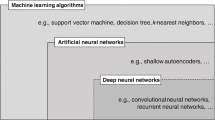
Abstract
At present, how to make use of massive medical information resources to provide scientific decision-making for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, summarize the curative effect of various treatment schemes, and better serve the decision-making management, medical treatment, and scientific research, has drawn more and more attention of researchers. Deep learning, as the focus of most concern by both academia and industry, has been effectively applied in many fields and has outperformed most of the machine learning methods. Under this background, deep learning based medical data analysis emerged. In this survey, we focus on reviewing and then categorizing the current development. Firstly, we fully discuss the scope, characteristic and structure of the heterogeneous medical data. Afterward and primarily, the main deep learning models involved in medical data analysis, including their variants and various hybrid models, as well as main tasks in medical data analysis are all analyzed and reviewed in a series of typical cases respectively. Finally, we provide a brief introduction to certain useful online resources of deep learning development tools.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackley, D.H., Hinton, G.E., Sejnowski, T.J.: A learning algorithm for Boltzmann machines. Cogn. Sci. 9(1), 147–169 (1985)
Beaulieu-Jones, B.K., Greene, C.S.: Semi-supervised learning of the electronic health record for phenotype stratification. J. Biomed. Inform. 64, 168–178 (2016)
Bowie, M., Begoli, E., Park, B.: Improving quality of observational streaming medical data by using long short-term memory networks (LSTMs). In: 2018 IEEE 34th international conference on data engineering workshops (ICDEW) 2018, pp. 48-53. IEEE
Che, Z., Purushotham, S., Cho, K., Sontag, D., Liu, Y.: Recurrent neural networks for multivariate time series with missing values. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 6085 (2018)
Cheng, Y., Wang, F., Zhang, P., Hu, J.: Risk prediction with electronic health records: a deep learning approach. In: proceedings of the 2016 SIAM international conference on data mining 2016, pp. 432-440. SIAM
Choi, E., Bahadori, M.T., Searles, E., Coffey, C., Thompson, M., Bost, J., Tejedor-Sojo, J., Sun, J.: Multi-layer representation learning for medical concepts. In: proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining 2016, pp. 1495-1504. ACM
Choi, E., Schuetz, A., Stewart, W.F., Sun, J.: Medical concept representation learning from electronic health records and its application on heart failure prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1602.03686 (2016)
Choi, E., Schuetz, A., Stewart, W.F., Sun, J.: Using recurrent neural network models for early detection of heart failure onset. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 24(2), 361–370 (2016)
Choi, Y., Chiu, C.Y.-I., Sontag, D.: Learning low-dimensional representations of medical concepts. AMIA Summits on Translational Science Proceedings 2016, 41 (2016)
Choi, E., Bahadori, M.T., Schuetz, A., Stewart, W.F., Sun, J.: Doctor AI: Predicting Clinical Events Via Recurrent Neural Networks. In: Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference 2016, pp. 301-318
Dernoncourt, F., Lee, J.Y., Uzuner, O., Szolovits, P.: De-identification of patient notes with recurrent neural networks. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 24(3), 596–606 (2017)
Esfandiari, N., Babavalian, M.R., Moghadam, A.-M.E., Tabar, V.K.: Knowledge discovery in medicine: current issue and future trend. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(9), 4434–4463 (2014)
Esteban, C., Staeck, O., Baier, S., Yang, Y., Tresp, V.: Predicting clinical events by combining static and dynamic information using recurrent neural networks. In: healthcare informatics (ICHI), 2016 IEEE international conference on 2016, pp. 93-101. Ieee
Fang, R., Pouyanfar, S., Yang, Y., Chen, S.-C., Iyengar, S.: Computational health informatics in the big data age: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR). 49(1), 1–36 (2016)
Fischer, A., Igel, C.: Training restricted Boltzmann machines: an introduction. Pattern Recogn. 47(1), 25–39 (2014)
Frid-Adar, M., Diamant, I., Klang, E., Amitai, M., Goldberger, J., Greenspan, H.: GAN-based Synthetic Medical Image Augmentation for increased CNN Performance in Liver Lesion Classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.01229 (2018)
Fries, J.A.: Brundlefly at SemEval-2016 Task 12: Recurrent neural networks vs. joint inference for clinical temporal information extraction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.01433 (2016)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Deep learning, vol. 1. MIT press Cambridge, (2016)
Heidari, A.A., Faris, H., Aljarah, I., Mirjalili, S.: An efficient hybrid multilayer perceptron neural network with grasshopper optimization. Soft. Comput. 23(17), 7941–7958 (2019)
Hess, M., Lenz, S., Blätte, T.J., Bullinger, L., Binder, H.: Partitioned learning of deep Boltzmann machines for SNP data. Bioinformatics. 33(20), 3173–3180 (2017)
Hinton, G.E., Salakhutdinov, R.R.: Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science. 313(5786), 504–507 (2006)
Hinton, G.E., Osindero, S., Teh, Y.-W.: A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 18(7), 1527–1554 (2006)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Jacobson, O., Dalianis, H.: Applying deep learning on electronic health records in Swedish to predict healthcare-associated infections. In: Proceedings of the 15th Workshop on Biomedical Natural Language Processing 2016, pp. 191–195
Jagannatha, A.N., Yu, H.: Bidirectional RNN for medical event detection in electronic health records. In: proceedings of the conference. Association for Computational Linguistics. North American chapter. Meeting 2016, p. 473. NIH Public Access
Jagannatha, A.N., Yu, H.: Structured prediction models for RNN based sequence labeling in clinical text. In: proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing. Conference on empirical methods in natural language processing 2016, p. 856. NIH Public Access
Jahangir, M., Afzal, H., Ahmed, M., Khurshid, K., Nawaz, R.: An expert system for diabetes prediction using auto tuned multi-layer perceptron. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 722–728 (2018)
Kavukcuoglu, K., Ranzato, M.A., LeCun, Y.: Fast inference in sparse coding algorithms with applications to object recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1010.3467 (2010)
Kayalibay, B., Jensen, G., van der Smagt, P.: CNN-based segmentation of medical imaging data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.03056 (2017)
Khatami, A., Babaie, M., Tizhoosh, H.R., Khosravi, A., Nguyen, T., Nahavandi, S.: A sequential search-space shrinking using CNN transfer learning and a radon projection pool for medical image retrieval. Expert Syst. Appl. 100, 224–233 (2018)
Khin, K., Burckhardt, P., Padman, R.: A Deep Learning Architecture for De-identification of Patient Notes: Implementation and Evaluation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.01570 (2018)
Kleesiek, J., Urban, G., Hubert, A., Schwarz, D., Maier-Hein, K., Bendszus, M., Biller, A.: Deep MRI brain extraction: a 3D convolutional neural network for skull stripping. NeuroImage. 129, 460–469 (2016)
Kumar, A., Kim, J., Lyndon, D., Fulham, M., Feng, D.: An ensemble of fine-tuned convolutional neural networks for medical image classification. IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics. 21(1), 31–40 (2016)
Kwon, B.C., Choi, M.-J., Kim, J.T., Choi, E., Kim, Y.B., Kwon, S., Sun, J., Choo, J.: RetainVis: visual analytics with interpretable and interactive recurrent neural networks on electronic medical records. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. (2018)
Lan, K., Wang, D.-t., Fong, S., Liu, L.-s., Wong, K.K., Dey, N.: A survey of data mining and deep learning in bioinformatics. J. Med. Syst. 42(8), 139 (2018)
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE. 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Lee, D.-H., Bengio, Y.: Backprop-free autoencoders. In: NIPS’2014 Deep Learning workshop 2014
Li, H., Li, X., Ramanathan, M., Zhang, A.: Identifying informative risk factors and predicting bone disease progression via deep belief networks. Methods. 69(3), 257–265 (2014)
Li, F., Tran, L., Thung, K.-H., Ji, S., Shen, D., Li, J.: A robust deep model for improved classification of AD/MCI patients. IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics. 19(5), 1610–1616 (2015)
Liang, K., Chang, H., Cui, Z., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Representation learning with smooth autoencoder. In: Asian conference on computer vision 2014, pp. 72-86. Springer
Liang, Z., Zhang, G., Huang, J.X., Hu, Q.V.: Deep learning for healthcare decision making with EMRs. In: bioinformatics and biomedicine (BIBM), 2014 IEEE international conference on 2014, pp. 556-559. IEEE
Lin, Z., Owen, A.B., Altman, R.B.: Genomic research and human subject privacy. In. American Association for the Advancement of Science (2004)
Lipton, Z.C., Kale, D.C., Elkan, C., Wetzel, R.: Learning to diagnose with LSTM recurrent neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.03677 (2015)
Litjens, G., Kooi, T., Bejnordi, B.E., Setio, A.A.A., Ciompi, F., Ghafoorian, M., Van Der Laak, J.A., Van Ginneken, B., Sánchez, C.I.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 42, 60–88 (2017)
Lu, N., Li, T., Ren, X., Miao, H.: A deep learning scheme for motor imagery classification based on restricted boltzmann machines. IEEE transactions on neural systems and rehabilitation engineering. 25(6), 566–576 (2016)
Luo, Y., Cheng, Y., Uzuner, Ö., Szolovits, P., Starren, J.: Segment convolutional neural networks (Seg-CNNs) for classifying relations in clinical notes. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 25(1), 93–98 (2017)
Lv, X., Guan, Y., Yang, J., Wu, J.: Clinical relation extraction with deep learning. IJHIT. 9(7), 237–248 (2016)
Makkie, M., Huang, H., Zhao, Y., Vasilakos, A.V., Liu, T.: Fast and scalable distributed deep convolutional autoencoder for fMRI big data analytics. Neurocomputing. 325, 20–30 (2019)
Mansoor, A., Cerrolaza, J.J., Idrees, R., Biggs, E., Alsharid, M.A., Avery, R.A., Linguraru, M.G.: Deep learning guided partitioned shape model for anterior visual pathway segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 35(8), 1856–1865 (2016)
Masci, J., Meier, U., Cireşan, D., Schmidhuber, J.: Stacked convolutional auto-encoders for hierarchical feature extraction. In: International conference on artificial neural networks 2011, pp. 52-59. Springer
Mehrabi, S., Sohn, S., Li, D., Pankratz, J.J., Therneau, T., Sauver, J.L.S., Liu, H., Palakal, M.: Temporal pattern and association discovery of diagnosis codes using deep learning. In: Healthcare informatics (ICHI), 2015 international conference on 2015, pp. 408-416. IEEE
Miotto, R., Li, L., Kidd, B.A., Dudley, J.T.: Deep patient: an unsupervised representation to predict the future of patients from the electronic health records. Sci. Rep. 6, 26094 (2016)
Nguyen, P., Tran, T., Wickramasinghe, N., Venkatesh, S.: $\mathtt {Deepr} $: A Convolutional Net for Medical Records. IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics. 21(1), 22–30 (2016)
Nickerson, P., Tighe, P., Shickel, B., Rashidi, P.: Deep neural network architectures for forecasting analgesic response. In: Conference proceedings:... Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Annual Conference 2016, p. 2966. NIH Public Access
Nie, L., Wang, M., Zhang, L., Yan, S., Zhang, B., Chua, T.-S.: Disease inference from health-related questions via sparse deep learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 27(8), 2107–2119 (2015)
Pham, T., Tran, T., Phung, D., Venkatesh, S.: Deepcare: A deep dynamic memory model for predictive medicine. In: Pacific-Asia conference on knowledge discovery and data mining 2016, pp. 30-41. Springer
Poultney, C., Chopra, S., Cun, Y.L.: Efficient Learning of Sparse Representations with an Energy-Based Model. In: Advances in neural information processing systems 2007, pp. 1137-1144
Raji, C., Chandra, S.V.: Long-term forecasting the survival in liver transplantation using multilayer perceptron networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems. 47(8), 2318–2329 (2017)
Ravı, D., Wong, C., Deligianni, F., Berthelot, M., Andreu-Perez, J., Lo, B., Yang, G.-Z.: Deep learning for health informatics. IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics. 21(1), 4–21 (2016)
Rifai, S., Vincent, P., Muller, X., Glorot, X., Bengio, Y.: Contractive auto-encoders: explicit invariance during feature extraction. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on international conference on machine learning 2011, pp. 833-840. Omnipress
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning internal representations by error propagation. In. California Univ San Diego La Jolla Inst for Cognitive Science (1985)
Salakhutdinov, R., Larochelle, H.: Efficient Learning of Deep Boltzmann Machines. In: Proceedings of the thirteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics 2010, pp. 693-700
Shickel, B., Tighe, P.J., Bihorac, A., Rashidi, P.: Deep EHR: a survey of recent advances in deep learning techniques for electronic health record (EHR) analysis. IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics. 22(5), 1589–1604 (2017)
Sokolovska, N., Chevaleyre, Y., Zucker, J.-D.: Risk scores learned by deep restricted Boltzmann machines with trained interval quantization. In: international conference on machine learning and data Mining in Pattern Recognition 2018, pp. 421-435. Springer
Sokolovska, N., Permiakova, O., Forslund, K., Zucker, J.-D.: Using unlabeled data to discover bivariate causality with deep restricted Boltzmann machines. IEEE/ACM transactions on computational biology and bioinformatics (2018)
Sweeney, L.: Simple demographics often identify people uniquely. Health (San Francisco). 671, 1–34 (2000)
Tran, T., Nguyen, T.D., Phung, D., Venkatesh, S.: Learning vector representation of medical objects via EMR-driven nonnegative restricted Boltzmann machines (eNRBM). J. Biomed. Inform. 54, 96–105 (2015)
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Bengio, Y., Manzagol, P.-A.: Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the 25th international conference on machine learning 2008, pp. 1096-1103. ACM
Williams, R.J., Zipser, D.: A learning algorithm for continually running fully recurrent neural networks. Neural Comput. 1(2), 270–280 (1989)
Wu, Y., Jiang, M., Lei, J., Xu, H.: Named entity recognition in Chinese clinical text using deep neural network. Studies in health technology and informatics. 216, 624 (2015)
Xu, Y., Biswal, S., Deshpande, S.R., Maher, K.O., Sun, J.: RAIM: Recurrent attentive and intensive model of multimodal patient monitoring data. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining 2018, pp. 2565-2573. ACM
Yadav, S., Ekbal, A., Saha, S., Bhattacharyya, P.: Deep learning architecture for patient data de-identification in clinical records. In: Proceedings of the Clinical Natural Language Processing Workshop (ClinicalNLP) 2016, pp. 32–41
Yadav, P., Steinbach, M., Kumar, V., Simon, G.: Mining electronic health records (EHRs): a survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR). 50(6), 85 (2018)
Yuste, R., Goering, S., Bi, G., Carmena, J.M., Carter, A., Fins, J.J., Friesen, P., Gallant, J., Huggins, J.E., Illes, J.: Four ethical priorities for neurotechnologies and AI. Nature News. 551(7679), 159 (2017)
Zhang, R., Zheng, Y., Mak, T.W.C., Yu, R., Wong, S.H., Lau, J.Y., Poon, C.C.: Automatic detection and classification of colorectal polyps by transferring low-level CNN features from nonmedical domain. IEEE J. Biomedical and Health Informatics. 21(1), 41–47 (2017)
Zhang, C., Li, Y., Du, N., Fan, W., Yu, P.S.: On the generative discovery of structured medical knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining 2018, pp. 2720-2728. ACM
Acknowledgments
This research has been supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. 2412017QD028 and 2412019FZ047), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2017M621192), Scientific and Technological Development Program of Jilin Province (Grant Nos. 20180520022JH and 20190302109GX).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, L., Tian, D., Chen, W. et al. Deep learning for heterogeneous medical data analysis. World Wide Web 23, 2715–2737 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-019-00764-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-019-00764-z