Abstract
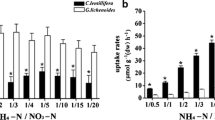
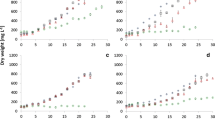
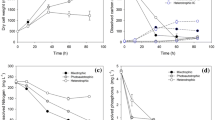
An experiment was designed to select economically valuable macroalga species with high nutrient uptake rates. Such species cultured on a large scale could be a potential solution to eutrophication. Three macroalgae species, Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta), Gelidium amansii (Rhodophyta) and Sargassum enerve (Phaeophyta), were chosen for the experiment because of their economic values and availability. Control and four nitrogen concentrations were achieved by adding NH +4 and NO −3 . The results indicate that the fresh weights of all species increase faster than that of control after 5 d culture. The fresh weight of Ulva pertusa increases fastest among the 3 species. However, different species show different responses to nitrogen source and its availability. They also show the advantage of using NH +4 than using NO −3 . U. pertusa grows best and shows higher capability of removing nitrogen at 200µmolL−1, but it has lower economical value. G. amansii has higher economical value but lower capability of removing nitrogen at 200 µmolL−1. The capability of nitrogen assimilation of S. enerve is higher than that of G. amansii at 200µmolL −1, but the former’s increase of fresh weight is lower than those of other two species. Then present preliminary study demonstrates that it is possible to use macroalgae as biofilters and further development of this approach could provide biologically valuable information on the source, fate, and transport of N in marine ecosystems. Caution is needed should we extrapolate these findings to natural environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brzeski, V., and G. Newkirk, 1997. Integrated coastal food production systems-a review of current literature. Ocean Coastal Management, 34: 55–71.
Buschmann, A. H., O. A. Mora, P. Gomez, M. Bottger, S. Buitano, et al., 1994. Gracilaria chilensis outdoor tank cultivation in Chile: use of land-based salmon cuture effulents. Aquacult. Eng., 13: 283–300.
Chopin, T., C. Yarish, R. Wilkes, E. Belyea, S. Lu, et al., 1999. Developing Porphyra/salmon integrated aquaculture for bioremediaton and diversification of the aquaculture industry. J. Appl. Phycol, 11: 463–472.
DeBoer, J.A., H.J. Guigli, T. L. Isreal, and C. F. D’Elia, 1978. Nutritional studies of two red algae. I. Growth rate as a function of nitrogen source and concentration. J. Phycol. 14: 261–266.
Falkowski, P. G., 1983. Enzymology of nitrogen assimilation. In: Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. E.J., Carpenter, and D. G. Capone, eds., Academic Press, New York, 839–868.
Gao, K., Y. Aruga, K. Asada, and M. Kiyohara, 1993. Influence of enhanced CO2 on growth and photosynthesis of the red algae Gracilaria sp. and G. chilensis. J. Appl. Phycol., 5: 563–571.
Grasshoff, K., K. Kremling, and M. Ehrhardt, 1999. Methods of Seawater Analysis. Wiley-Vch, New York, 1–600.
Hanisak, M.D., 1983. The nitrogen relationships of marine macroalgae. In: Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. E. J., Carpenter, and D. G., Capone, eds., Academic Press, New York, 699–730.
Krom, M. D., S. Ellner, Van J. Rijn, and A. Neori, 1995. Nitrogen and phosphorus cycling and transformations in a prototype ‘non-polluting’ integrated mariculture system, Eilat, Isreal. Mar. Eco. Prog. Ser., 118: 25–36.
Neori, A., M. D., Krom, S. P. Ellner, B. E. Claude, D. Popper, et al., 1996. Seaweed biofilter as regulators of water quality in integrated fish-seaweed culture units. Aquaculture, 141: 183–199.
Neori, A., M. Shpigel, and D. Ben-Ezra, 2000. A sustainable integrated system for culture of fish, seaweed and Abalone. Aquaculture, 186:279–291.
Slawyk, G., and J.J. MacIsaac, 1972. Comparison of two automated ammonium methods in a region of coastal up-welling. Deep-Sea Res., 19:521–524.
Stead, S. M., and L. Laird, 2002. Handbook of Salmon Farming. Springer, London, 163–166.
Taylor, R. B., J. T. A. Peek, and T. A. V. Rees, 1998. Scaling of ammonia uptake by seeweeds to surface area: volume ratio: geographical variation and the role of uptake by passive diffusion. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 169:143–148.
Troell, M., C. Hailing, A. Nilsson, A.H. Buschmann, L. Kautsky, et al., 1997. Integrated marine cultivation of Gracilaria chilensis and salmon cages for reduced environmental impact and increased economic output. Aquaculture, 156: 63–69.
Troell, M., N. Kautsky, and C. Folke. 1999. Ammonium uaptake using Ulva in intensive fishpond systems: mass culture and treatment of effluent. J. Appl. Biol, 2; 363–374.
Wood, E. D., F. A. J. Armstrong, and F. A. Richards, 1967. Determination of nitrate in seawater by cadmium-copper reduction to nitrite. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc, U. K., 47: 23–31.
Xu, Z. N., Lin, X. T., Ji, X. L., Wang, Z. H., and Huang, C.J., 2001. Effect of environmental factors on N and P uptake by Gracilaria tenuistipitata var. liui Zhang et Xia. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 12(3): 417–421.
Yarish, C, and C. Neefus, 2001. Integrated seaweeds into marine aquaculture systems: a key toward sustainability. J. Phycol. 37: 975–986.
Zhou, M.J., Yan, T., and Zou, J. Z., 2003. Preliminary analysis of the characteristics of red tide areas in Changjiang River estuary and its adjacent sea. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 14(7): 1031–1038.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Amy, P. & Sun, J. Preliminary study on the responses of three marine algae, Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta), Gelidium amansii (Rhodophyta) and Sargassum enerve (Phaeophyta), to nitrogen source and its availability. J Ocean Univ. China 3, 75–79 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-004-0013-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-004-0013-z