Abstract
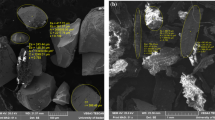
In the present study, response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to maximize As(V) removal from aqueous solutions by using modified magnetic nanoparticles with ascorbic acid (AA-MNPs). The structural features of the produced material were characterized by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption–desorption, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), thermogravimetric analyses (TGA), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). More specifically, the effects of pH, temperature, arsenic ion concentration, and sorbent dosage were investigated on the arsenic adsorption. A total of 20 sets of experiments were designed by the software to achieve maximum adsorption capacity (q e ) and removal efficiency (R). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) of the two-factor interaction (2FI) model suggested that the predicted values were in good agreement with experimental data. The best local maximum values for pH, arsenic concentration, and sorbent dosage were found to be 2, 5 mg L−1, and 0.1 g L−1, respectively, that yielding maximum q e of 44.99 mg g−1 and a maximum R of 42.69 %. Additionally, the obtained value for desirability was equal to 0.862. The results indicated that the Langmuir model provided the best correlation of the equilibrium data. Moreover, the obtained results revealed that the pseudo-second-order kinetic model could best describe the adsorption kinetics.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anbia, M., Kargosha, K., & Khoshbooei, S. (2015). Heavy metal ions removal from aqueous media by modified magnetic mesoporous silica MCM-48. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 93, 779–788.
Atashkar, B., Rostami, A., & Tahmasbi, B. (2013). Magnetic nanoparticle-supported guanidine as a highly recyclable and efficient nanocatalyst for the cyanosilylation of carbonyl compounds. Catalysis Science & Technology, 3, 2140–2146.
Boruah, P. K., Borah, D. J., Handique, J., Sharma, P., Sengupta, P., & Das, M. R. (2015). Facile synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 nanopowder and Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for methyl blue adsorption: a comparative study. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3, 1974–1985.
Brechbühl, Y., Christl, I., Elzinga, E. J., & Kretzschmar, R. (2012). Competitive sorption of carbonate and arsenic to hematite: combined ATR-FTIR and batch experiments. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 377, 313–321.
Bujňáková, Z., Baláž, P., Zorkovská, A., Sayagués, M. J., Kováč, J., & Timko, M. (2013). Arsenic sorption by nanocrystalline magnetite: an example of environmentally promising interface with geosphere. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 262, 1204–1212.
Burks, T., Avila, M., Akhtar, F., Gothelid, M., Lansaker, P. C., Toprak, M. S., Muhammed, M., & Uheida, A. (2014). Studies on the adsorption of chromium(VI) onto 3-mercaptopropionic acid coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 425, 36–43.
Cao, J., Wu, Y., Jin, Y., Yilihan, P., & Huang, W. (2014). Response surface methodology approach for optimization of the removal of chromium(VI) by NH2-MCM-41. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 45, 860–868.
Caporale, A. G., Punamiya, P., Pigna, M., Violante, A., & Sarkar, D. (2013). Effect of particle size of drinking-water treatment residuals on the sorption of arsenic in the presence of competing ions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 260, 644–651.
Chen, H., Zhao, J., Dai, G., Wu, J., & Yan, H. (2010). Adsorption characteristics of Pb(II) from aqueous solution onto a natural biosorbent, fallen Cinnamomum camphora leaves. Desalination, 262, 174–182.
Chen, F., Xie, S., Zhang, J., & Liu, R. (2013). Synthesis of spherical Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles by co-precipitation in choline chloride/urea deep eutectic solvent. Materials Letters, 112, 177–179.
Chowdhury, S. R., & Yanful, E. K. (2010). Arsenic and chromium removal by mixed magnetite-maghemite nanoparticles and the effect of phosphate on removal. Journal of Environmental Management, 91, 2238–2247.
Dabrowski, A., Hubicki, Z., Podkoscielny, P., & Robens, E. (2004). Selective removal of the heavy metal ions from waters and industrial wastewaters by ion-exchange method. Chemosphere, 56, 91–106.
Dong, H., Guan, X., & Lo, I. M. C. (2012). Fate of As(V)-treated nano zero-valent iron: determination of arsenic desorption potential under varying environmental conditions by phosphate extraction. Water Research, 46, 4071–4080.
Feng, R., Wei, C., Tu, S., & Sun, X. (2009). Interactive effects of selenium and arsenic on their uptake by Pteris vittata L. under hydroponic conditions. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 65, 363–368.
Feng, L., Cao, M., Ma, X., Zhu, Y., & Hu, C. (2012). Superparamagnetic high-surface-area Fe3O4 nanoparticles as adsorbents for arsenic removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 217–218, 439–446.
Ghaedi, A. M., Ghaedi, M., Vafaei, A., Iravani, N., Keshavarz, M., Rad, M., Tyagi, I., Agarwal, S., & Gupta, V. K. (2015). Adsorption of copper (II) using modified activated carbon prepared from Pomegranate wood: optimization by bee algorithm and response surface methodology. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 206, 195–206.
Ghorbani, F., Younesi, H., Ghasempouri, S. M., Zinatizadeh, A. A., Amini, M., & Daneshi, A. (2008). Application of response surface methodology for optimization of cadmium biosorption in an aqueous solution by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chemical Engineering Journal, 145, 267–275.
Ghorbani, F., Younesi, H., Mehraban, Z., Sabri Çelikc, M., Ghoreyshid, A. A., & Anbiae, M. (2013). Aqueous cadmium ions removal by adsorption on APTMS grafted mesoporous silica MCM-41 in batch and fixed bed column processes. International Journal of Engineering, 26, 473–488.
Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A., Darvishnejad, Z., & Tahmasbi, B. (2015). Schiff base complexes of Ni, Co, Cr, Cd and Zn supported on magnetic nanoparticles: As efficient and recyclable catalysts for the oxidation of sulfides and oxidative coupling of thiols. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 435, 223–231.
Haw, C. Y., Mohamed, F., Chia, C. H., Radiman, S., Zakaria, S., Huang, N. M., & Lim, H. N. (2010). Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Ceramics International, 36, 1417–1422.
Hu, J., Chen, G., & Lo, I. M. C. (2005). Removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from wastewater by maghemite nanoparticles. Water Research, 39, 4528–4536.
Jabeen, H., Kemp, K. C., & Chandra, V. (2013). Synthesis of nano zerovalent iron nanoparticles—graphene composite for the treatment of lead contaminated water. Journal of Environmental Management, 130, 429–435.
Kakavandi, B., Kalantary, R., Farzadkia, M., Mahvi, A., Esrafili, A., Azari, A., Yari, A., & Javid, A. (2014). Enhanced chromium (VI) removal using activated carbon modified by zero valent iron and silver bimetallic nanoparticles. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 12, 1–10.
Kilianova, M., Prucek, R., Filip, J., Kolarik, J., Kvitek, L., Panacek, A., Tucek, J., & Zboril, R. (2013). Remarkable efficiency of ultrafine superparamagnetic iron(III) oxide nanoparticles toward arsenate removal from aqueous environment. Chemosphere, 93, 2690–2697.
Landaburu-Aguirre, J., García, V., Pongrácz, E., & Keiski, R. (2006). Applicability of membrane technologies for the removal of heavy metals. Desalination, 200, 272–273.
Martinson, C. A., & Reddy, K. J. (2009). Adsorption of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) by cupric oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 336, 406–411.
Meng, J., Yang, G., Yan, L., & Wang, X. (2005). Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanometer pigment Fe3O4. Dyes and Pigments, 66, 109–113.
Mirzabe, G. H., & Keshtkar, A. R. (2015). Application of response surface methodology for thorium adsorption on PVA/Fe3O4/SiO2/APTES nanohybrid adsorbent. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 26, 277–285.
Pang, Y., Zeng, G., Tang, L., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Lei, X., Li, Z., Zhang, J., Liu, Z., & Xiong, Y. (2011). Preparation and application of stability enhanced magnetic nanoparticles for rapid removal of Cr(VI). Chemical Engineering Journal, 175, 222–227.
Ranjan, D., Talat, M., & Hasan, S. H. (2009). Biosorption of arsenic from aqueous solution using agricultural residue ‘rice polish’. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1050–1059.
Rostamizadeh, S., Shadjou, N., Azad, M., & Jalali, N. (2012). (α-Fe2O3)-MCM-41 as a magnetically recoverable nanocatalyst for the synthesis of pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridines at room temperature. Catalysis Communications, 26, 218–224.
Shan, H., Ma, T., Wang, Y., Zhao, J., Han, H., Deng, Y., He, X., & Dong, Y. (2013). A cost-effective system for in-situ geological arsenic adsorption from groundwater. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 154, 1–9.
Singh, D., Gautam, R. K., Kumar, R., Shukla, B. K., Shankar, V., & Krishna, V. (2014). Citric acid coated magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and application in removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 4, 233–241.
Srivastava, P. K., Vaish, A., Dwivedi, S., Chakrabarty, D., Singh, N., & Tripathi, R. D. (2011). Biological removal of arsenic pollution by soil fungi. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 2430–2442.
Tang, S. C., & Lo, I. M. (2013). Magnetic nanoparticles: essential factors for sustainable environmental applications. Water Research, 47, 2613–2632.
Tuutijarvi, T., Lu, J., Sillanpaa, M., & Chen, G. (2009). As(V) adsorption on maghemite nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1415–1420.
Wu, Y., Zhang, J., Tong, Y., & Xu, X. (2009). Chromium (VI) reduction in aqueous solutions by Fe3O4-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172, 1640–1645.
Wu, S., Sun, A., Zhai, F., Wang, J., Xu, W., Zhang, Q., & Volinsky, A. A. (2011). Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles synthesis from tailings by ultrasonic chemical co-precipitation. Materials Letters, 65, 1882–1884.
Wu, Y., Jin, Y., Cao, J., Yilihan, P., Wen, Y. & Zhou, J. (2014). Optimizing adsorption of arsenic(III) by NH2-MCM-41 using response surface methodology. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20(5), 2792–2800.
Xin, X., Wei, Q., Yang, J., Yan, L., Feng, R., Chen, G., Du, B., & Li, H. (2012). Highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions by amine-functionalized mesoporous Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 184, 132–140.
Yantasee, W., Warner, C. L., Sangvanich, T., Addleman, R. S., Carter, T. G., Wiacek, R. J., Fryxell, G. E., Timchalk, C., & Warner, M. G. (2007). Removal of heavy metals from aqueous systems with thiol functionalized superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 5114–5119.
Yavuz, C. T., Mayo, J. T., Suchecki, C., Wang, J., Ellsworth, A. Z., D’Couto, H., Quevedo, E., Prakash, A., Gonzalez, L., Nguyen, C., Kelty, C., & Colvin, V. L. (2010). Pollution magnet: nano-magnetite for arsenic removal from drinking water. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 32, 327–334.
Yu, X., Tong, S., Ge, M., Wu, L., Zuo, J., Cao, C., & Song, W. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of multi-amino-functionalized cellulose for arsenic adsorption. Carbohydrate Polymers, 92, 380–387.
Zhang, S., Niu, H., Cai, Y., Zhao, X., & Shi, Y. (2010). Arsenite and arsenate adsorption on coprecipitated bimetal oxide magnetic nanomaterials: MnFe2O4 and CoFe2O4. Chemical Engineering Journal, 158, 599–607.
Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Xu, Q., Xiao, H., Wang, X., Xu, H., & Zhou, J. (2013). Thiol modified Fe3O4@SiO2 as a robust, high effective, and recycling magnetic sorbent for mercury removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 226, 30–38.
Zuo, J.-C., Tong, S.-R., Yu, X.-L., Wu, L.-Y., Cao, C.-Y., Ge, M.-F., & Song, W.-G. (2012). Fe3+ and amino functioned mesoporous silica: preparation, structural analysis and arsenic adsorption. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 235–236, 336–342.
Acknowledgments
The present research was made possible through a university grant, sponsored by University of Kurdistan (UOK), Ministry of Science, Iran. The authors wish to thank Mr. Hoshyar Gavilian, the technician of environment laboratory at environmental science departments, for his assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikraftar, N., Ghorbani, F. Adsorption of As(V) Using Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles with Ascorbic Acid: Optimization by Response Surface Methodology. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 178 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2876-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2876-1