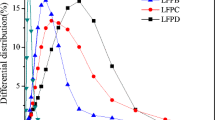
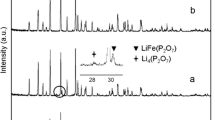
Abstract
Blended spherical cathodes of lithium iron phosphate with different morphology were prepared using a physical mixing method. The lithium iron phosphate spherical material with high tapped density and non-spherical lithium iron phosphate material with good processing properties were compounded in different proportions. The processability and electrochemical properties of blended spherical cathodes were systematically investigated. The characterization results suggest that the blended spherical cathode material not only exerts the complementary advantages of the spherical and non-spherical material, but also produces a synergistic effect, which improves the processing property of the spherical material. This unique property reduces the internal resistance of the contact between the particles, thereby reducing the internal resistance of battery and improving the overall performance of battery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsieh CT, Pai CT, Chen YF, Chen IL, Chen WY (2014) Preparation of lithiumiron phosphate cathode materials with different carbon contents using glucose additive for Li-ion batteries. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:1501–1508
Jegal JP, Kim KB (2013) Carbon nanotube-embedding LiFePO4 as a cathode material for high rate lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 243:859–864
Huang B, Zheng XD, Fan XP, Song GH, Lu M (2011) Enhanced rate performance of nano–micro structured LiFePO4/C by improved process for high-power Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 56:4865–4868
Fergus JW (2010) Recent developments in cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 195:939–954
Gong C, Xue Z, Wen S, Ye Y, Xie X (2016) Advanced carbon materials/olivine LiFePO4 composites cathode for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 318:93–112
Kucinskis G, Bajars G, Kleperis J (2013) Graphene in lithium ion battery cathode materials: a review. J Power Sources 240:66–79
Vicente N, Haro M, Cíntora-Juárez D, Vicente CP, Tirado JL (2015) LiFePO4 particle conductive composite strategies for improving cathode rate capability. Electrochim Acta 163:323–329
Yan CC, Jang JH, Jiang JR (2016) Study of electrochemical performances of lithium titanium oxide–coated LiFePO4/C cathode composite at low and high temperatures. Appl Energy 162:1419–1427
Chung SY, Bloking JT, Chiang YM (2002) Electronically conductive phospho-olivines as lithium storage electrodes. Nat Mater 1:123–128
Prosini PP, Lisi M, Zane D, Pasquali M (2002) Determination of the chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium in LiFePO4. Solid State Ionics 148:45–51
Xu D, Chu X, He YB, Ding Z, Li B, Han W, Du H, Kang F (2015) Enhanced performance of interconnected LiFePO4/C microspheres with excellent multiple conductive network and subtle mesoporous structure. Electrochim Acta 152:398–407
Tang H, Tan L, Xu J (2013) Synthesis and characterization of LiFePO4 coating with aluminum doped zinc oxide. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 23:451–455
Ni JF, Morishita M, Kawabe Y, Watada M, Takeichi N (2010) T. Sakaia hydrothermal preparation of LiFePO4 nanocrystals mediated by organic acid. J Power Sources 195:2877–2882
Goktepe H, Sahan H, Patat S (2016) Effect of silver and carbon double coating on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:9774–9779
He JC (2014) Effect of carbon source on the particles morphology and carbon structure of LiFePO4/C composites. Adv Mater Res 968:53–57
Ni JF, Gao LJ, Lu L (2014) Carbon coated lithium cobalt phosphate for Li-ion batteries: comparison of three coating techniques. J Power Sources 221:35–41
Starke B, Seidlmayer S, Jankowsky S, Dolotko O, Gilles R, Pettinger KH (2017) Influence of particle morphologies of LiFePO4 on water and solvent-based processing and electrochemical properties. Sustain Sci 9:888
Shao DQ, Wang JX, Dong XT (2014) Preparation and electrochemical performances of LiFePO4/C composite nanobelts via facile electrospinning. J Mater Sci-Mater Electron 25:1040–1046
Li YC, Geng GW, Hao JH, Zhang JM, Yang CC, Li BJ (2015) Optimized synthesis of LiFePO4 composites via rheological phase assisted method from FePO4 with acetic acid as dispersant. Electrochim Acta 186:157–164
Lim S, Yoon CS, Cho J (2008) Synthesis of nanowire and hollow LiFePO4 cathodes for high-performance lithium batteries. Chem Mater 20:4560–4564
Chikkannanavar SB, Bernardi DM, Liu LY (2014) A review of blended cathode materials for use in Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 248:91–100
Kim HS, Kim SI, Kim WS (2006) A study on electrochemical characteristics of LiCoO2/LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 mixed cathode for Li secondary battery. J Electrochim Acta 52:1457–1461
Liu L, Yan X, Wang YH, Wei YJ (2014) Studies of the electrochemical properties and thermal stability of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2/LiFePO4 composite cathodes for lithium ion batteries. Ionics 20:1087–1093
Myung ST, Hosoya K, Komaba S, Yashiro H, Sun YK, Kumagai N (2006) Improvement of cycling performance of Li1.1Mn1.9O4 at 60°C by NiO addition for Li-ion secondary batteries. Electrochim Acta 51:5912–5919
Calderon CA, Thomas JE, Lener G, Barraco DE, Visintin A (2017) Electrochemical comparison of LiFePO4 synthesized by a solidstate method using either microwave heating or a tube furnace. J Appl Electrochem 44:1179
Khakani S, Rochefort D, MacNeil DD (2016) Study of LiFePO4 with different morphologies prepared via three synthetic routes. J Electrochem Soc 163:A1131–A1316
Zhang YP, Wu LL, Zhao JB, Yu WY (2015) Controllable synthesis and electrochemical properties of LiFePO4 nano- and microcrystals with multiform morphologies. Mater Chem Phys 166:182–189
Zhao T, Zhang XJ, Li X, Lu SG (2015) Crystallinity dependence of electrochemical properties for LiFePO4. Rare Metals 34:334–337
Sun JC, Li ZF, Ren X, Wang L, Liang GC (2019) High volumetric energy density of LiFePO4/C microspheres based on xylitol-polyvinyl alcohol complex carbon sources. J Alloys Compd 773:788–795
Wu Y, Wen Z, Li J (2011) Hierarchical carbon-coated LiFePO4 nanoplate microspheres with high electrochemical performance for Li-ion batteries. Adv Mater 23:1126–1129
Jiang Y, Liao S, Liu Z, Xiao G, Liu Q, Song H (2013) High performance LiFePO4 microsphere composed of nanofibers with an alcohol-thermal approach. J Mater Chem A 1:4546–4551
Karkar T, Jaouhair A, Tranchot D (2017) How silicon electrodes can be calendered without altering their mechanical strength and cycle life. J Power Source 371:136–147
Liu H, Liu YY, An LW, Zhao XX, Wang L, Liang GC (2017) High energy density LiFePO4/C cathode material synthesized by wet ball milling combined with spray drying method. J Electrochem Soc 164:A3666–A3672
Bitsch B, Dittmann J, Schmitt M, Scharfer P, Schabel W, Willenbacher N (2014) A novel slurry concept for the fabrication of lithium-ion battery electrodes with beneficial properties. J Power Sources 265:81–90
Zhang ZA, Zeng T, Qu CM (2012) Cycle performance improvement of LiFePO4 cathode with polyacrylicacid acid as binder. Electrochim Acta 80:440–444
Funding
This work received financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (grant number 18JCTPJC52800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, L., Wang, X., Liu, X. et al. Blending of LiFePO4/C microparticles with different sizes and its effect on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C-based batteries. Ionics 25, 5269–5276 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-03086-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-03086-2