Abstract
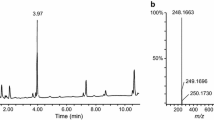
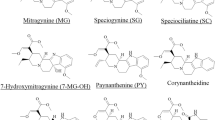
We describe a homicide case involving Aconitum tuberous roots, in which formalin-fixed solid tissues were analyzed for diester-type Aconitum alkaloids and their hydrolysates by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS-MS). The specimens were taken from a cadaver 12 days after death, and preserved in formalin solution for 5 years. Polymer-based solid-phase extraction was employed for sample cleanup. This procedure allowed detection of 0.10 ng/g for each of the spiked alkaloids from the formalin-fixed liver by quadrupole LC-MS-MS, and 10 pg/g for benzoylaconine and benzoylmesaconine by ion-trap LC-MS-MS. Sub-parts-per-billion levels of benzoylaconine and benzoylmesaconine could be detected from the formalin-fixed liver, kidney, and lung specimens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mizugaki M, Ohyama Y, Kimura K, Ishibashi M, Ohno Y, Uchima E, Nagamori H, Suzuki Y (1988) Analysis of aconitum alkaloids by means of gas chromatography/selected ion monitoring. Eisei Kagaku 34:359–365
Ohno Y, Chiba S, Uchigasaki S, Uchima E, Nagamori H, Mizugaki M, Ohyama Y, Kimura K, Suzuki Y (1992) The inuence of tetrodotoxin on the toxic effects of aconitine in vivo. Tohoku J Exp Med 167:155–158
Catterall WA (1988) Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science 242:50–61
Ito K, Ohyama Y, Hishinuma T, Mizugaki M (1996) Determination of Aconitum alkaloids in the tubers of Aconitum japonicum using gas chromatography/selected ion monitoring. Planta Med 62:57–59
Baselt RC (2008) Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. Biomedical, Foster City, CA, pp 25–27
Mizugaki M, Ito K (2005) Aconite toxins. In: Suzuki O, Watanabe K (eds) Drugs and poisons in humans. A handbook of practical analysis. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 455–467
Nihira M, Ohno Y, Tanaka M, Hayashida M, Tomita Y, Hirakawa K, Uekusa K, Yamada T, Hayakawa H (2003) Gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric analysis of aconitine: changes of aconitine level in several organs after its administration to mice. Jpn J Forensic Toxicol 21:38–46
Beike J, Frommherz L, Wood M, Brinkmann B, Kohler H (2004) Determination of aconitine in body uids by LC-MS-MS. Int J Legal Med 118:289–293
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Niitsu H, Oikawa K, Terui K, Akatsu T, Kikuchi M, Sato N, Aoki H, Takahashi K, Endo S (2005) A simple and rapid method for analysis of Aconitum alkaloids in serum and urine using liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Trad Med 22:49–54
Hattori H, Hirata Y, Hamajima M, Kaneko R, Ito K, Ishii A, Suzuki O, Seno H (2009) Simultaneous analysis of aconitine, mesaconitine, hypaconitine, and jesaconitine in whole blood by LC-MS-MS using a new polymer column. Forensic Toxicol 27:7–11
Hara K, Kashiwagi M, Kageura M, Matsusue A, Kubo S (2009) Solid-phase microextraction for amphetamines in solid tissues: washing the homogenates with ethyl ether enables their measurements by GC-MS after heptauorobutyryl derivatization. Forensic Toxicol 27:52–53
Ito K, Tanaka S, Funayama M, Mizugaki M (2000) Distribution of Aconitum alkaloids in body fluids and tissues in a suicidal case of aconite ingestion. J Anal Toxicol 24:348–353
Cingolani M, Froldi R, Mencarelli R, Mirtella D, Rodriguez D (2001) Detection and quantitation of morphine in fixed tissues and formalin solutions. J Anal Toxicol 25:31–34
Cingolani M, Cippitelli M, Froldi R, Gambaro V, Tassoni G (2004) Detection and quantitation analysis of cocaine and metabolites in fixed liver tissue and formalin solutions. J Anal Toxicol 28:16–19
Cingolani M, Cippitelli M, Froldi R, Tassoni G, Mirtella D (2005) Stability of barbiturates in fixed tissues and formalin solutions. J Anal Toxicol 29:205–208
Ramagiri S, Shukla SK, Sai Prakash PK (2006) Stability study of uoxetine in formalin-fixed liver tissue. J Anal Toxicol 30:692–696
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyaguchi, H., Sekine, H. Homicide involving Aconitum tuberous root: LC-MS-MS analysis of Aconitum alkaloids and their hydrolysates in formalin-fixed tissues. Forensic Toxicol 28, 47–51 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-009-0078-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-009-0078-x