley CJ, Connor JR, Beard JL, Malecki EA, Epstein DK, Allen RP. Abnormalities in csf concentrations of ferritin and transferrin in restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2000;54(8):1698–700.
Allen RP, Barker PB, Wehrl F, Song HK, Earley CJ. Mri measurement of brain iron in patients with restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2001;56(2):263–5.
Astrakas LG, Konitsiotis S, Margariti P, Tsouli S, Tzarouhi L, Argyropoulou MI. T2 relaxometry and fmri of the brain in late-onset restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2008;71(12):911–6.
Schmidauer C, Sojer M, Stocckner H, Hogel B, Wenning W, Poewe W. Brain parenchyma sonography differentiates rls patients from normal controls and patients with parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2005;20(supple10):S43.
Godau J, Klose U, Di Santo A, Schweitzer K, Berg D. Multiregional brain iron deficiency in restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord. 2008;23(8):1184–7.
Connor JR, Wang XS, Patton SM, Menzies SL, Troncoso JC, Earley CJ, et al. Decreased transferrin receptor expression by neuromelanin cells in restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2004;62(9):1563–7.
Snyder AM, Wang X, Patton SM, Arosio P, Levi S, Earley CJ, et al. Mitochondrial ferritin in the substantia nigra in restless legs syndrome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009;68(11):1193–9.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Larrosa O, Granizo JJ, de la Llave Y, Hening WA. Circadian variation in neuroendocrine response to l-dopa in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep. 2004;27(4):669–73.
Earley CJ, Hyland K, Allen RP. Circadian changes in csf dopaminergic measures in restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2006;7(3):263–8.
Walters AS, Ondo WG, Zhu W, Le W. Does the endogenous opiate system play a role in the restless legs syndrome? A pilot post-mortem study. J Neurol Sci. 2009;279(1–2):62–5.
Connor JR, Boyer PJ, Menzies SL, Dellinger B, Allen RP, Ondo WG, et al. Neuropathological examination suggests impaired brain iron acquisition in restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2003;61(3):304–9.
Pittock SJ, Parrett T, Adler CH, Parisi JE, Dickson DW, Ahlskog JE. Neuropathology of primary restless leg syndrome: absence of specific tau- and alpha-synuclein pathology. Mov Disord. 2004;19(6):695–9.
Connor JR, Wang XS, Allen RP, Beard JL, Wiesinger JA, Felt BT, et al. Altered dopaminergic profile in the putamen and substantia nigra in restless leg syndrome. Brain. 2009;132(Pt 9):2403–12.
Staedt J, Stoppe G, Kogler A, Riemann H, Hajak G, Munz DL, et al. Nocturnal myoclonus syndrome (periodic movements in sleep) related to central dopamine d2-receptor alteration. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1995;245(1):8–10.
Trenkwalder C, Walters AS, Hening WA, Chokroverty S, Antonini A, Dhawan V, et al. Positron emission tomographic studies in restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord. 1999;14(1):141–5.
Turjanski N, Lees AJ, Brooks DJ. Striatal dopaminergic function in restless legs syndrome: 18f-dopa and 11c-raclopride pet studies. Neurology. 1999;52(5):932–7.
Tribl GG, Asenbaum S, Happe S, Bonelli RM, Zeitlhofer J, Auff E. Normal striatal d2 receptor binding in idiopathic restless legs syndrome with periodic leg movements in sleep. Nucl Med Commun. 2004;25(1):55–60.
Earley CJ, Kuwabara H, Wong DF, Gamaldo C, Salas RE, Brasic JR, et al. Increased synaptic dopamine in the putamen in restless legs syndrome. Sleep. 2013;36(1):51–7.
Allen RP, Connor JR, Hyland K, Earley CJ. Abnormally increased csf 3-ortho-methyldopa (3-omd) in untreated restless legs syndrome (rls) patients indicates more severe disease and possibly abnormally increased dopamine synthesis. Sleep Med. 2009;10(1):123–8.
Lee SJ, Kim JS, Song IU, An JY, Kim YI, Lee KS. Poststroke restless legs syndrome and lesion location: anatomical considerations. Mov Disord. 2009;24(1):77–84.
Ondo WG, He Y, Rajasekaran S, Le WD. Clinical correlates of 6-hydroxydopamine injections into a11 dopaminergic neurons in rats: a possible model for restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord. 2000;15(1):154–8.
Qu S, Le W, Zhang X, Xie W, Zhang A, Ondo WG. Locomotion is increased in a11-lesioned mice with iron deprivation: a possible animal model for restless legs syndrome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007;66(5):383–8.
Earley CJ, Allen RP, Connor JR, Ferrucci L, Troncoso J. The dopaminergic neurons of the a11 system in rls autopsy brains appear normal. Sleep Med. 2009;10(10):1155–7.
Ben-Shachar D, Finberg JP, Youdim MB. Effect of iron chelators on dopamine d2 receptors. J Neurochem. 1985;45(4):999–1005.
Zhao H, Zhu W, Pan T, Xie W, Zhang A, Ondo WG, et al. Spinal cord dopamine receptor expression and function in mice with 6-ohda lesion of the a11 nucleus and dietary iron deprivation. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85(5):1065–76.
Ye Z, Connor JR. Identification of iron responsive genes by screening cdna libraries from suppression subtractive hybridization with antisense probes from three iron conditions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(8):1802–7.
Wang X, Wiesinger J, Beard J, Felt B, Menzies S, Earley C, et al. Thy1 expression in the brain is affected by iron and is decreased in restless legs syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2004;220(1–2):59–66.
Jeng CJ, McCarroll SA, Martin TF, Floor E, Adams J, Krantz D, et al. Thy-1 is a component common to multiple populations of synaptic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1998;140(3):685–98.
Shults CW, Kimber TA. Thy-1 immunoreactivity distinguishes patches/striosomes from matrix in the early postnatal striatum of the rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1993;75(1):136–40.
von Spiczak S, Whone AL, Hammers A, Asselin MC, Turkheimer F, Tings T, et al. The role of opioids in restless legs syndrome: an [11c] diprenorphine pet study. Brain. 2005;128(Pt 4):906–17.
Stiasny-Kolster K, Magerl W, Oertel WH, Moller JC, Treede RD. Static mechanical hyperalgesia without dynamic tactile allodynia in patients with restless legs syndrome. Brain. 2004;127(Pt 4):773–82.
Stiasny-Kolster K, Pfau DB, Oertel WH, Treede RD, Magerl W. Hyperalgesia and functional sensory loss in restless legs syndrome. Pain. 2013;154(8):1457–63.
Allen RP, Barker PB, Horska A, Earley CJ. Thalamic glutamate/glutamine in restless legs syndrome: increased and related to disturbed sleep. Neurology. 2013;80(22):2028–34.
Winkelman JW, Schoerning L, Platt S, Jensen J. Restless legs syndrome and central nervous system gamma-aminobutyric acid: preliminary associations with periodic limb movements in sleep and restless leg syndrome symptom severity. Sleep Med (2014).
Patton SM, Cho YW, Clardy TW, Allen RP, Earley CJ, Connor JR. Proteomic analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with restless legs syndrome/willis-ekbom disease. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2013;10(1):20.
Bucher SF, Seelos KC, Oertel WH, Reiser M, Trenkwalder C. Cerebral generators involved in the pathogenesis of the restless legs syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1997;41(5):639–45.
Etgen T, Draganski B, Ilg C, Schroder M, Geisler P, Hajak G, et al. Bilateral thalamic gray matter changes in patients with restless legs syndrome. Neuroimage. 2005;24(4):1242–7.
Ondo W, Jankovic J. Restless legs syndrome: clinicoetiologic correlates. Neurology. 1996;47(6):1435–41.
Ondo WG, Vuong KD, Wang Q. Restless legs syndrome in monozygotic twins: clinical correlates. Neurology. 2000;55(9):1404–6.
Xiong L, Jang K, Montplaisir J, Levchenko A, Thibodeau P, Gaspar C, et al. Canadian restless legs syndrome twin study. Neurology. 2007;68(19):1631–3.
Winkelmann J, Muller-Myhsok B, Wittchen HU, Hock B, Prager M, Pfister H, et al. Complex segregation analysis of restless legs syndrome provides evidence for an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance in early age at onset families. Ann Neurol. 2002;52(3):297–302.
Stefansson H, Rye DB, Hicks A, Petursson H, Ingason A, Thorgeirsson TE, et al. A genetic risk factor for periodic limb movements in sleep. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(7):639–47.
Winkelmann J, Schormair B, Lichtner P, Ripke S, Xiong L, Jalilzadeh S, et al. Genome-wide association study of restless legs syndrome identifies common variants in three genomic regions. Nat Genet. 2007;39(8):1000–6.
Schormair B, Kemlink D, Roeske D, Eckstein G, Xiong L, Lichtner P, et al. Ptprd (protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type delta) is associated with restless legs syndrome. Nat Genet. 2008;40(8):946–8.
Desautels A, Turecki G, Montplaisir J, Brisebois K, Sequeira A, Adam B, et al. Evidence for a genetic association between monoamine oxidase a and restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2002;59(2):215–9.
Winkelmann J, Lichtner P, Schormair B, Uhr M, Hauk S, Stiasny-Kolster K, et al. Variants in the neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nnos, nos1) gene are associated with restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord. 2008;23(3):350–8.
Desautels A, Turecki G, Montplaisir J, Xiong L, Walters AS, Ehrenberg BL, et al. Restless legs syndrome: confirmation of linkage to chromosome 12q, genetic heterogeneity, and evidence of complexity. Arch Neurol. 2005;62(4):591–6.
Bonati MT, Ferini-Strambi L, Aridon P, Oldani A, Zucconi M, Casari G. Autosomal dominant restless legs syndrome maps on chromosome 14q. Brain. 2003;126(Pt 6):1485–92.
Chen S, Ondo WG, Rao S, Li L, Chen Q, Wang Q. Genomewide linkage scan identifies a novel susceptibility locus for restless legs syndrome on chromosome 9p. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;74(5):876–85.
Pichler I, Schwienbacher C, Zanon A, Fuchsberger C, Serafin A, Facheris MF, et al. Fine-mapping of restless legs locus 4 (rls4) identifies a haplotype over the spats2l and kctd18 genes. J Mol Neurosci. 2012;49(3):600–5.
Levchenko A, Provost S, Montplaisir JY, Xiong L, St-Onge J, Thibodeau P, et al. A novel autosomal dominant restless legs syndrome locus maps to chromosome 20p13. Neurology. 2006;67(5):900–1.
Sas AM, Di Fonzo A, Bakker SL, Simons EJ, Oostra BA, Maat-Kievit AJ, et al. Autosomal dominant restless legs syndrome maps to chromosome 20p13 (rls-5) in a dutch kindred. Mov Disord. 2010;25(11):1715–22.
Lohmann-Hedrich K, Neumann A, Kleensang A, Lohnau T, Muhle H, Djarmati A, et al. Evidence for linkage of restless legs syndrome to chromosome 9p: are there two distinct loci?[see comment]. Neurology. 2008;70(9):686–94.
Levchenko A, Montplaisir JY, Asselin G, Provost S, Girard SL, Xiong L, et al. Autosomal-dominant locus for restless legs syndrome in french-canadians on chromosome 16p12.1. Mov Disord. 2009;24(1):40–50.
Skehan EB, Abdulrahim MM, Parfrey NA, Hand CK. A novel locus for restless legs syndrome maps to chromosome 19p in an irish pedigree. Neurogenetics. 2012;13(2):125–32.
Balaban H, Bayrakli F, Kartal U, Pinarbasi E, Topaktas S, Kars HZ. A novel locus for restless legs syndrome on chromosome 13q. Eur Neurol. 2012;68(2):111–6.
Weissbach A, Siegesmund K, Bruggemann N, Schmidt A, Kasten M, Pichler I, et al. Exome sequencing in a family with restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord. 2012;27(13):1686–9.
Vilarino-Guell C, Soto AI, Young JE, Lin SC, Uitti RJ, Wszolek ZK, et al. Susceptibility genes for restless legs syndrome are not associated with parkinson disease. Neurology. 2008;71(3):222–3.
Lin CH, Chen ML, Wu VC, Li WY, Sy HN, Wu SL, et al. Association of candidate genetic variants with restless legs syndrome in end stage renal disease: a multicenter case-control study in taiwan. Eur J Neurol. 2014;21(3):492–8.
Huiqi Q, Shan L, Mingcai Q. Restless legs syndrome (rls) in uremic patients is related to the frequency of hemodialysis sessions. Nephron. 2000;86(4):540.
Yasuda T, Nishimura A, Katsuki Y, Tsuji Y. Restless legs syndrome treated successfully by kidney transplantation--a case report. Clin Transpl (1986) 138.
Winkelmann J, Stautner A, Samtleben W, Trenkwalder C. Long-term course of restless legs syndrome in dialysis patients after kidney transplantation. Mov Disord. 2002;17(5):1072–6.
Azar SA, Hatefi R, Talebi M. Evaluation of effect of renal transplantation in treatment of restless legs syndrome. Transplant Proc. 2007;39(4):1132–3.
Manconi M, Govoni V, De Vito A, Economou NT, Cesnik E, Casetta I, et al. Restless legs syndrome and pregnancy. Neurology. 2004;63(6):1065–9. Largest study of RLS during pregnancy.
Tunc T, Karadag YS, Dogulu F, Inan LE. Predisposing factors of restless legs syndrome in pregnancy. Mov Disord. 2007;22(5):627–31.
Ondo WG, Vuong KD, Jankovic J. Exploring the relationship between parkinson disease and restless legs syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2002;59(3):421–4.
Ondo W, Chen S, Dragan E. Does idiopathic restless legs syndrome delay onset and reduce severity of parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2014;29(Supple1):S303.
Ondo WG, Jia JJ. Effect of tetrabenazine use on restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2010;11(9):958–9.
Jagota P, Asawavichienjinda T, Bhidayasiri R. Prevalence of neuroleptic-induced restless legs syndrome in patients taking neuroleptic drugs. J Neurol Sci. 2012;314(1–2):158–60.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Ferini-Strambi L, Kohnen R, O'Keeffe S, Trenkwalder C, Hogl B, et al. European guidelines on management of restless legs syndrome: report of a joint task force by the European federation of neurological societies, the European neurological society and the European sleep research society. Eur J Neurol. 2012;19(11):1385–96.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Kohnen R, Silber MH, Winkelman JW, Earley CJ, Hogl B, et al. The long-term treatment of restless legs syndrome/willis-ekbom disease: evidence-based guidelines and clinical consensus best practice guidance: a report from the international restless legs syndrome study group. Sleep Med. 2013;14(7):675–84. Only review of long-term management of disease.
Silber MH, Becker PM, Earley C, Garcia-Borreguero D, Ondo WG. Willis-ekbom disease foundation revised consensus statement on the management of restless legs syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013;88(9):977–86. Recent review of treatment options.
Hornyak M, Scholz H, Kohnen R, Bengel J, Kassubek J, Trenkwalder C. What treatment works best for restless legs syndrome? Meta-analyses of dopaminergic and non-dopaminergic medications. Sleep Med Rev. 2014;18(2):153–64.
Ondo WG, Hossain MM, Gordon MF, Reess J. Predictors of placebo response in restless legs syndrome studies. Neurology. 2013;81(2):193–4.
Trenkwalder C, Garcia-Borreguero D, Montagna P, Lainey E, de Weerd AW, Tidswell P, et al. Ropinirole in the treatment of restless legs syndrome: results from the treat rls 1 study, a 12 week, randomised, placebo controlled study in 10 European countries. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75(1):92–7.
Walters AS, Ondo WG, Dreykluft T, Grunstein R, Lee D, Sethi K. Ropinirole is effective in the treatment of restless legs syndrome. Treat rls 2: a 12-week, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study. Mov Disord. 2004;19(12):1414–23.
Bogan R, Connolly G, Rederich G. Ropinirole is effective, well tolerated treatment for moderate-to-severe rls: results of a u.S. Study. Mov Disord. 2005;20(supple10):S61.
Oertel WH, Stiasny-Kolster K, Bergtholdt B, Hallstrom Y, Albo J, Leissner L, et al. Efficacy of pramipexole in restless legs syndrome: a six-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind study (effect-rls study). Mov Disord. 2007;22(2):213–9.
Trenkwalder C, Stiasny-Kolster K, Kupsch A, Oertel WH, Koester J, Reess J. Controlled withdrawal of pramipexole after 6 months of open-label treatment in patients with restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord. 2006;21(9):1404–10.
Partinen M, Hirvonen K, Jama L, Alakuijala A, Hublin C, Tamminen I, et al. Efficacy and safety of pramipexole in idiopathic restless legs syndrome: a polysomnographic dose-finding study-the prelude study. Sleep Med. 2006;7(5):407–17.
Trenkwalder C, Benes H, Poewe W, Oertel WH, Garcia-Borreguero D, de Weerd AW, et al. Efficacy of rotigotine for treatment of moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(7):595–604.
Oertel WH, Benes H, Garcia-Borreguero D, Geisler P, Hogl B, Saletu B, et al. Efficacy of rotigotine transdermal system in severe restless legs syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, six-week dose-finding trial in europe. Sleep Med. 2008;9(3):228–39.
Earley CJ, Yaffee JB, Allen RP. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pergolide in restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 1998;51(6):1599–602.
Staedt J, Wassmuth F, Ziemann U, Hajak G, Ruther E, Stoppe G. Pergolide: Treatment of choice in restless legs syndrome (rls) and nocturnal myoclonus syndrome (nms). A double-blind randomized crossover trial of pergolide versus l-dopa. J Neural Transm (Budapest). 1997;104(4-5):461–8.
Trenkwalder C, Brandenburg U, Hundemer H, Lledo A, Quail D. A randomized long-term placebo controlled multicenter trial of pergolide in the treatment of restless legs syndrome with central evaluation of polysomnographic data. Neurology. 2001;56(Supple 3):A5.
Wetter TC, Stiasny K, Winkelmann J, Buhlinger A, Brandenburg U, Penzel T, et al. A randomized controlled study of pergolide in patients with restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 1999;52(5):944–50.
Walters AS, Hening WA, Kavey N, Chokroverty S, Gidro-Frank S. A double-blind randomized crossover trial of bromocriptine and placebo in restless legs syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1988;24(3):455–8.
Reuter I, Ellis CM, Ray Chaudhuri K. Nocturnal subcutaneous apomorphine infusion in parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand. 1999;100(3):163–7.
Happe S, Trenkwalder C. Role of dopamine receptor agonists in the treatment of restless legs syndrome. CNS Drugs. 2004;18(1):27–36.
Benes H. Transdermal lisuride: short-term efficacy and tolerability study in patients with severe restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2006;7(1):31–5.
Benes H, Kurella B, Kummer J, Kazenwadel J, Selzer R, Kohnen R. Rapid onset of action of levodopa in restless legs syndrome: a double-blind, randomized, multicenter, crossover trial. Sleep. 1999;22(8):1073–81.
Saletu M, Anderer P, Hogl B, Saletu-Zyhlarz G, Kunz A, Poewe W, et al. Acute double-blind, placebo-controlled sleep laboratory and clinical follow-up studies with a combination treatment of rr-l-dopa and sr-l-dopa in restless legs syndrome. J Neural Transm. 2003;110(6):611–26.
Trenkwalder C, Benes H, Grote L, Happe S, Hogl B, Mathis J, et al. Cabergoline compared to levodopa in the treatment of patients with severe restless legs syndrome: results from a multi-center, randomized, active controlled trial. Mov Disord. 2007;22(5):696–703.
Pellecchia MT, Vitale C, Sabatini M, Longo K, Amboni M, Bonavita V, et al. Ropinirole as a treatment of restless legs syndrome in patients on chronic hemodialysis: an open randomized crossover trial versus levodopa sustained release. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2004;27(4):178–81.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Kohnen R, Hogl B, Ferini-Strambi L, Hadjigeorgiou GM, Hornyak M, et al. Validation of the augmentation severity rating scale (asrs): a multicentric, prospective study with levodopa on restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2007;8(5):455–63.
Hogl B, Garcia-Borreguero D, Kohnen R, Ferini-Strambi L, Hadjigeorgiou G, Hornyak M, et al. Progressive development of augmentation during long-term treatment with levodopa in restless legs syndrome: results of a prospective multi-center study. J Neurol. 2010;257(2):230–7.
Allen RP, Chen C, Garcia-Borreguero D, Polo O, DuBrava S, Miceli J, et al. Comparison of pregabalin with pramipexole for restless legs syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(7):621–31.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Hogl B, Ferini-Strambi L, Winkelman J, Hill-Zabala C, Asgharian A, et al. Systematic evaluation of augmentation during treatment with ropinirole in restless legs syndrome (willis-ekbom disease): results from a prospective, multicenter study over 66 weeks. Mov Disord. 2012;27(2):277–83.
Benes H, Garcia-Borreguero D, Ferini-Strambi L, Schollmayer E, Fichtner A, Kohnen R. Augmentation in the treatment of restless legs syndrome with transdermal rotigotine. Sleep Med. 2012;13(6):589–97.
Inoue Y, Hirata K, Hayashida K, Hattori N, Tomida T, Garcia-Borreguero D. Efficacy, safety and risk of augmentation of rotigotine for treating restless legs syndrome. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013;40:326–33.
Ondo W, Romanyshyn J, Vuong KD, Lai D. Long-term treatment of restless legs syndrome with dopamine agonists. Arch Neurol. 2004;61(9):1393–7.
Silber MH, Girish M, Izurieta R. Pramipexole in the management of restless legs syndrome: an extended study. Sleep. 2003;26(7):819–21.
Yaltho TC, Ondo WG. The use of gabapentin enacarbil in the treatment of restless legs syndrome. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2010;3(5):269–75.
Merlino G, Serafini A, Young JJ, Robiony F, Gigli GL, Valente M. Gabapentin enacarbil, a gabapentin prodrug for the treatment of the neurological symptoms associated with disorders such as restless legs syndrome. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;10(1):91–102.
Allen R, Chen C, Soaita A, Wohlberg C, Knapp L, Peterson BT, et al. A randomized, double-blind, 6-week, dose-ranging study of pregabalin in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2010;11(6):512–9.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Larrosa O, Williams AM, Albares J, Pascual M, Palacios JC, et al. Treatment of restless legs syndrome with pregabalin: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurology. 2010;74(23):1897–904.
Lee DO, Ziman RB, Perkins AT, Poceta JS, Walters AS, Barrett RW. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin enacarbil in subjects with restless legs syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2011;7(3):282–92.
VanMeter SA, Kavanagh ST, Warren S, Barrett RW. Dose response of gabapentin enacarbil versus placebo in subjects with moderate-to-severe primary restless legs syndrome: an integrated analysis of three 12-week studies. CNS Drugs. 2012;26(9):773–80.
Inoue Y, Hirata K, Uchimura N, Kuroda K, Hattori N, Takeuchi M. Gabapentin enacarbil in japanese patients with restless legs syndrome: a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013;29(1):13–21.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Larrosa O, de la Llave Y, Verger K, Masramon X, Hernandez G. Treatment of restless legs syndrome with gabapentin: a double-blind, cross-over study. Neurology. 2002;59(10):1573–9.
Walters AS, Winkelmann J, Trenkwalder C, Fry JM, Kataria V, Wagner M, et al. Long-term follow-up on restless legs syndrome patients treated with opioids. Mov Disord. 2001;16(6):1105–9.
Walters AS, Wagner ML, Hening WA, Grasing K, Mills R, Chokroverty S, et al. Successful treatment of the idiopathic restless legs syndrome in a randomized double-blind trial of oxycodone versus placebo. Sleep. 1993;16(4):327–32.
Kaplan PW, Allen RP, Buchholz DW, Walters JK. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the treatment of periodic limb movements in sleep using carbidopa/levodopa and propoxyphene. Sleep. 1993;16(8):717–23.
Trenkwalder C, Benes H, Grote L, Garcia-Borreguero D, Hogl B, Hopp M, et al. Prolonged release oxycodone-naloxone for treatment of severe restless legs syndrome after failure of previous treatment: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial with an open-label extension. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12(12):1141–50.
Lindvall P, Hariz GM, Blomstedt P. Overall self-perceived health in restless legs treated with intrathecal morphine. Acta Neurol Scand. 2012;127(4):268–73.
Ondo WG. Methadone for refractory restless legs syndrome. Mov Disord. 2005;20(3):345–8.
Silver N, Allen RP, Senerth J, Earley CJ. A 10-year, longitudinal assessment of dopamine agonists and methadone in the treatment of restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2011;12(5):440–4.
Walters AS. Review of receptor agonist and antagonist studies relevant to the opiate system in restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2002;3(4):301–4.
Di Chiara G, Imperato A. Opposite effects of mu and kappa opiate agonists on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and in the dorsal caudate of freely moving rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988;244(3):1067–80.
Trotti LM, Bhadriraju S, Becker LA. Iron for restless legs syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;5:CD007834.
Lee CS, Lee SD, Kang SH, Park HY, Yoon IY. Comparison of the efficacies of oral iron and pramipexole for the treatment of restless legs syndrome patients with low serum ferritin. Eur J Neurol. 2013;21(2):260–6.
Cho YW, Allen RP, Earley CJ. Lower molecular weight intravenous iron dextran for restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2013;14(3):274–7.
Earley CJ, Horska A, Mohamed MA, Barker PB, Beard JL, Allen RP. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of intravenous iron sucrose in restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2009;10(2):206–11.
Lettieri CJ, Eliasson AH. Pneumatic compression devices are an effective therapy for restless legs syndrome: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded, sham-controlled trial. Chest. 2009;135(1):74–80.
Nahab FB, Peckham EL, Hallett M. Double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot trial of botulinum toxin a in restless legs syndrome. Neurology. 2008;71(12):950–1.
Ondo W. Vim deep brain stimulation does not improve pre-existing restless legs syndrome in patients with essential tremor. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2006;12(2):113–4.
Ondo WG, Jankovic J, Simpson R, Jimenez-Shahed J. Globus pallidus deep brain stimulation for refractory idiopathic restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2012;13(9):1202–4.
Tilma J, Tilma K, Norregaard O, Ostergaard JR. Early childhood-onset restless legs syndrome: symptoms and effect of oral iron treatment. Acta Paediatr. 2013;102(5):e221–6.
Grim K, Lee B, Sung AY, Kotagal S. Treatment of childhood-onset restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder using intravenous iron sucrose. Sleep Med. 2013;14(11):1100–4.
Mohri I, Kato-Nishimura K, Kagitani-Shimono K, Kimura-Ohba S, Ozono K, Tachibana N, et al. Evaluation of oral iron treatment in pediatric restless legs syndrome (rls). Sleep Med. 2012;13(4):429–32.
Amos LB, Grekowicz ML, Kuhn EM, Olstad JD, Collins MM, Norins NA, et al. Treatment of pediatric restless legs syndrome. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2013;53(4):331–6.
England SJ, Picchietti DL, Couvadelli BV, Fisher BC, Siddiqui F, Wagner ML, et al. L-dopa improves restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movements in sleep but not attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder in a double-blind trial in children. Sleep Med. 2011;12(5):471–7.
de Oliveira MM, Conti CF, Valbuza JS, de Carvalho LB, do Prado GF. The pharmacological treatment for uremic restless legs syndrome: Evidence-based review. Mov Disord. 2010;25(10):1335–42.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
William G. Ondo reports grants and personal fees from Lundbeck, USWorld Meds, and Merz, as well as personal fees from Avanir, TEVA, UCBPharma, and Xenoport, outside the submitted work.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Sleep Disorders
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ondo, W.G. Restless Legs Syndrome: Pathophysiology and Treatment. Curr Treat Options Neurol 16, 317 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-014-0317-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-014-0317-2