Abstract
Purpose of Review
Osteitis is recognized as a common factor in recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). There is evidence for the association of osteitis with revision surgeries and CRS severity, in terms of higher Lund-Mackay scores. This is a narrative review on the osteitis in CRS patients.
Recent Findings
Evidence to date is inconclusive with regard to the etiology and pathogenesis of this bony thickening. Histopathology of osteitis in primary CRS is likely a process of neo-osteogenesis and bone remodeling. For better understanding, various associating factors have been studied including an inflammatory pattern of rhinosinusitis. Recent studies have associated osteitis with nasal polyps and tissue eosinophilia with the increase in periostin expression and P-glycoprotein mucosal expression. There is no association of osteitis to symptoms or quality of life. Osteitis is an outcome of neo-osteogenesis rather than inflammatory processes in CRS patients without a prior history of surgery. While CT has become a staple in osteitis assessment, the standards for grading osteitic severity remain in an experimental stage. There is no association between the presence or severity of osteitis at the time of surgery and clinical outcomes at 1 year after surgery.
Summary
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the pathogenesis, epidemiology, and correlation with clinical and biological factors of osteitis in CRS patients.


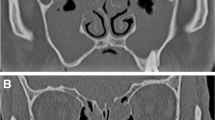
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Erlebacher A, Filvaroff EH, Gitelman SE, Derynck R. Toward a molecular understanding of skeletal development. Cell. 1995;80(3):371–8.
Snidvongs K, McLachlan R, Chin D, Pratt E, Sacks R, Earls P, et al. Osteitic bone: a surrogate marker of eosinophilia in chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology. 2012;50(3):299–305.
Lee JT, Kennedy DW, Palmer JN, Feldman M, Chiu AG. The incidence of concurrent osteitis in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: a clinicopathological study. Am J Rhinol. 2006;20(3):278–82.
Videler WJ, van Drunen CM, van der Meulen FW, Fokkens WJ. Radical surgery: effect on quality of life and pain in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;136(2):261–7.
Park CS, Park YS, Park YJ, Cho JH, Kang JM, Kim SY. The inhibitory effects of macrolide antibiotics on bone remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;137(2):274–9.
Schaberg MR, Anand VK, Singh A. Hyperostotic chronic sinusitis as an indication for outpatient intravenous antibiotics. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(Suppl 4):S245.
Tovi F, Benharroch D, Gatot A, Hertzanu Y. Osteoblastic osteitis of the maxillary sinus. Laryngoscope. 1992;102(4):426–30.
Kacker A, Huang C, Anand V. Incidence of chronic hyperostotic rhinosinusitis in patients undergoing primary sinus surgery compared to revision surgery. Rhinology. 2002;40(2):80–2.
• Snidvongs K, Earls P, Dalgorf D, Sacks R, Pratt E, Harvey RJ. Osteitis is a misnomer: a histopathology study in primary chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014;4(5):390–6 A human study which investigated the inflammatory characterization of osteitis in primary chronic rhinosinusitis.
Campos CA, Dolci EL, Silva L, Dolci JE, Campos CA, Dolci RL. Osteitis and mucosal inflammation in a rabbit model of sinusitis. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;81(3):312–20.
Antunes MB, Feldman MD, Cohen NA, Chiu AG. Dose-dependent effects of topical tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis. Am J Rhinol. 2007;21(4):423–7.
Khalid AN, Hunt J, Perloff JR, Kennedy DW. The role of bone in chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2002;112(11):1951–7.
Perloff JR, Gannon FH, Bolger WE, Montone KT, Orlandi R, Kennedy DW. Bone involvement in sinusitis: an apparent pathway for the spread of disease. Laryngoscope. 2000;110(12):2095–9.
Bolger WE, Leonard D, Dick EJ Jr, Stierna P. Gram negative sinusitis: a bacteriologic and histologic study in rabbits. Am J Rhinol. 1997;11(1):15–25.
Norlander T, Westrin KM, Stierna P. The inflammatory response of the sinus and nasal mucosa during sinusitis: implications for research and therapy. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1994;515:38–44.
Westrin KM, Norlander T, Stierna P, Carlsoo B, Nord CE. Experimental maxillary sinusitis induced by Bacteroides fragilis. A bacteriological and histological study in rabbits. Acta Otolaryngol. 1992;112(1):107–14.
Stevens PR, Tessema B, Brown SM, Parham K, Gronowicz G. Chronic rhinosinusitis osteoblasts differ in cellular properties from normal bone. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015;5(2):124–31.
Cho SH, Min HJ, Han HX, Paik SS, Kim KR. CT analysis and histopathology of bone remodeling in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;135(3):404–8.
Giacchi RJ, Lebowitz RA, Yee HT, Light JP, Jacobs JB. Histopathologic evaluation of the ethmoid bone in chronic sinusitis. Am J Rhinol. 2001;15(3):193–7.
Kennedy DW, Senior BA, Gannon FH, Montone KT, Hwang P, Lanza DC. Histology and histomorphometry of ethmoid bone in chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1998;108(4 Pt 1):502–7.
Biedlingmaier JF, Whelan P, Zoarski G, Rothman M. Histopathology and CT analysis of partially resected middle turbinates. Laryngoscope. 1996;106(1 Pt 1):102–4.
Emre IE, Celebi I, Ercan I. The radiologic evaluation of osteitis type and formation in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyposis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015;29(6):e201–4.
Catalano PJ, Dolan R, Romanow J, Payne SC, Silverman M. Correlation of bone SPECT scintigraphy with histopathology of the ethmoid bulla: preliminary investigation. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2007;116(9):647–52.
Cho SH, Kim SY, Lee KY, Lee HC. New bone formation in unilateral rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol. 2007;21(1):37–9.
Jang YJ, Koo TW, Chung SY, Park SG. Bone involvement in chronic rhinosinusitis assessed by 99mTc-MDP bone SPECT. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 2002;27(3):156–61.
Nishimura T, Iizuka T. Diagnostic value of spect bone scintigraphy for odontogenic maxillary sinusitis. Clin Nucl Med. 2001;26(6):509–14.
Javer AR, Stevens HE, Stillwell M, Jafar AM. Efficacy of nuclear scintigraphy in the diagnosis and management of sinusitis. J Otolaryngol. 1996;25(6):375–82.
Kim HY, Dhong HJ, Lee HJ, Chung YJ, Yim YJ, Oh JW, et al. Hyperostosis may affect prognosis after primary endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;135(1):94–9.
• Dong Y, Zhou B, Huang Z, Huang Q, Cui S, Li Y, et al. Evaluating bone remodeling by measuring Hounsfield units in a rabbit model of rhinosinusitis: is it superior to measuring bone thickness? Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018;8(11):1342–8 An animal study which compared the diagnostic threshold values between the computed tomography value in Hounsfield units and bone thickness measurements.
Dong Y, Zhou B, Wang X, Huang Z, Wang M, Li Y, et al. Computed tomography and histopathological evaluation of osteitis in rabbit models with rhinosinusitis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017;137(5):534–40.
Tian P, Zou H, Liu X, Chen QJ, Xie CC, Pan Z, et al. The radiologic evaluation of bony density change in chronic rhinosinusitis. Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi. 2016;30(22):1793–6.
Bhandarkar ND, Sautter NB, Kennedy DW, Smith TL. Osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis: a review of the literature. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013;3(5):355–63.
Georgalas C, Videler W, Freling N, Fokkens W. Global Osteitis Scoring Scale and chronic rhinosinusitis: a marker of revision surgery. Clin Otolaryngol. 2010;35(6):455–61.
Huang Z, Hajjij A, Li G, Nayak JV, Zhou B, Hwang PH. Clinical predictors of neo-osteogenesis in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015;5(4):303–9.
Snidvongs K, McLachlan R, Sacks R, Earls P, Harvey RJ. Correlation of the Kennedy Osteitis Score to clinico-histologic features of chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013;3(5):369–75.
Li YX, Lin F, Cheng L, Huang Q, Huang ZX, Zhang XQ, et al. Clinical application of modified global osteitis score in chronic rhinosinusitis. Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi. 2017;31(21):1666–70.
Telmesani LM, Al-Shawarby M. Osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: a comparative study between primary and recurrent cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;267(5):721–4.
Zuo K, Guo J, Chen F, Xu R, Xu G, Shi J, et al. Clinical characteristics and surrogate markers of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in southern China. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;271(9):2461–8.
Bhandarkar ND, Mace JC, Smith TL. The impact of osteitis on disease severity measures and quality of life outcomes in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011;1(5):372–8.
Mehta V, Campeau NG, Kita H, Hagan JB. Blood and sputum eosinophil levels in asthma and their relationship to sinus computed tomographic findings. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83(6):671–8.
Dong D, Yulin Z, Xiao W, Hongyan Z, Jia L, Yan X, et al. Correlation between bacterial biofilms and osteitis in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2014;124(5):1071–7.
•• Gunel C, Feldman RE, Bleier BS. Osteitis is associated with P-glycoprotein overexpression in patients with chronic sinusitis without nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2014;28(2):99–102 An experiment which assessed gene expression profiles between osteitic bone and the adjacent diseased mucosa in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis by microarray following RNA isolation.
Ishida A, Ohta N, Suzuki Y, Kakehata S, Okubo K, Ikeda H, et al. Expression of pendrin and periostin in allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol Int. 2012;61(4):589–95.
Wang M, Ye T, Liang N, Huang Z, Cui S, Li Y, et al. Differing roles for TGF-beta/Smad signaling in osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015;29(5):e152–9.
Gunel C, Bleier BS, Bozkurt G, Eliyatkin N. Microarray analysis of the genes associated with osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2017;127(3):E85–90.
•• Wu D, Nocera AL, Mueller SK, Finn K, Libermann TA, Bleier BS. Osteitis is associated with dysregulated pro-osteoblastic activity in patients with nasal polyps. Laryngoscope. 2018;129(3):E102-E109. An experiment which assessed the bone morphogenetic protein pathway and its correlation with the degree of osteitis in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.
Barham HP, Osborn JL, Snidvongs K, Mrad N, Sacks R, Harvey RJ. Remodeling changes of the upper airway with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015;5(7):565–72.
Kawaguchi H, Nemoto K, Raisz LG, Harrison JR, Voznesensky OS, Alander CB, et al. Interleukin-4 inhibits prostaglandin G/H synthase-2 and cytosolic phospholipase A2 induction in neonatal mouse parietal bone cultures. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;11(3):358–66.
Onoe Y, Miyaura C, Kaminakayashiki T, Nagai Y, Noguchi K, Chen QR, et al. IL-13 and IL-4 inhibit bone resorption by suppressing cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin synthesis in osteoblasts. J Immunol. 1996;156(2):758–64.
Silfversward CJ, Larsson S, Ohlsson C, Frost A, Nilsson O. Reduced cortical bone mass in mice with inactivation of interleukin-4 and interleukin-13. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(6):725–31.
Wang Y, Wu NN, Mou YQ, Chen L, Deng ZL. Inhibitory effects of recombinant IL-4 and recombinant IL-13 on UHMWPE-induced bone destruction in the murine air pouch model. J Surg Res. 2013;180(2):e73–81.
Ebenezer JA, Christensen JM, Oliver BG, Oliver RA, Tjin G, Ho J, et al. Periostin as a marker of mucosal remodelling in chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology. 2017;55(3):234–41.
Arjomandi H, Gilde J, Zhu S, Delaney S, Hochstim C, Mazhar K, et al. Relationship of eosinophils and plasma cells to biofilm in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2013;27(4):e85–90.
Cho SH, Shin KS, Lee YS, Jeong JH, Lee SH, Tae K, et al. Impact of chronic rhinosinusitis and endoscopic sinus surgery on bone remodeling of the paranasal sinuses. Am J Rhinol. 2008;22(5):537–41.
Sacks PL, Snidvongs K, Rom D, Earls P, Sacks R, Harvey RJ. The impact of neo-osteogenesis on disease control in chronic rhinosinusitis after primary surgery. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013;3(10):823–7.
Richtsmeier WJ. Top 10 reasons for endoscopic maxillary sinus surgery failure. Laryngoscope. 2001;111(11 Pt 1):1952–6.
Chiu AG. Osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 2005;38(6):1237–42.
Georgalas C. Osteitis and paranasal sinus inflammation: what we know and what we do not. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;21(1):45–9.
Beule AG, Scharf C, Biebler KE, Gopferich A, Steinmeier E, Wolf E, et al. Effects of topically applied dexamethasone on mucosal wound healing using a drug-releasing stent. Laryngoscope. 2008;118(11):2073–7.
Beule A, Athanasiadis T, Athanasiadis E, Field J, Wormald PJ. Efficacy of different techniques of sinonasal irrigation after modified Lothrop procedure. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2009;23(1):85–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Kornkiat Snidvongs has served speakers’ bureau for the Merck Sharp Dolme and Menarini. Raymond Sacks is a consultant for the Medtronic and Olympus and speakers’ bureau for Seqiris Pharmaceutical. Richard J Harvey is a consultant with the Medtronic, Olympus, and NeilMed pharmaceuticals; he has been on the speakers’ bureau for the GlaxoSmithKlin, Seqiris, and Astra Zeneca.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Rhinosinusitis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snidvongs, K., Sacks, R. & Harvey, R.J. Osteitis in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 19, 24 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-019-0855-5
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-019-0855-5