Abstract
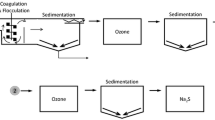
The feasibility of using enhanced coagulation, which combined polyaluminum chloride (PAC) with diatomite for improving coagulation performance and reducing the residual aluminum (Al), was discussed. The effects of PAC and diatomite dosage on the coagulation performance and residual Al were mainly investigated. Results demonstrated that the removal efficiencies of turbidity, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), and UV254 were significantly improved by the enhanced coagulation, compared with PAC coagulation alone. Meaningfully, the five forms of residual Al (total Al (TAl), total dissolved Al (TDAl), dissolved organic Al (DOAl), dissolved monomeric Al (DMAl), and dissolved organic monomeric Al (DOMAl)) all had different degrees of reduction in the presence of diatomite and achieved the lowest concentrations (0.185, 0.06, 0.053, 0.014, and 0 mg L−1, respectively) at a PAC dose of 15 mg L−1 and diatomite dose of 40 mg L−1. In addition, when PAC was used as coagulant, the majority of residual Al existed in dissolved form (about 31.14–70.16 %), and the content of DOMAl was small in the DMAl.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthon G (2002) Aluminum speciation in relation to aluminum bioavailability, metabolism and toxicity. Coord Chem Rev 228:319–341
Cheng WP, Chi FH, Li CC, Yu RF (2008) A study on the removal of organic substances from low-turbidity and low-alkalinity water with metal–polysilicate coagulants. Colloids Surf A 312:238–244
Erdem E, Colgecen G, Donat R (2005) The removal of textile dyes by diatomite earth. J Colloid Interf Sci 282:314–319
Flaten TP (2001) Aluminium as a risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, with emphasis on drinking water. Brain Res Bull 55:187–196
Jiang JQ (2001) Development of coagulation theory and pre-polymerized coagulants for water treatment. Sep Purif Methods 30:127–141
Khraisheh M, Al-degs YS, Mcminn W (2004) Remediation of wastewater containing heavy metals using raw and modified diatomite. Chem Eng J 99:177–184
Kimura M, Matsui Y, Kondo K, Ishikawa TB, Matsushita T, Shirasaki N (2013) Minimizing residual aluminum concentration in treated water by tailoring properties of polyaluminum coagulants. Water Res 47:2075–2084
Marco S, Patrizia M, Antonio C (1998) Aluminum fractions in drinking water from reservoirs. Environ Res 8:29–33
National Standards of the People’s Republic of China (2006) Standard examination methods for drinking water-metal parameters. GB/T 5750:6–2006
Panyue Z, Zhen W, Guangming Z, Gguangming Z, Haiyan Z, Juan L, Xiangguo S, Jinhua D (2008) Coagulation and characteristics of polyaluminum chlorides PAC-Al30 on humic acid removal from water. Sep Purif Technol 63:642–647
Reiber S, Kukull W, Standish-Lee P (1995) Drinking-water aluminum and bioavailability. J Am Water Works Ass 87:86–100
Schintu M, Meloni P, Contu A (2000) Aluminum fractions in drinking water fromreservoirs. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:29–33
Sheng G, Wang S, Hu J, Lu Y, Li J, Dong Y, Wang X (2009) Adsorption of Pb (II) on diatomite as affected via aqueous solution chemistry and temperature. Colloids Surf A 339:159–166
Srinivasan PT, Viraraghavan T (2002) Characterization and concentration profile of aluminum during drinking-water treatment. Water SA 28:99–106
Srinivasan PT, Viraraghavan T, Surbramanian KS (1999) Alumnium in drinking water: an overview. Water SA 25:47–56
Van Benschoten JE, Edzwald JK (1990) Measuring aluminum during water treatment: methodology and application. J Am Water Works Ass 82:71–78
Wu J, Yang YS, Lin J (2005) Advanced tertiary treatment of municipal wastewater using raw and modified diatomite. J Hazard Mater 127:196–203
Wu CD, Xu XJ, Liang JL, Wang Q, Dong Q, Liang WL (2011) Enhanced coagulation for treating slightly polluted algae-containing surface water combining polyaluminum chloride (PAC) with diatomite. Desalination 279:140–145
Yang ZL, Gao BY, Yue QY, Wang Y (2010a) Effect of pH on the coagulation performance of Al-based coagulants and residual aluminum speciation during the treatment of humic acid-kaolin synthetic water. J Hazard Mater 178:596–603
Yang ZL, Gao BY, Yue QY (2010b) Coagulation performance and residual aluminum speciation of Al2(SO4)3 and polyaluminum chloride (PAC) in Yellow River water treatment. Chem Eng J 165:122–132
Yu JF, Wang DS, Yan MQ, Ye CQ, Yang M, Ge XP (2007) Optimized coagulation of high alkalinity, low temperature and particle water: pH adjustment and polyelectrolytes as coagulant aids. Environ Monit Assess 131:377–386
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China [Nos. 51078148 and 41173103].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W., Wu, C. Enhanced coagulation for improving coagulation performance and reducing residual aluminum combining polyaluminum chloride with diatomite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 498–503 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5282-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5282-0