Abstract
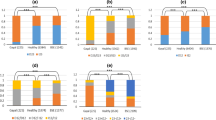
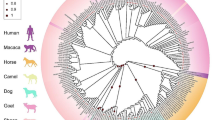
The gayal (Bos frontalis) is a rare semi-wild bovid species in which bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) has not been reported. Polymorphisms of the prion protein gene (PRNP) have been correlated significantly with resistance to BSE. In this study, the coding region of PRNP was cloned and characterized in samples from 125 gayal. A total of ten single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), including six silent mutations (C60T, G75A, A108T, G126A, C357T and C678T) and four mis-sense mutations (C8A, G145A, G461A and C756G), corresponding to amino acids T3K, G49S9, N154S and I252M were identified, revealing high genetic diversity. Three novel SNPs including C60T, G145A and C756G, which have not been reported previously in bovid species, were retrieved. There also was one insertion–deletion (187Del24) at the N-terminal octapeptide repeat region. Alignment of nucleotide and amino acid sequences showed a high degree of similarity with other bovid species. Using phylogenetic analyses it was revealed that gayal has a close genetic relationship with Zebu cattle. In short, preliminary information is provided about genotypes of the PRNP in gayal. This could assist with the study of the pathogenesis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies and cross species transmission as well as a molecular breeding project for gayal in China.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prusiner SB (1996) Molecular biology and pathogenesis of prion diseases. Trends Biochem Sci 21:482–487
Prusiner SB (1998) Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13363–13383
Prusiner SB, Scott MR, De Armond SJ, Cohen FE (1998) Prion protein biology. Cell 93:337–348
Aguzzi A (2006) Prion diseases of humans and farm animals: epidemiology, genetics, and pathogenesis. J Neurochem 97:1726–1739
Wang F, Wang X, Yuan CG, Ma J (2010) Generating a prion with bacterially expressed recombinant prion protein. Science 327:1132–1135
Vaccari G, Panagiotidis CH, Acin C, Peletto S, Barillet F, Acutis P, Bossers A, Langeveld J, van Keulen L, Sklaviadis T, Badiola JJ, Andreéoletti O, Groschup MH, Agrimi U, Foster J, Goldmann W (2009) State-of-the-art review of goat TSE in the European Union, with special emphasis on PRNP genetics and epidemiology. Vet Res 40:48
Mondal M, Dhali A, Rajkhowa C, Prakash BK (2004) Secretion patterns of growth hormone in growing captive mithuns (Bos frontalis). Zool Sci 21:1125–1129
Rajkhowa S, Sarma DK, Rajkhowa C (2006) Seroprevalence of toxoplasma gondii antibodies in captive mithuns (Bos frontalis) from India. Vet Parasitol 135:369–374
Chi J, Fu B, Nie W, Wang J, Graphodatsky AS, Yang F (2005) New insights into the karyotypic relationships of Chinese muntjac (Muntiacus reevesi), forest musk deer (Moschus berezovskii) and gayal (Bos frontalis). Cytogenet Genome Res 108:310–316
Mao HM, Deng WD, Wen JK (2005) The biology characteristics of gayal (Bos frontalis) and potential exploitation and utilization. J Yunnan Agric Univ 20:258–261 (In Chinese with English abstract available)
Bhambhani R, Kuspira J (1969) The somatic karyotypes of American bison and domestic cattle. Can J Genet Cytol 11:243–249
Gallagher DS, Womack JE (1992) Chromosome conservation in the Bovidae. J Hered 83:287–298
Zhao KD, Ou CH, Huang YL, He TB (2003) Rare animal germplasm resources in Yunnan Province: Present situation and countermea sures of preservation and research on Dulong cattle (Bos frontalis). J Yellow Cattle Sci 29:71–74 (In Chinese with English abstract available)
Xi DM, Wanapat M, Deng WD, He TB, Yang ZF, Mao HM (2007) Comparison of gayal (Bos frontalis) and Yunnan Yellow Cattle (Bos taurus): in vitro dry matter digestibility and gas production for a range of forages. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 20:1208–1214
Mohan M, Chandan R, Prakash BS (2007) Development and validation of a highly sensitive economic enzymeimmunoassay for prolactin determination in blood plasma of mithun (Bos frontalis) and its application during milk let down and cyclicity. Anim Reprod Sci 99:182–195
Heaton MP, Leymaster KA, Freking BA, Hawk DA, Smith TP, Keele JW, Snelling WM, Fox JM, Chitko-McKown CG, Laegreid WW (2003) Prion gene sequence variation within diverse groups of U.S. sheep, beef cattle, and deer. Mamm Genome 14:765–777
Zhang L, Li N, Fan B, Fang M, Xu W (2004) PRNP polymorphisms in Chinese ovine, caprine and bovine breeds. Anim Genet 35:457–461
Kues WA, Ollhoff RD, Carnwath JW, de Souza FP, Madeira HMF, Niemann H (2006) High incidence of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the prion protein gene of native Brazilian Caracu cattle. J Anim Breed Genet 123:326–330
Zhao H, Wang XY, Zou W, Zhang YP (2010) Prion protein gene (PRNP) polymorphisms in native Chinese cattle. Genome 53:138–145
Brunelle BW, Greenlee JJ, Seabury CM, Brown CE II, Nicholson EM (2008) Frequencies of polymorphisms associated with BSE resistance differ significantly between Bos taurus, Bos indicus, and composite cattle. BMC Vet Res 4:36
Seabury CM, Honeycutt RL, Rooney AP, Halbert ND, Derr JN (2004) Prion protein gene (PRNP) variants and evidence for strong purifying selection in functionally important regions of bovine exon 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15142–15147
Peletto S, Perucchini M, Acín C, Dalgleish MP, Reid HW, Rasero R, Sacchi P, Stewart P, Caramelli M, Ferroglio E, Bozzetta E, Meloni D, Orusa R, Robetto S, Gennero S, Goldmann W, Acutis PL (2009) Genetic variability of the prion protein gene (PRNP) in wild ruminants from Italy and Scotland. J Vet Sci 10:115–120
Wang Y, Qin Z, Bao Y, Qiao J, Yang L, Zhao D (2009) Sequence analysis of the prion protein gene in Mongolian gazelles (Procapra gutturosa). Virus Genes 39:273–278
Gou X, Wang YQ, Yang SL, Deng WD, Mao HM (2010) Genetic diversity and origin of gayal and cattle in Yunnan revealed by mtDNA D-loop and SRY gene sequence variation. J Anim Breed Genet 127:154–160
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Hresko S, Mojzis M, Tkacikova L (2009) Prion protein gene polymorphism in healthy and BSE-affected Slovak cattle. J Appl Genet 50:371–374
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21:263–265
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleaes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Zhao M, Chen H, Wang X, Yu H, Wang M, Wang J, Lan XY, Zhang CF, Zhang LZ, Guo YK, Zhang B, Hu SR (2009) aPCR-SSCP and DNA sequencing detecting two silent SNPs at KAP8.1 gene in the Cashmere goat. Mol Biol Rep 36:1387–1391
Wu R, Xie QG, Liu XT, Chen HT (2004) Cloning and sequence analysis of the Bovine prion protein (bPrPc) gene. Acta Vet Zootech Sin 35:318–332 (In Chinese with English abstract available)
Qin LH, Zhao YM, Bao YH, Bai WL, Chong J, Zhang GL, Zhang JB, Zhao ZH (2010) Polymorphism of the prion protein gene (PRNP) in two Chinese indigenous cattle breeds. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0541-0
Takasuga A, Abe T, Ito T, Watanabe T, Kamatani N, Sugimoto Y (2003) Novel prion protein polymorphisms in cattle. Anim Genet 34:396–397
Sakudo A, Xue G, Kawashita N, Ano Y, Takagi T, Shintani H, Tanaka Y, Onodera T, Ikuta K (2010) Structure of the prion protein and its gene: an analysis using bioinformatics and computer simulation. Curr Protein Pept Sci 11:166–179
Wopfner F, Weidenhofer G, Schneider R, von Brunn A, Gilch S, Schwarz TF (1999) Analysis of 27 mammalian and 9 avian PrPs reveals high conservation of flexible regions of the prion protein. J Mol Biol 289:1163–1178
Kim SJ, Rahbar R, Hegde RS (2001) Combinatorial control of prion protein biogenesis by the signal sequence and transmembrane domain. J Biol Chem 276:26132–26140
Hegde RS, Mastrianni JA, Scott MR, DeFea KA, Tremblay P, Torchia M, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB, Lingappa VR (1998) A transmembrane form of the prion protein in neurodegenerative disease. Science 279:827–834
Hegde RS, Tremblay P, Groth D, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB, Lingappa VR (1999) Transmissible and genetic prion diseases share a common pathway of neurodegeneration. Nature 402:822–826
Lawson VA, Priola SA, Meade-White K, Lawson M, Chesebro B (2004) Flexible N-terminal region of prion protein influences conformation of protease-resistant prion protein isoforms associated with cross-species scrapie infection in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem 279:13689–13695
Viles JH, Klewpatinond M, Nadal RC (2008) Copper and the structural biology of the prion protein. Biochem Soc Trans 36:1288–1292
López García F, Zahn R, Riek R, Wüthrich K (2000) NMR structure of the bovine prion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8334–8339
Kupfer L, Eiden M, Buschmann A, Groschup MH (2007) Amino acid sequence and prion strain specific effects on the in vitro and in vivo convertibility of ovine/murine and bovine/murine prion protein chimeras. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:704–713
Baron BS, Caughey B (2003) Effect of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor-dependent and -independent prion protein association with model raft membranes on conversion to the protease-resistant isoform. J Biol Chem 278:14883–14892
Bate C, Tayebi M, Williams A (2010) The glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor is a major determinant of prion binding and replication. Biochem J 428:95–101
Taraboulos A, Scott M, Semenov A, Avrahami D, Laszlo L, Prusiner SB (1995) Cholesterol depletion and modification of COOH-terminal targeting sequence of the prion protein inhibit formation of the scrapie isoform. J Cell Biol 129:121–132
Baron T (2002) Mouse models of prion disease transmission. Trends Mol Med 8:495–500
Abe T, Hasebe H, Kobayashi E (2006) Frequencies of bovine prp gene polymorphisms in Holstein and Japanese Holstein and Japanese black bulls in Japan. Anim Sci J 77:395–398
Msalya G, Shimogiri T, Nishitani K, Okamoto S, Kawabe K, Minesawa M, Maeda Y (2010) Indels within promoter and intron 1 of bovine prion protein gene modulate the gene expression levels in the medulla oblongata of two Japanese cattle breeds. Anim Genet 41:218–221
Jeong BH, Lee YJ, Kim NH, Carp RI, Kim YS (2006) Genotype distribution of the prion protein gene (PRNP) promoter polymorphisms in Korean cattle. Genome 49:1539–1544
Jeong BH, Sohn HJ, Lee JO, Kim NH, Kim JI, Lee SY, Cho IS, Joo YS, Carp RI, Kim YS (2005) Polymorphisms of the prion protein gene (PRNP) in Hanwoo (Bos taurus coreanae) and Holstein cattle. Genes Genet Syst 80:303–308
Choi SH, Chae SH, Choi HH, Kim JS, Kang BR, Yeo JS, Choi I, Lee YS, Choy YH, Park HS (2007) Genomic sequence variability of the prion gene (PRNP) in Korean cattle. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 20:653–660
Kim Y, Kim JB, Sohn H, Lee C (2009) A national survey on the allelic, genotypic, and haplotypic distribution of PRNP insertion and deletion polymorphisms in Korean cattle. J Genet 88:99–103
Shimogiri T, Msalya G, Myint SL, Okamoto S, Kawabe K, Tanaka K, Mannen H, Minezawa M, Namikawa T, Amano T, Yamamoto Y, Maeda Y (2010) Allele distributions and frequencies of the six prion protein gene (PRNP) polymorphisms in Asian native cattle, Japanese breeds, and mythun (Bos frontalis). Biochem Genet 48:829–839
Muramatsu Y, Sakemi Y, Horiuchi M, Ogawa T, Suzuki K, Kanameda M, Hanh TT, Tamura Y (2008) Frequencies of PRNP gene polymorphisms in Vietnamese dairy cattle for potential association with BSE. Zoonoses Public Health 55:267–273
Clawson ML, Heaton MP, Keele JW, Smith TP, Harhay GP, Laegreid WW (2006) Prion gene haplotypes of U.S. cattle. BMC Genet 7:51
Premzl M, Bozic P, Gamulin V (2000) PRNP octarepeat allele genotype frequencies among the modern and rare cattle breeds in Croatia. Anim Genet 31:408–409
Tkacikova A, Voralek R, Filipaik P, Mikula I Sr (2007) Octapeptide polymorphism analysis of Slovak autochthonous cattle breeds. Acta Vet Brno 76:47–50
Walawski K, Czarnik U (2003) Prion octapeptide-repeat polymorphism in Polish Black-and-White cattle. J Appl Genet 44:191–195
Sander P, Hamann H, Pfeiffer I, Wemheuer W, Brenig B, Groschup MH, Ziegler U, Distl O, Leeb T (2004) Analysis of sequence variability of the bovine prion protein gene (PRNP) in German cattle breeds. Neurogenetics 5:19–25
Nakamitsu S, Miyazava T, Horuichi M, Onoe S, Ohoba Y, Kitagawa H, Ishiguro N (2006) Sequence variation of bovine prion protein gene in Japanese cattle (Holstein and Japanese Black). J Vet Med Sci 68:27–33
Hunter N, Goldmann W, Smith G, Hope J (1994) Frequencies of PrP gene variants in healthy cattle and cattle with BSE in Scotland. Vet Rec 135:400–403
Goldmann W (2008) PrP genetics in ruminant transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Vet Res 39:30
Castilla J, Gutiérrez-Adán A, Brun A, Pintado B, Parra B, Ramírez MA, Salguero FJ, Díaz San Segundo F, Rábano A, Cano MJ, Torres JM (2004) Different behavior toward bovine spongiform encephalopathy infection of bovine prion protein transgenic mice with one extra repeat octapeptide insert mutation. J Neurosci 24:2156–2164
Castilla J, Gutiérrez-Adán A, Brun A, Pintado B, Salguero FJ, Parra B, Segundo FD, Ramírez MA, Rábano A, Cano MJ, Torres JM (2005) Transgenic mice expressing bovine PrP with a four extra repeat octapeptide insert mutation show a spontaneous, non-transmissible, neurodegenerative disease and an expedited course of BSE infection. FEBS Lett 579:6237–6246
Heaton MP, Keele JW, Harhay GP, Richt JA, Koohmaraie M, Wheeler TL, Shackelford SD, Casas E, King DA, Sonstegard TS, Van Tassell CP, Neibergs HL Jr, Chase CC, Kalbfleisch TS, Smith TP, Clawson ML, Laegreid WW (2008) Prevalence of the prion protein gene E211K variant in U.S. cattle. BMC Vet Res 4:25
Nicholson EM, Brunelle BW, Richt JA, Kehrli ME Jr, Greenlee JJ (2008) Identification of a heritable polymorphism in bovine PRNP associated with genetic transmissible spongiform encephalopathy: evidence of heritable BSE. PLoS ONE 3:e2912
Richt JA, Hall SM (2008) BSE case associated with prion protein gene mutation. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000156
Acknowledgments
Major funding was provided from the State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Etiological Biology, Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (SKLVEB2009KFKT010) and in part funding was also provided by the Open-funded Project (to DMX) of the Faculty of Animal Science and Technology, Yunnan Agricultural University. We thank to our team members for sharing and using samples from gayal which were collected between 2005 and 2008 with financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan Province (2005C0038M), the National “863” Program (2008AA101001) and the National Technology Support Project (2008BADB2B01-14). We acknowledge with gratitude the financial support provided. The authors thank Professor G. H. McDowell for invaluable comments on the manuscript. The authors also appreciated the help of staff from the Gongshan County Animal Science and Veterinary Bureau during samples collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
D. Xi and Q. Liu contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, D., Liu, Q., Guo, J. et al. Genetic variability of the coding region for the prion protein gene (PRNP) in gayal (Bos frontalis). Mol Biol Rep 39, 2011–2020 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0948-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0948-2