Abstract
Introduction
Kidney transplantation improves the quality of life of end-stage renal disease patients. The quality of life benefits, however, pertain to patients on average, not to all transplant recipients. The aim of this study was to identify factors associated with health-related quality of life after kidney transplantation.
Methods
Population-based study with a cross-sectional design was carried out and quality of life was assessed by SF-36 Health Survey Version 1. A multivariate linear regression model was constructed with sociodemographic, clinical and laboratory data as independent variables.
Results
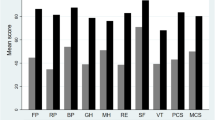
Two hundred and seventy-two kidney recipients with a functioning graft were analyzed. Hypertension, diabetes, higher serum creatinine and lower hematocrit were independently and significantly associated with lower scores for the SF-36 oblique physical component summary (PCSc). The final regression model explained 11% of the PCSc variance. The scores of oblique mental component summary (MCSc) were worse for females, patients with a lower income, unemployed and patients with a higher serum creatinine. The regression model explained 9% of the MCSc variance.
Conclusions
Among the studied variables, comorbidity and graft function were the main factors associated with the PCSc, and sociodemographic variables and graft function were the main determinants of MCSc. Despite comprehensive, the final regression models explained only a little part of the heath-related quality of life variance. Additional factors, such as personal, environmental and clinical ones might influence quality of life perceived by the patients after kidney transplantation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laupacis, A., Keown, P., Pus, N., Krueger, H., Ferguson, B., Wong, C., et al. (1996). A study of quality of life and cost-utility of renal transplantation. Kidney International, 50, 235–242.
Sesso, R., Eisenberg, J. M., Stabile, C., Draibe, S., Ajzen, H., & Ramos, O. (1990). Cost-effectiveness analysis of the treatment of end-stage renal disease in Brazil. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care, 6(1), 107–114.
Evans, R. W., & Kitzmann, D. J. (1998). An economic analysis of kidney transplantation. Surgical Clinics of North America, 78, 149–174.
Wolfe, R. A., Ashby, V. B., & Milford, E. L. (1999). Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. New England Journal of Medicine, 341, 1725–1730.
Dew, M. A., Switzer, G. E., Goycoolea, J. M., Allen, A. S., DiMartini, A., Kormos, R. L., et al. (1997). Does transplantation produce quality of life benefits: A quantitative analysis of the literature. Transplantation, 64(9), 1261–1273.
Jofre, R., Lopez-Gomez, J. M., Moreno, F., Sanz-Guajardo, D., & Valderrabano, F. (1998). Changes in quality of life after renal transplantation. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 32, 93–100.
Evans, R. W., Manninen, D. L., Garrison, L. P., Jr., et al. (1985). The quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease. New England Journal of Medicine, 312, 553–559.
Liem, Y. S., Bosch, J. L., Arends, L. R., Heijenbrok-Kal, M. H., & Hinink, M. G. M. (2007). Quality of life assessed with the medical outcomes study short form 36-item health survey of patients on renal replacement therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Value in Health, 10(5), 390–397.
Van der Mei, S. F., Krol, B., Van Son, W. J., Jong, P. E., Groothoff, J. W., & Van den Heuvel, W. J. A. (2006). Social participation and employment status after kidney transplantation: A systematic review. Quality of Life Research, 15, 979–994.
Rebollo, P., Ortega, F., Baltar, J. M., et al. (2000). Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of kidney transplant patients: Variables that influence it. Clinical Transplantation, 14, 199–207.
Rebollo, P., Gonzalez, M. P., Bobes, J., Saiz, P., & Ortega, F. (2000). Interpretación de los resultados de la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud de pacientes en terapia substitutiva de la insuficiencia renal terminal. Nefrologia, 20, 431–439.
Zimmermann, P. R., Poli de Figueiredo, C. E., & Fonseca, N. A. (2001). Depression, anxiety and adjustment in renal replacement therapy: A quality of life assessment. Clinical Nephrology, 56(5), 387–390.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Earlbaum Associates.
Ciconelli, R. M., Ferraz, M. B., Santos, W., Meinão, I., & Quaresma, M. R. (1999). Brazilian-Portuguese version of the SF-36. A reliable and valid quality of life outcome measure. Revista Brasileira De Reumatologia, 39, 143–150.
Farivar, S. S., Cunningham, W. E., & Hays, R. D. (2007). Correlated physical and mental health summary scores for the SF-36 and SF-12 health survey, V.1. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 5, 54.
Hosmer, D. W., & Lemeshow, S. (2000). Applied logistic regression. New York: Wiley.
Butt, Z., Yount, S. E., Caicedo, J. C., Abecassis, M. M., & Cella D. (2008). Quality of life assessment in renal transplant: Review and future directions. Clinical Transplantation, 22(3), 292–303.
Reimer, J., Franke, G. H., Philipp, T., & Heemann, U. (2002). Quality of life in kidney recipients: Comparison of tacrolimus and cyclosporine-micro emulsion. Clinical Transplantation, 16, 48–54.
Oberbauer, R., Hutchison, B., Eris, J., Arias, M., Claesson, K., Mota, A., et al. (2003). Health-related quality-of-life outcomes of sirolimus-treated kidney transplant patients after elimination of cyclosporin A: Results of a 2-year randomized clinical trial. Transplantation, 75, 1277–1285.
Ware, J. E., Kosinski, M., & Keller, S. D. (1994). SF-36 physical and mental health summary scales: A user’s manual. Boston, MA: The Health Institute.
Wight, J. P., Edwards, L., & Brazier, J. (1998). The SF36 as an outcome measure of services for end stage renal failure. Quality in Health Care, 7, 209–221.
Griva, K., Ziegelmann, J., & Thompson, D. (2002). Quality of life and emotional responses in cadaver and living related renal transplant recipients. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 17, 2204–2211.
Hathaway, D. K., Winsett, R. P., & Johnson, C. (1998). Post kidney transplant quality of life prediction models. Clinical Transplantation, 12, 168–174.
Chiu, S. F. A., Wong, H. S., Morad, Z., & Loo, L. H. (2004). Quality of life in cadaver and living-related renal transplant recipient in Kuala Lumpur Hospital. Transplantation Proceedings, 36, 2030–2031.
Julius, M., Hawthorne, V. M., & Carpentier Alting, P. (1989). Independence in activities of daily living for end-stage renal patients: Biomedical and demographic correlates. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 13, 61–69.
Khedmat, H., Karami, G. R., Pourfarziani, V., Assari, S., Rezailashkajani, M., & Naghizadeh, M. M. (2007). A logistic regression model for predicting health-related quality of life in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation Proceedings, 39, 917–922.
Matas, A. J., Halbert, R. J., Barr, M. L., Helderman, J. H., Hricik, D. E., Pirsch, J. D., et al. (2002). Life satisfaction and adverse effects in renal transplant recipients: A longitudinal analysis. Clinical Transplantation, 16, 113–121.
Rosenberger, J., van Dijk, J. P., Nagyova, I., Zezula, I., Geckova, A. M., Roland, R., et al. (2006). Predictors of perceived health status in patients after kidney transplantation. Transplantation, 81, 1306–1310.
Rosenberger, J., van Dijk, J. P., Nagyova, I., Roland, R., Geckova, A. M., van den Heuvel, W. J. A., et al. (2005). Do dialysis and transplantation related medical factors affect perceived health status? Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 20(10), 2153–2158.
Baiardi, F., Degli, E. E., Cocchi, R., Fabbri, A., Sturani, A., Valpiani, G., et al. (2002). Effects of clinical and individual variables on quality of life in chronic renal failure patients. Journal of Nephrology, 15(1), 61–67.
Kasiske, B. L., Snyder, J. J., Gilbertson, D., & Matas, A. J. (2003). Diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation in the United States. American Journal of Transplantation, 3, 178–185.
Winkelmayer, W. C., Kewalramani, R., Rutstein, M., Gabardi, S., Vonvisger, T., & Chandraker, A. (2004). Pharmacoepidemiology of anemia in kidney transplant recipients. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 15, 1347–1352.
Muehrer, R. J., & Becker, B. N. (2005). Life after transplantation: New transitions in quality of life and psychological distress. Seminars in Dialysis, 18, 124–131.
Keogh, A. M., & Feehally, J. (1999). A quantitative study comparing adjustment and acceptance of illness in adults on renal replacement therapy. ANNA Journal, 26, 471–477.
Fujisawa, M., Ichikawa, Y., Yoshiya, K., Isotani, S., Higuchi, A., Nagano, S., et al. (2000). Assessment of health-related quality of life in renal transplant and hemodialysis patients using the SF-36 Health Survey. Urology, 56, 201–206.
Saracino, A., Gollo, I., Di Noia, I., Caldone, M. G., Santarsia, G., Procida, C., et al. (2008). Loss of renal function is associated with deterioration of health-related quality of life in kidney transplant patients. Transplantation Proceedings, 40, 3460–3465.
Lubetkin, E. I., Jia, H., Franks, P., & Gold, M. R. (2005). Relationship among sociodemographic factors, clinical conditions, and health-related quality of life: Examining the EQ-5D in the US general population. Quality of Life Research, 14, 2187–2196.
Johnson, C. D., Wicks, M. N., Milstead, J., Hartwig, M., & Hathaway, D. K. (1998). Racial and gender differences in quality of life following kidney transplantation. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 30, 125–130.
Muennig, P., Franks, P., Jia, H., Lubetkin, E., & Gold, M. (2005). The income-associated burden of disease in the United States. Social Science and Medicine, 61, 2018–2026.
Krupski, T., Fink, A., Kwan, L., et al. (2005). Health-related quality of life in low-income, uninsured men with prostate cancer. Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Underserved, 16, 375–390.
Hann, D., Jacobsen, P., Martin, S., Kronish, L., Azzarello, L., & Fields, K. (1997). Quality of life following bone marrow transplantation for breast cancer: A comparative study. Bone Marrow Transplantation, 19, 257–264.
Short, P., & Mallonee, E. (2006). Income disparities in the quality of life of cancer survivors. Medical Care, 44, 16–23.
McCabe, M., & de Judicibus, M. (2005). The effects of economic disadvantage on psychological well-being and quality of life among people with multiple sclerosis. Journal of Health Psychology, 10, 163–173.
Wubben, D., & Porterfield, D. (2005). Health-related quality of life among North Carolina adults with diabetes mellitus. North Carolina Medical Journal, 66, 179–185.
Sesso, R., Rodrigues-Neto, J. F., & Ferraz, M. B. (2003). Impact of socioeconomic status on the quality of life of end-stage renal disease patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 41(1), 186–195.
Grady, K., Naftel, D., White-Williams, C., et al. (2005). Predictors of quality of life at 5–6 years after heart transplantation. Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, 24, 1431.
Vanderbilt.edu [homepage na Internet]. Nashville: Vanderbilt University Medical Center; c 2004 [atualizada em 2005 Feb 02; acesso em 2008 Jan 10]. Available at: www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/transplant/html/supportservices.html.
Ware, J. E., Jr., & Sherbourne, C. D. (1992). The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care, 30, 473–483.
Seršić, D. M., & Vuletić, G. (2006). Psychometric evaluation and establishing norms of croatian SF-36 health survey: Framework for subjective health research. Croatian Medical Journal, 47(1), 95–102.
Behavioral Epidemiology Unit. South Australian population norms for the Short Form 36 (SF-36) Health Status Questionnaire. Adelaide, South Australian Health Commission, August 1995.
Aaronson, N. K., Muller, M., Cohen, P. D., Essink-Bot, M. L., Fekkes, M., Sanderman, R., et al. (1998). Translation, validation, and norming of the Dutch language version of the SF-36 health survey in community and chronic disease populations. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 51, 1055–1068.
Apolone, G., & Mosconi, P. (1998). The Italian SF-36 health survey: Translation, validation and norming. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 51, 1025–1036.
Leplege, A., Ecosse, E., Verdier, A., & Perneger, T. V. (1998). The French SF-36 health survey: Translation, cultural adaptation and preliminary psychometric evaluation. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 51, 1013–1023.
Bjorner, J. B., Kreiner, S., Ware, J. E., Damsgaard, M. T., & Bech, P. (1998). Differential item functioning in the Danish translation of the SF-36. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 51, 1189–1202.
Phipps, S. (2003). The impact of poverty on health. Ottawa: Canadian Institute for Health Information.
Russ, G., Jamieson, N., Oberbauer, R., Arias, M., Murgia, M. G., Blancho, G., et al. (2007). Three-year health-related quality-of-life outcomes for sirolimus-treated kidney transplant patients after elimination of cyclosporine. Transplant International, 20(10), 875–883.
Chambers, E. S., Bridge, M. W., & Jones, D. A. (2009). Carbohydrate sensing in the human mouth: Effects on exercise performance and brain activity. Journal of Physiology, 587, 1779–1794.
Unruh, M. L., Weisbord, S. D., & Kimmel, P. L. (2005). Health-related quality of life in nephrology research and clinical practice. Seminars in Dialysis, 18(2), 82–90.
Ortega, F., Valdés, C., & Ortega, T. (2007). Quality of life after solid organ transplantation. Transplantation Reviews, 21, 155–170.
Diaz-Buxo, J. A., Lowrie, E. G., Lew, N. L., Zhang, H., & Lazarus, J. M. (2000). Quality of life evaluation using short form 36: Comparison in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 35, 293–300.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bohlke, M., Marini, S.S., Rocha, M. et al. Factors associated with health-related quality of life after successful kidney transplantation: a population-based study. Qual Life Res 18, 1185–1193 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-009-9536-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-009-9536-5