Abstract
Background
A continuous feeling of hunger is the major cause of dietary treatment failure in obese patients, making dietary leave. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of percutaneous electrical neurostimulation (PENS) of T6 dermatome on appetite, weight loss and dietary compliance.
Methods
A prospective, randomized study was performed. The patients were randomized into two groups: those undergoing PENS of dermatome T6 associated with the implementation of a 1,200-Kcal diet (group 1) and those following only a 1,200-Kcal diet (group 2). A third group of obese patients (BMI > 30 Kg/m2) with fecal incontinence undergoing PENS of posterior tibial nerve was evaluated.
Results
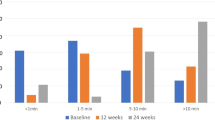
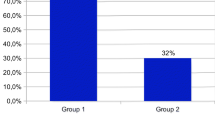
One hundred five patients were included in the study, 45 in groups 1 and 2, and 15 in group 3. The median pain perception after PENS of dermatome T6 was 1. There were no complications. Only the patients in group 1 experienced significant reductions of weight, BMI, and appetite. All of the patients in group 1 experienced appetite reduction compared to 20 % of the patients in group 2 and 30 % of the patients in group 3 (p < 0.001). Weight loss ≥5 Kg was achieved in 76.7 % of the patients in group 1, 6.7 % of the patients in group 2, and 0 % of the patients in group 3 (p < 0.001). Dietary compliance after 12 weeks was 93.3 % in group 1, 56.7 % in group 2, and 50 % in group 3(p = 0.006).
Conclusions
PENS of dermatome T6 was associated with appetite reduction in all of the patients and, along with a proper diet, achieved a significantly greater weight reduction than diet alone.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray GA. Medical consequences of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2583–9.
Sullivan PW, Ghushchyan VH, Ben-Joseph R. The impact of obesity on diabetes, hyperlipidemia and hypertension in the United States. Qual Life Res. 2008;17:1063–71.
Nguyen NT, Magno CP, Lane KT, et al. Association of hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome with obesity: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999 to 2004. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;207:928–34.
Martin Duce A, Diez del Val I. Cirugía de la obesidad mórbida. Guías Clínicas de la Asociación Española de Cirujanos. Madrid, Aran, 2007
Chen J. Mechanisms of action of the implantable gastric stimulator for obesity. Obes Surg. 2004;14 Suppl 1:S28–32.
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:1724–37.
Yao SK, Ke MY, Wang ZF, et al. Visceral response to acute retrograde gastric electrical stimulation in healthy human. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:4541–6.
De Luca M, Segato G, Busetto L, et al. Progress in implantable gastric stimulation: summary of results of the European multi-center study. Obes Surg. 2004;14:33–9.
Van der Pal F, Van Balken MR, Heesakkers JP, et al. Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation in the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome: is maintenance treatment a necessity? BJU Int. 2006;97:547–50.
Boyle DJ, Prosser K, Allison ME, et al. Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation for the treatment of urge fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum. 2010;53:432–7.
Sileri P, Franceschilli L, Cadeddu F, et al. Prevalence of defaecatory disordersin morbidly obese patients before and after bariatric surgery. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012;16:62–6.
Pereira E, Foster A. Appetite suppression and weight loss incidental to spinal cord stimulation for pain relief. Obes Surg. 2007;17:1272–4.
Wang J, Song J, Hou X, et al. Effects of cutaneous gastric electrical stimulation on gastric emptying and postprandial satiety and fullness in lean and obese subjects. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;44:335–9.
Yin J, Ouyang H, Wang Z, et al. Cutaneous gastric electrical stimulation alters gastric motility in dogs: new option for gastric electrical stimulation? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:149–54.
Abell TL, Minocha A, Abidi N. Looking to the future: electrical stimulation for obesity. Am J Med Sci. 2006;331:226–32.
Lemanu DP, Srinivasa S, Singh PP, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: its place in bariatric surgery for the severely obese patient. N Z Med J. 2012;125:41–9.
Monga AK, Tracey MR, Subbaroyan J. A systematic review of clinical studies of electrical stimulation for treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction. Int Urogynecol J. 2012;23:993–1005.
Findlay JM, Maxwell-Armstrong C. Posterior tibial nerve stimulation and faecal incontinence: a review. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011;26:265–73.
Conflict of Interests
All authors (Jaime Ruiz-Tovar, M.D., Ph.D., Inmaculada Oller, M.D., Ph.D., María Diez, M.D., Lorea Zubiaga, M.D., Antonio Arroyo, M.D., Ph.D., and Rafael Calpena, M.D., Ph.D.) declare that they have no conflict of interests in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Tovar, J., Oller, I., Diez, M. et al. Percutaneous Electrical Neurostimulation of Dermatome T6 for Appetite Reduction and Weight Loss in Morbidly Obese Patients. OBES SURG 24, 205–211 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-013-1091-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-013-1091-z