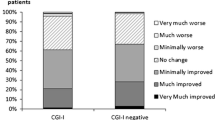
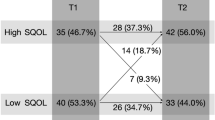
Abstract
Purpose
To provide data on long-term health-related quality of life (HRQL) outcomes among patients with schizophrenia (SZ) and schizoaffective (SA) disorders and determine the predictive value of disorder-related factors.
Methods
A total of 108 patients with SZ/SA were assessed during stabilization phase and over 10 years with the Quality of Life Enjoyment and Life Satisfaction Questionnaire (Q-LES-Q), Clinical Global Impression Scale, Positive and Negative Syndromes Scale (PANSS), Distress Scale for Adverse Symptoms (DSAS), Talbieh Brief Distress Inventory (TBDI), Brief Symptom Inventory-Somatization Scale (BSI-S), and Global Assessment of Functioning Scale (GAF). Variability and relationships between Q-LES-Q and disorder-related dimensions over time were analyzed.
Results
There were no differences in Q-LES-Q dimensions between patients with SZ and SA disorders. Poor outcomes were found among 76% of the patients with SZ/SA disorders who remained dissatisfied (64%) or worsened (12%) with their HRQL over time. However, 24% of patients reported improved quality of life (16%), or remained satisfied (8%). Changes in TBDI, DSAS, BSI-S, PANSS, and GAF measures accounted for 20–50% of the total variance in satisfaction changes in Q-LES-Q domains across time.
Conclusions
Long-term quality of life outcomes are characterized by four different types that fit changes over time in emotional distress, side effects, somatization, symptom dimensions, and general functioning scores. Revealed predictors are factors that can be ameliorated and thereby enhance satisfaction with quality of life over time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lehman, A. F. (1996). Measures of quality of life among persons with severe and persistent mental disorders. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 31, 78–88.
Priebe, S. I., Roeder-Wanner, U. U., & Kaiser, W. (2000). Quality of life in first-admitted schizophrenia patients: A follow-up study. Psychological Medicine, 30, 225–230.
Ritsner, M., Modai, I., Endicott, J., Rivkin, O., Nechamkin, Y., Barak, P., et al. (2000). Differences in quality of life domains and psychopathologic and psychosocial factors in psychiatric patients. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 61, 880–889.
Ritsner, M.S., & Gibel, A. (2007). Quality of life impairment syndrome in schizophrenia. In: M. S. Ritsner, A. G. Awad (Eds.), (173–226) Netherlands: Springer.
Dickerson, F. B., Ringel, N. B., & Parente, F. (1998). Subjective quality of life in out-patients with schizophrenia: Clinical and utilization correlates. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 98, 124–127.
Packer, S., Husted, J., Cohen, S., & Tomlinson, G. (1998). Psychopathology and quality of life in schizophrenia. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, 22, 231–234.
Fitzgerald, P. B., Williams, C. L., & Corteling, N. (2001). Subject and observer-rated quality of life in schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 103, 387–392.
Bechdolf, A., Klosterkotter, J., Hambrecht, M., Knost, B., Kuntermann, C., Schiller, S., et al. (2003). Determinants of subjective quality of life in post acute patients with schizophrenia. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 253, 228–235.
Voruganti, L. N., Heslegrave, R. J., & Awad, A. G. (1997). Quality of life measurement during antipsychotic drug therapy of schizophrenia. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, 22, 267–274.
Young, A. S., Sullivan, G., & Burnam, M. A. (1998). Measuring the quality of outpatient treatment for schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry, 28, 1221–1230.
Ritsner, M., Ponizovsky, A., Endicott, J., Nechamkin, Y., Rauchverger, B., Silver, H., et al. (2002). Relatively small impact adverse events of antipsychotics on life satisfaction of schizophrenia patients: A naturalistic study. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 12, 31–38.
Lasalvia, A., Ruggeri, M., & Santolini, N. (2002). Subjective quality of life: Its relationship with clinician-rated and patient-rated psychopathology. The South-Verona outcome project 6. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 71, 275–284.
Ritsner, M., & Kurs, R. (2002). Impact of antipsychotic agents and their side effects on the quality of life in schizophrenia. Expert Review in Pharmacoeconomics Outcomes Research, 2, 89–98.
Ritsner, M., & Kurs, R. (2003). Quality of life outcomes in mental illness: Schizophrenia, mood and anxiety disorders. Expert Review in Pharmacoeconomics Outcomes Research, 3, 189–199.
Awad, A. G., & Voruganti, L. N. (2004). Impact of atypical antipsychotics on quality of life in patients with schizophrenia. CNS Drugs, 18, 877–893.
Lambert, M., & Naber, D. (2004). Current issues in schizophrenia: Overview of patient acceptability, functioning capacity and quality of life. CNS Drugs 18(Suppl 2), 5–17.
Ritsner, M., Gibel, A., & Ratner, Y. (2006). Determinants of changes in perceived quality of life in the course of schizophrenia. Quality of Life Research, 15, 515–526.
Bengtsson-Tops, A., & Hansson, L. (2001). Quantitative and qualitative aspects of the social network in schizophrenic patients living in the community. Relationship to sociodemographic characteristics and clinical factors and subjective quality of life. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 47, 67–77.
Barry, M. M., & Crosby, C. (1996). Quality of life as an evaluative measure in assessing the impact of community care on people with long-term psychiatric disorders. British Journal of Psychiatry, 168, 210–216.
Bow-Thomas, C. C., Velligan, D. I., Miller, A. L., & Olsen, J. (1999). Predicting quality of life from symptomatology in schizophrenia at exacerbation and stabilization. Psychiatry Research, 86, 131–142.
Browne, S. (1999). Rehabilitation programmes and quality of life in severe mental illness. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 45(4), 302–309.
Lenz, G., & Demal, U. (2000). Quality of life in depression and anxiety disorders: An exploratory follow-up study after intensive inpatient cognitive behaviour therapy. Psychopathology, 33(6), 297–302.
Holloway, F., & Carson, J. (1999). Subjective quality of life, psychopathology, satisfaction with care and insight: An exploratory study. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 45, 259–267.
Jarema, M., & Konieczynska, Z. (2001). Quality of life in schizophrenia: Impact of psychopathology, patients’ gender and antipsychotic treatment. International Journal of Psychiatry in Clinical Practice, 5(1), 19–26.
Tempier, R., Mercier, C., Leouffre, P., & Caron, J. (1997). Quality of life and social integration of severely mentally ill patients: A longitudinal study. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, 22, 249–255.
Salokangas, R. K., Honkonen, T., Stengård, E., & Koivisto, A. M. (2006). Subjective life satisfaction and living situations of persons in Finland with long-term schizophrenia. Psychiatric Services, 57(3), 373–381.
Skantze, K. (1998). Subjective quality of life and standard of living: A 10-year follow-up of out-patients with schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 98(5), 390–399.
Lehman, A. F. (1988). A quality of life interview for the chronically mental ill. Evaluation and Program Planning, 11, 51–62.
Sullivan, G., Wells, K. B., & Leake, B. (1991). Quality of life of seriously mentally ill persons in Mississippi. Hospital & Community Psychiatry, 42, 752–755.
Malla, A., & Payne, J. (2005). First-episode psychosis: Psychopathology, quality of life, and functional outcome. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 31, 650–671.
Ritsner, M.S. (2007). The Distress/Protection Vulnerability Model of the quality of life impairment syndrome: Current evidence and new directions for research. In: M. S. Ritsner, A. G. Awad (Eds.), Quality of Life Impairment in Schizophrenia, Mood and Anxiety Disorders (pp. 3–19). Netherlands: Springer.
Awad, G. (1992). Quality of life of schizophrenic patients on medication and implications for new drug trials. Hospital & Community Psychiatry, 43, 262–266.
Skantze, K., & Malm, U. (1994). A new approach to facilitation of working alliances based on patients’ quality of life goals. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry, 1, 37–55.
Zissi, A., Barry, M. M., & Cochrane, R. (1998). A mediational model of quality of life for individuals with severe mental health problems. Psychological Medicine, 28, 1221–1230.
Ritsner, M., Kurs, R., Gibel, A., Hirschmann, S., Shinkarenko, E., & Ratner, Y. (2003). Predictors of quality of life in major psychoses: A naturalistic follow-up study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 64, 308–315.
Ritsner, M., & Kurs, R. (2006). Quality-of-life impairment in severe mental illness: Focus on schizoaffective disorders. In William. H. Murray (Ed.), Schizoaffective disorder: New research (pp. 69–107). New York: NOVA Publishers.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Ritsner, M., Ben-Avi, I., Ponizovsky, A., Timinsky, I., Bistrov, E., & Modai, I. (2003). Quality of life and coping with schizophrenia symptoms. Quality of Life Research, 12, 1–9.
Ritsner, M. (2003). Predicting changes in domain-specific quality of life of schizophrenia patients. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 191, 287–294.
Endicott, J., Nee, J., Harrison, W., & Blumenthal, R. (1993). Quality of life enjoyment and satisfaction questionnaire: A new measure. Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 29, 321–326.
Guy, W. (1976). ECDU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. Rockville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services.
Kay, S. R., Fiszbein, A., & Opler, L. A. (1987). The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 13, 261–276.
Ritsner, M., Modai, I., Rivkin, O., Bystrov, E., Nehamkin, Y., & Ponizovsky, A. (1999). Distress scale for adverse symptoms: A new instrument for measuring the relationship between adverse drug symptoms and associated distress. 12th ECNP Congress, London—United Kingdom, September 21–25, 1999. European Neuropsychopharmacology 9(Suppl. 5), S258.
Ritsner, M., Rabinowitz, J., & Slyuzberg, M. (1995). The Talbieh brief distress inventory: A brief instrument to measure psychological distress among immigrants. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 36, 448–453.
Ritsner, M., Modai, I., & Ponizovsky, A. (2002). Assessing psychological distress in psychiatric patients: Validation of the Talbieh brief distress inventory. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 43, 229–234.
Derogatis, L. R., & Spencer, P. M. (1982). The brief symptom inventory (BSI): Administration, scoring and procedures manual. School of Medicine: Johns Hopkins University.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Hintze, J. L. (1998). NCSS 6.0. Statistical System for Windows. User’s Guide. Kaysville Utah: Number Cruncher Statistical Systems.
Skantze, K., Malm, U., Dencker, S. J., May, P. R., & Corrigan, P. (1992). Comparison of quality of life with standard of living in schizophrenic outpatients. British Journal of Psychiatry, 161, 797–801.
Lambert, M., Schimmelmann, B. G., Schacht, A., Karow, A., Wagner, T., Wehmeier, P. M., et al. (2009). Long-term patterns of subjective wellbeing in schizophrenia: Cluster, predictors of cluster affiliation, and their relation to recovery criteria in 2,842 patients followed over 3 years. Schizophrenia Research, 107(2–3), 165–172.
Warner, R. (2009). Recovery from schizophrenia and the recovery model. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 22(4), 374–380.
Srivastava, A. K., Stitt, L., Thakar, M., Shah, N., & Chinnasam, G. (2009). The abilities of improved schizophrenia patients to work and live independently in the community: A 10-year long-term outcome study from Mumbai, India. Annals of General Psychiatry, 8, 24.
Awad, A. G., Voruganti, L. N., & Heslegrave, R. J. (1997). A conceptual model of quality of life in schizophrenia: Description and preliminary clinical validation. Quality of Life Research, 6, 21–26.
Franz, M., Meyer, T., Reber, T., & Gallhofer, B. (2000). The importance of social comparisons for high levels of subjective quality of life in chronic schizophrenic patients. Quality of Life Research, 9(5), 481–489.
Heinrichs, D. W., Hanlon, T. E., & Carpenter, W. T., Jr. (1984). The quality of life scale: An instrument for rating the schizophrenic deficit syndrome. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 10, 388–398.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the clinical staff of Sha’ar Menashe Mental Health Center, particularly Drs. O. Rivkin, E. Shinkarenko, I. Timisky, Y. Ratner, A. Gibel, H. Farkash, G. Perelroyzen, A. Ponizovsky, and Mrs R. Kurs, for their valuable participation in conducting previous stages of this project. And special thanks to Mrs R. Kurs for editing this manuscript.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ritsner, M.S., Lisker, A. & Arbitman, M. Ten-year quality of life outcomes among patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorders: I. Predictive value of disorder-related factors. Qual Life Res 21, 837–847 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-011-9988-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-011-9988-2