Abstract
Purpose
To characterize factor(s) contained in apical medium of primary cultured rat alveolar epithelial type II cell-like monolayers (RAECM-II) that enhance insulin absorption across alveolar epithelial cells.
Materials and Methods
Primary rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers cultured on Transwells in the presence and absence of 10 ng/ml keratinocyte growth factor for 6 days were dosed from the apical compartment with radiolabeled insulin in: newborn bovine serum-containing medium (SM), conditioned medium from apical compartment of rat alveolar epithelial type I cell-like monolayers (RAECM-I) (CMI), or conditioned medium from apical compartment of RAECM-II (CMII). At the end of 2 h incubation, basolateral medium was collected and amounts of transported radiolabeled insulin were determined using a gamma counter. In order to determine the molecular size range of the enhancing factor(s), CMII was centrifuged in 50 kDa molecular weight cut-off Centricon tubes, and both retentate and filtrate were used as separate dosing solutions. Heat denaturation and ammonium sulphate precipitation were used to determine if the involved factor(s) represent proteins or other smaller soluble factors. Transalveolar transport rates of a paracellular marker, 14C-mannitol, and fluid-phase marker, horseradish peroxidase, were determined in the presence and absence of the factors. Effects of temperature (4, 16 and 37°C) on radiolabeled insulin fluxes were also measured.
Results
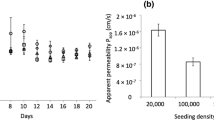
Conditioned medium obtained from the apical compartment of RAECM-II, CMII, increased transport of insulin across the monolayers when compared to SM or CMI. The enhancing effect of CMII was retained in the precipitate following ammonium sulfate treatment and in the retentate after Centricon filtration. The enhancing effect of CMII was significantly decreased when heated at 80°C for 15 min. CMII did not affect the transport of 14C-mannitol or HRP, while its effect on insulin transport was decreased by 87% when temperature was lowered to 4°C from 37°C.
Conclusions
Conditioned medium from type II cell-like monolayer cultures appears to contain protein factor(s) which seem to be involved in facilitating active transcellular transport of insulin across primary cultured RAECM-II.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. Patton, J. Bukar, and S. Nagarajan. Inhaled insulin. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 35:235–247 (1999).
F. W. Wigley, J. H. Londono, S. H. Wood, J. C. Shipp, and R. H. Waldman. Insulin across respiratory mucosae by aerosol delivery. Diabetes 20:552–556 (1971).
J. S. Patton, C. S. Fishburn, and J. G. Weers. The lungs as a portal of entry for systemic drug delivery. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 1:338–344 (2004).
J. S. Patton. Mechanisms of macromolecule absorption by the lungs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 19:3–36 (1996).
A. Yamamoto, S. Umemori, S. Muranishi and S. Muranishi. Absorption enhancement of intrapulmonary administered insulin by various absorption enhancers and protease inhibitors in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 46:14–18 (1994).
F. Komada, S. Iwakawa, F. N. Yamamoto, H. Sakakibara, and K. Okumura. Intratracheal delivery of insulin: absorption from solution and aerosol by rat lung. Int. J. Pharm. 88:63–73 (1992).
F. Johansson, E. Hjertberg, S. Eirefelt, A. Tronde, and U. Hultkvist Bengtsson. Mechanisms for absorption enhancement of inhaled insulin by sodium taurocholate. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 17:63–71 (2002).
L. Li, N. R. Mathias, C. L. Heran, P. Moench, D. A. Wall, and R. L. Smith. Carbopol-mediated paracellular transport enhancement in Calu-3 cell layers. J. Pharm. Sci. 95:326–335 (2006).
Y. Fukuda, T. Tsuji, T. Fujita, A. Yamamoto, and S. Muranishi. Susceptibility of insulin to proteolysis in rat lung homogenate and its protection from proteolysis by various protease inhibitors. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 18:891–894 (1995).
Z. Shen, Q. Zhang, S. Wei, and T. Nagai. Proteolytic enzymes as a limitation for pulmonary absorption of insulin: in vitro and in vivo investigations. Int. J. Pharm. 192:115–121 (1999).
S. Kobayashi, S. Kondo, and K. Juni. Study on pulmonary delivery of salmon calcitonin in rats: effects of protease inhibitors and absorption enhancers. Pharm. Res. 11:239–1243 (1994).
A. J. Bitonti, J. A. Dumont, S. C. Low, R. T. Peters, K. E. Kropp, V. J. Palombella, J. M. Stattel, Y. Lu, C. A. Tan, J. J. Song, A. M. Garcia, N. E. Simister, G. M. Spiekermann, W. I. Lencer, and R. S. Blumberg. Pulmonary delivery of an erythropoietin Fc fusion protein in non-human primates through an immunoglobulin transport pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:9763–9768 (2004).
A. J. Bitonti and J. A. Dumont. Pulmonary administration of therapeutic proteins using an immunoglobulin transport pathway. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58:1106–1118 (2006).
A. Widera, K. J. Kim, E. D. Crandall, and W. C. Shen. Transcytosis of GCSF-transferrin across rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers. Pharm. Res. 20:1231–1238 (2003).
D. Deshpande, D. Toledo-Velasquez, L. Y. Wang, C. J. Malanga, J. K. Ma, and Y. Rojanasakul. Receptor-mediated peptide delivery in pulmonary epithelial monolayers. Pharm. Res. 11:1121–1126 (1994).
M. E. Brandes and J. N. Finkelstein. Stimulated rabbit alveolar macrophages secrete a growth factor for type II pneumocytes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1:101–109 (1989).
Y. Matsukawa, H. Yamahara, F. Yamashita, V. H. Lee, E. D. Crandall, and K. J. Kim. Rates of protein transport across rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers. J. Drug Target. 7:335–342 (2000).
M. Bur, H. Huwer, C. M. Lehr, N. Hagen, M. Guldbrandt, K. J. Kim, and C. Ehrhardt. Assessment of transport rates of proteins and peptides across primary human alveolar epithelial cell monolayers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 28:196–203 (2006).
Z. Borok, R. L. Lubman, S. I. Danto, X. L. Zhang, S. M. Zabski, L. S. King, D. M. Lee, P. Agre, and E. D. Crandall. Keratinocyte growth factor modulates alveolar epithelial cell phenotype in vitro: expression of aquaporin 5. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 18:554–561 (1998).
R. Mitra, I. Pezron, Y. Li, and A. K. Mitra. Enhanced pulmonary delivery of insulin by lung lavage fluid and phospholipids. Int. J. Pharm. 217:25–31 (2001).
P. J. McConahey and F. J. Dixon. Radioiodination of proteins by the use of the chloramine-T method. Methods Enzymol. 70:210–213 (1980).
V. Herzog and H. D. Fahimi. A new sensitive colorimetric assay for peroxidase using 3,3′-diaminobenzidine as hydrogen donor. Anal. Biochem. 55:554–562 (1973).
A. Hussain, J. J. Arnold, M. A. Khan, and F. Ahsan. Absorption enhancers in pulmonary protein delivery. J. Control. Release 94:15–24 (2004).
T. Y. Ma, D. Nguyen, V. Bui, H. Nguyen, and N. Hoa. Ethanol modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am. J. Physiol. 276:G965–G974 (1999).
V. A. K. Dodane, M. Amin Khan, and J. R. Merwin. Effect of chitosan on epithelial permeability and structure. Int. J. Pharm. 10:21–32 (1999).
M. Machida, M. Hayashi, and S. Awazu. The effects of absorption enhancers on the pulmonary absorption of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rhG-CSF) in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 23:84–86 (2000).
T. Morita, A. Yamamoto, Y. Takakura, M. Hashida, and H. Sezaki. Improvement of the pulmonary absorption of (Asu1,7)-eel calcitonin by various protease inhibitors in rats. Pharm. Res. 11:909–913 (1994).
B. Forbes, C. G. Wilson, and M. Gumbleton. Temporal dependence of ectopeptidase expression in alveolar epithelial cell culture: implications for study of peptide absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 180:225–234 (1999).
M. C. Hsu and J. P. Bai. Investigation into the presence of insulin-degrading enzyme in cultured type II alveolar cells and the effects of enzyme inhibitors on pulmonary bioavailability of insulin in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 50:507–514 (1998).
S. Y. Hirai, T. Yashiki, and H. Mima. Mechanisms for the enhancement of the nasal absorption of insulin by surfactants. Int. J. Pharm. 9:173–184 (1981).
G. S. Gordon, A. C. Moses, R. D. Silver, J. S. Flier, and M. C. Carey. Nasal absorption of insulin: enhancement by hydrophobic bile salts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:7419–7423 (1985).
R. H. Hastings, H. G. Folkesson, and M. A. Matthay. Mechanisms of alveolar protein clearance in the intact lung. Am. J. Physiol. 286:L679–L689 (2004).
D. Shah and W. C. Shen. The paradox of transferrin receptor-mediated drug delivery-intracellular targeting or transcellular transport? J. Drug Target. 3:243–245 (1995).
L. G. Dobbs, M. C. Williams, and A. E. Brandt. Changes in biochemical characteristics and pattern of lectin binding of alveolar type II cells with time in culture. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 846:155–166 (1985).
M. Sakagami. In vivo, in vitro and ex vivo models to assess pulmonary absorption and disposition of inhaled therapeutics for systemic delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58:1030–1060 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank Ray Alvarez for preparing freshly isolated alveolar epithelial type II cells for this study. This work was supported by research grants HL64365, HL62569, HL38578, HL38621, and HL38658 from the National Institutes of Health and the Hastings Foundation. E. D. C. is Kenneth T. Norris Chair and Hastings Professor of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahhady, R., Kim, KJ., Borok, Z. et al. Enhancement of Insulin Transport Across Primary Rat Alveolar Epithelial Cell Monolayers by Endogenous Cellular Factor(s). Pharm Res 24, 1713–1719 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9301-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9301-9