Abstract
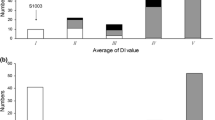
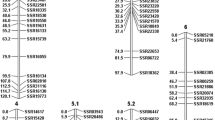
Powdery mildew limits cucumber production worldwide. Most resistant cucumber cultivars become susceptible to powdery mildew at low temperatures. Resistance within a wide temperature range is therefore desirable for cucumber production. We constructed a cucumber genetic linkage map based on a population of 111 recombinant inbred lines derived from a cross between CS-PMR1, with strong and temperature-independent resistance, and Santou, with moderate and temperature-dependent resistance. The map spans 693.0 cM and consists of 296 markers segregating into seven linkage groups; the markers include 289 simple sequence repeats (SSRs), six sequence characterized amplified regions, and one inter simple sequence repeat. Due to the presence of 150 common SSR markers, we were able to compare our map with previously published maps obtained by using populations derived from inter- or intra-variety crosses. We also evaluated powdery mildew resistance of the recombinant inbred lines and identified seven quantitative trait loci (QTL) contributed by CS-PMR1 and two QTL contributed by Santou. Four QTL (pm3.1, pm5.1, pm5.2 and pm5.3) were successfully validated by using populations derived from residual heterozygous lines. Some of the QTL identified in our study are in good agreement with previously published results obtained with materials of different origin. The markers reported here would be useful for introducing high and temperature-independent resistance by accumulation of QTL from CS-PMR1 and Santou.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfandi M, Shen L, Qi X, Xu Q, Chen X (2009) A SCAR marker linked to powdery mildew resistance for selection of the near-isogenic lines in cucumber. In: Abstracts of the 4th international Cucurbitaceae symposium, pp 20–21
Danin-Poleg Y, Reis N, Tzuri G, Katzir N (2001) Development and characterization of microsatellite markers in Cucumis. Theor Appl Genet 102:61–72
Diaz A, Fergany M, Formisano G et al (2011) A consensus linkage map for molecular markers and quantitative trait loci associated with economically important traits in melon (Cucumis melo L.). BMC Plant Biol 11:111. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-111
Fernandez-Silva I, Eduardo I, Blanca J, Esteras C, Picó B, Nuez F, Arús P, Garcia-Mas J, Monforte AJ (2008) Bin mapping of genomic and EST-derived SSRs in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Theor Appl Genet 118:139–150. doi:10.1007/s00122-008-0883-3
Fu D, Uauy C, Distelfeld A, Blechl A, Epstein L, Chen X, Sela H, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J (2009) A kinase-START gene confers temperature-dependent resistance to wheat stripe rust. Science 323:1357–1360. doi:10.1126/science.1166289
Fukino N, Kunihisa M, Matsumoto S (2004) Characterization of recombinant inbred lines derived from crosses in melon (Cucumis melo L.), ‘PMAR No. 5’ × ‘Harukei No. 3’. Breed Sci 54:141–145
Fukino N, Sakata Y, Kunihisa M, Matsumoto S (2007) Characterisation of novel simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for melon (Cucumis melo L.) and their use for genotype identification. J Hort Sci Biotechnol 82:330–334
Fukino N, Ohara T, Monforte AJ, Sugiyama M, Sakata Y, Kunihisa M, Matsumoto S (2008a) Identification of QTLs for resistance to powdery mildew and SSR markers diagnostic for powdery mildew resistance genes in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Theor Appl Genet 118:165–175. doi:10.1007/s00122-008-0885-1
Fukino N, Yoshioka Y, Kubo N, Hirai M, Sugiyama M, Sakata Y, Matsumoto S (2008b) Development of 101 novel SSR markers and construction of an SSR-based genetic linkage map of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Breed Sci 58:475–483
Fukino N, Ohara T, Sugiyama M, Kubo N, Hirai M, Sakata Y, Matsumoto S (2012) Mapping of a gene that confers short lateral branching (slb) in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Euphytica 187:133–143. doi:10.1007/s10681-012-0667-3
Fukuoka S, Okuno K (2001) QTL analysis and mapping of pi21, a recessive gene for field resistance to rice blast in Japanese upland rice. Theor Appl Genet 103:185–190
Gonzalo MJ, Oliver M, Garcia-Mas J, Monfort A, Dolcet-Sanjuan R, Katzir N, Arús P, Monforte AJ (2005) Simple-sequence repeat markers used in merging linkage maps of melon (Cucumis melo L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:802–811. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1814-6
Horejsi T, Staub JE, Thomas C (2000) Linkage of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers to downy mildew resistance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Euphytica 115:105–113
Huang S, Li R, Zhang Z et al (2009) The genome of the cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Nat Genet 41:1275–1281. doi:10.1038/ng.475
Kang H, Weng Y, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Mao Z, Cheng G, Gu X, Huang S, Xie B (2011) Fine genetic mapping localizes cucumber scab resistance gene Ccu into an R gene cluster. Theor Appl Genet 122:795–803. doi:10.1007/s00122-010-1487-2
Kong Q, Xiang C, Yu Z (2006) Development of EST-SSRs in Cucumis sativus from sequence database. Mol Ecol Notes 6:1234–1236. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01500.x
Kong Q, Xiang C, Yu Z, Zhang C, Liu F, Peng C, Peng X (2007) Mining and charactering microsatellites in Cucumis melo expressed sequence tags from sequence database. Mol Ecol Notes 7:281–283. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01580.x
Kosambi D (1943) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Kukita Y, Hayashi K (2002) Multicolor post-PCR labeling of DNA fragments with fluorescent ddNTPs. Biotechniques 33:502–506. doi:91200217
Lander E, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly M, Lincoln S, Newberg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lehmann EL (1975) Nonparametrics. McGraw-Hill, New York
Liu L, Cai R, Yuan X, He H, Pan J (2008a) QTL molecular marker location of powdery mildew resistance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Sci China, Ser C Life Sci 51:1003–1008. doi:10.1007/s11427-008-0110-0
Liu L, Yuan X, Cai R, Pan J, He H, Yuan L, Guan Y, Zhu L (2008b) Quantitative trait loci for resistance to powdery mildew in cucumber under seedling spray inoculation and leaf disc infection. J Phytopathol 156:691–697. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0434.2008.01427.x
Miao H, Zhang S, Wang X, Zhang Z, Li M, Mu S, Cheng Z, Zhang R, Huang S, Xie B, Fang Z, Zhang Z, Weng Y, Gu X (2011) A linkage map of cultivated cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) with 248 microsatellite marker loci and seven genes for horticulturally important traits. Euphytica 182:167–176. doi:10.1007/s10681-011-0410-5
Morishita M, Sugiyama K, Saito T, Sakata Y (2003) Powdery mildew resistance in cucumber. Jpn Agr Res Q 37:7–14
Park Y, Katzir N, Brotman Y, King J, Bertrand F, Havey M (2004) Comparative mapping of ZYMV resistances in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) and melon (Cucumis melo L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:707–712. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1684-y
Ren Y, Zhang Z, Staub J, Cheng Z, Li X, Lu J, Miao H, Kang H, Xie B, Gu X (2009) An integrated genetic and cytogenetic map of the cucumber genome. PLoS ONE 4:1–8. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005795
Sakata Y, Kubo N, Morishita M, Kitadani E, Sugiyama M, Hirai M (2006) QTL analysis of powdery mildew resistance in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:243–250. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0121-1
Sakata Y, Morishita M, Kitadani E, Sugiyama M, Ohara T, Sugiyama K, Kojima A (2008) Development of a powdery mildew resistant cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.), ‘Kyuri Chukanbohon Nou 5 Go’. Hort Res (Japan) 7:173–179
van Ooijen JW (2004) MapQTL® 5, Software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations. Kyazma B. V., Wageningen, The Netherlands
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2007) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Watcharawongpaiboon N, Chunwongse J (2008) Development and characterization of microsatellite markers from an enriched genomic library of cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Plant Breed 127:74–81. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2007.01425.x
Weng Y, Staub J, Johnson S, Huang S (2010) An extended intervarietal microsatellite linkage map of cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Hort Sci 45:882–886
Yamanaka N, Watanabe S, Toda K, Hayashi M, Fuchigami H, Takahashi R, Harada K (2005) Fine mapping of the FT1 locus for soybean flowering time using a residual heterozygous line derived from a recombinant inbred line. Theor Appl Genet 110:634–639. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1886-3
Yuan XJ, Pan JS, Cai R, Guan Y, Liu LZ, Zhang WW, Li Z, He HL, Zhang C, Si LT, Zhu LH (2008) Genetic mapping and QTL analysis of fruit and flower related traits in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) using recombinant inbred lines. Euphytica 164:473–491. doi:10.1007/s10681-008-9722-5
Zeng ZB (1993) Theoretical basis for separation of multiple linked gene effects in mapping quantitative trait loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10972–10976
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Zhang WW, Pan JS, He HL, Zhang C, Li Z, Zhao JL, Yuan XJ, Zhu LH, Huang SW, Cai R (2012) Construction of a high density integrated genetic map for cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor Appl Genet 124:249–259. doi:10.1007/s00122-011-1701-x
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. M. Yano for his valuable advice and Dr. S. Huang for kindly providing SSR marker information prior to publication. We are grateful to S. Negoro, T. Yamakawa, K. Takeuchi and S. Toyoda for their technical assistance. This work was supported by NARO Research Project No. 211 ‘Establishment of Integrated Basis for Development and Application of Advanced Tools for DNA Marker-Assisted Selection in Horticultural Crops’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2013_9867_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
ESM 1 Comparison of marker distribution and linkage group lengths in the maps from 3 studies: hs map (Ren et al. 2009)a, ss map (Miao et al. 2011)b and CS map (this study)c (PDF 49 kb)
11032_2013_9867_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
ESM 2 Comparison of marker order and map distance in the linkage maps constructed by using RILs derived from inter-varietal (center: hs map, Ren et al. 2009) and intra-varietal crosses (left: ss map, Miao et al. 2011; right: CS map, this study). Common markers are connected with lines. Ruler on the left indicates linkage group length (PDF 427 kb)
11032_2013_9867_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
ESM 3 Positions and LOD scores of QTL pm4.1 for powdery mildew resistance in 109 RILs derived from C. sativus CS-PMR1 × ‘Santou’. Horizontal lines represent LOD thresholds at the 0.05 level of significance. LD25 and LD20, leaf disc assays at 25 and 20 °C, respectively; GH-S and GH-A, evaluation of naturally occurring disease in late spring to summer and in autumn, respectively (PDF 353 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukino, N., Yoshioka, Y., Sugiyama, M. et al. Identification and validation of powdery mildew (Podosphaera xanthii)-resistant loci in recombinant inbred lines of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Mol Breeding 32, 267–277 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9867-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9867-3