Abstract
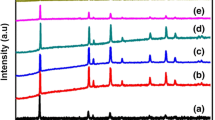
Lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4) has been prepared using sol-gel technique under acidic (pH = 5.8) and alkaline (pH = 9) conditions with tartaric acid as chelating agent. X-ray studies show that under acidic condition, an Mn2O3 peak was observed indicating the presence of impurities. No impurity was observed for LiMn2O4 under alkaline conditions. The particle size is mostly in the range of 124 to 185 nm from HR-TEM. The lithium diffusion coefficient, D Li+ in LiMn2O4 is of the order 10−9 cm2 s−1. By using density functional theory (DFT) calculations, structural properties have been obtained. The specific discharge capacity of the cells with LiMn2O4 prepared under alkaline condition and with LiMn2O4 prepared under acidic condition discharged at 0.5 C is in the ranges of 132 to 142 and 128 to 139 mAh g−1, respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ji LW, Lin Z, Alcoutlabi M, Zhang XW (2011) Recent developments in nanostructured anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energ Environ Sci 4(8):2682–2699
Goodenough JB, Kim Y (2010) Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries. Chem Mater 22(3):587–603
Luo JY, Li XL, Xia YY (2007) Synthesis of highly crystalline spinel LiMn2O4 by a soft chemical route and its electrochemical performance. Electrochim Acta 52(13):4525–4531
Wu HM, Tu JP, Chen XT, Li Y, Zhao XB, Cao GS (2006) Electrochemical study on LiMn2O4 as cathode material for lithium ion batteries. J Electroanal Chem 586(2):180–183
Myung ST, Chung HT, Komaba S, Kumagai N, Gu HB (2000) Capacity fading of LiMn2O4 electrode synthesized by the emulsion drying method. J Power Sources 90(1):103–108
Sun YK, Oh IH, Choi JG (1999) Characteristics of spinel LiMgxMn2-xO4 cathode materials prepared by a sol-gel method. J New Mat Elect Syst 2(1):51–57
Shen PZ, Jia DZ, Huang YD, Liu L, Guo ZP (2006) LiMn2O4 cathode materials synthesized by the cellulose-citric acid method for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 158(1):608–613
Michalska M, Lipinska L, Mirkowska M, Aksienionek M, Diduszko R, Wasiucionek M (2011) Nanocrystalline lithium-manganese oxide spinels for Li-ion batteries—sol-gel synthesis and characterization of their structure and selected physical properties. Solid State Ionics 188(1):160–164
Suryakala K, Marikkannu K, Kalaignan GP, Vasudevan T (2008) Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of LiMn2O4 and LiNd0.3Mn1.7O4 as cathode for lithium ion battery. Int J Electrochem Sc 3(2):136–144
Yue HJ, Huang XK, Lv DP, Yang Y (2009) Hydrothermal synthesis of LiMn2O4/C composite as a cathode for rechargeable lithium-ion battery with excellent rate capability. Electrochim Acta 54(23):5363–5367
Ragavendran KR, Lu L, Barner K, Arof AK (2013) Synthesis methods and electrochemical performance: a theory on the valence disproportionation in LiMyMn2-yO4 (M = Mn, Co) with Interalia guiding principles for a photo-chargeable lithium battery. J Phys Chem C 117(45):23547–23557
Qiao Y, Li SR, Yu Y, Chen CH (2013) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of high performance yolk-structured LiMn2O4 microspheres for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 1(3):860–867
Goriparti S, Miele E, De Angelis F, Di Fabrizio E, Zaccaria RP, Capiglia C (2014) Review on recent progress of nanostructured anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 257:421–443
Hwang BJ, Santhanam R, Liu DG (2001) Effect of various synthetic parameters on purity of LiMn2O4 spinel synthesized by a sol-gel method at low temperature. J Power Sources 101(1):86–89
Seyedahmadian M, Houshyarazar S, Amirshaghaghe A (2013) Synthesis and characterization of nanosized of spinel LiMn2O4 via sol-gel and freeze drying methods. B Kor Chem Soc 34(2):622–628
Hwang BJ, Santhanam R, Liu DG (2001) Characterization of nanoparticles of LiMn2O4 synthesized by citric acid sol-gel method. J Power Sources 97-8:443–446
Hon YM, Lin SP, Fung KZ, Hon MH (2002) Synthesis and characterization of nano-LiMn2O4 powder by tartaric acid gel process. J Eur Ceram Soc 22(5):653–660
Lee YS, Sun YK, Nahm KS (1998) Synthesis of spinel LiMn2O4 cathode material prepared by an adipic acid-assisted sol-gel method for lithium secondary batteries. Solid State Ionics 109(3–4):285–294
Thirunakaran R, Sivashanmugam A, Gopukumar S, Dunnill CW, Gregory DH (2008) Studies on chromium/aluminium-doped manganese spinel as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries—a novel chelated sol-gel synthesis. J Mater Process Technol 208(1–3):520–531
Thirunakaran R, Kim KT, Kang YM, Young-Lee J (2005) Cr (3+) modified LiMn2O4 spinel intercalation cathodes through oxalic acid assisted sol-gel method for lithium rechargeable batteries. Mater Res Bull 40(1):177–186
Zhao TL, Chen S, Li L, Zhang XF, Chen RJ, Belharouak I, Wu F, Amine K (2013) Synthesis, characterization, and electrochemistry of cathode material Li [Li0.2Co0.13Ni0.13Mn0.54]O-2 using organic chelating agents for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 228:206–213
Sun HZ, Li HY, Sadler PJ (1997) The biological and medicinal chemistry of bismuth. Chemische Berichte-Recueil 130(6):669–681
Zhang Y, Shin HC, Dong J, Liu M (2004) Nanostructured LiMn2O4 prepared by a glycine-nitrate process for lithium-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 171(1–2):25–31
Rousse G, Tarascon JM (2014) Sulfate-based polyanionic compounds for Li-ion batteries: synthesis, crystal chemistry, and electrochemistry aspects. Chem Mater 26(1):394–406
Anisimov VI, Gunnarsson O (1991) Density-functional calculation of effective coulomb interactions in metals. Phys Rev B 43(10):7570–7574
Liechtenstein AI, Anisimov VI, Zaanen J (1995) Density-functional theory and strong-interactions—orbital ordering in Mott-Hubbard insulators. Phys Rev B 52(8):R5467–R5470
Yi TF, Zhu YR, Zhu RS (2008) Density functional theory study of lithium intercalation for 5V LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials. Solid State Ionics 179(38):2132–2136
Hasegawa A, Yoshizawa K, Yamabe T (2000) Crystal orbital overlap population analysis of the capacity fading of metal-substituted spinel lithium manganate LiMn2O4. J Electrochem Soc 147(11):4052–4057
Yahya R, Yahya AH, Basirun WJ, Puteh R, Arof AK, Yahya MZA, Vengidason S (2005) Synthesis of lithium intercalation oxides based on manganese and copper by the sol-gel method. Indonesian Journal of Physics 16(1):21–24
Singh G, Panwar A, Sil A, Ghosh S (2009) Synthesis and characterization of citric acid assisted Cr doped lithium manganese oxide spinel. Ceramics-Silikaty 53(4):260–267
Liu H, Wu YP, Rahm E, Holze R, Wu HQ (2004) Cathode materials for lithium ion batteries prepared by sol-gel methods. J Solid State Electr 8(7):450–466
Lee YS, Kumada N, Yoshio M (2001) Synthesis and characterization of lithium aluminum-doped spinel (LiAlxMn2-xO4) for lithium secondary battery. J Power Sources 96(2):376–384
Wei YJ, Nam KW, Kim KB, Chen G (2006) Spectroscopic studies of the structural properties of Ni substituted spinel LiMn2O4. Solid State Ionics 177(1–2):29–35
Wang JL, Li ZH, Yang J, Tang JJ, Yu JJ, Nie WB, Lei GT, Xiao QZ (2012) Effect of Al-doping on the electrochemical properties of a three-dimensionally porous lithium manganese oxide for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 75:115–122
Vediappan K, Lee CW (2010) Preliminary studies of biominerals-coated spinel LiMn2O4 as a cathode material on electrochemical performances for Li-ion rechargeable batteries. Phys Scr 2010(T139):014040
Molenda J, Swierczek K, Kucza W, Marzec J, Stoklosa A (1999) Electrical properties of LiMn2O4-delta at temperatures 220-1100 K. Solid State Ionics 123(1–4):155–163
Hoang K (2014) Understanding the electronic and ionic conduction and lithium over-stoichiometry in LiMn2O4 spinel. J Mater Chem A 2(43):18271–18280
Das SR, Majumder SB, Katiyar RS (2005) Kinetic analysis of the Li+ ion intercalation behavior of solution derived nano-crystalline lithium manganate thin films. J Power Sources 139(1–2):261–268
Cheng B, Chen XL, Li XW, Xu HY, Yang J, Qian YT (2012) High rate performance of LiM0.1Mn1.9O4 (M = Mn, Al, Fe) as cathodes of lithium ion battery at 25 degrees C and 55 degrees C. Int J Electrochem Sc 7(7):6453–6464
Ilango PR, Prasanna K, Do SJ, Jo YN, Lee CW (2016) Eco-friendly nitrogen-containing carbon encapsulated LiMn2O4 cathodes to enhance the electrochemical properties in rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Sci Rep 6:29826
Peng CC, Bai HL, Xiang MW, Su CW, Liu GY, Guo JM (2014) Effect of calcination temperature on the electrochemical properties of spinel LiMn2O4 prepared by solid-state combustion synthesis. Int J Electrochem Sc 9(4):1791–1798
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge funding support from the MOSTI – NANOTEKNOLOGI TOP-DOWN (NANOFUND), Grant No.: 53-02-03-1089 and University of Malaya, Grant No.: RP003C-13AFR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arof, A.K., Kufian, M.Z., Aziz, N. et al. Electrochemical properties of LiMn2O4 prepared with tartaric acid chelating agent. Ionics 23, 1663–1674 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-1997-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-1997-x