Abstract
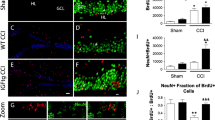
Pediatric traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of acquired cognitive dysfunction in children. Hippocampal Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) is important for normal cognition. Little is known about the effects of TBI on BDNF levels in the developing hippocampus. We used controlled cortical impact (CCI) in the 17 day old rat pup to test the hypothesis that CCI would first increase rat hippocampal BDNF mRNA/protein levels relative to SHAM and Naïve rats by post injury day (PID) 2 and then decrease BDNF mRNA/protein by PID14. Relative to SHAM, CCI did not change BDNF mRNA/protein levels in the injured hippocampus in the first 2 days after injury but did decrease BDNF protein at PID14. Surprisingly, BDNF mRNA decreased at PID 1, 3, 7 and 14, and BDNF protein decreased at PID 2, in SHAM and CCI hippocampi relative to Naïve. In conclusion, TBI decreased BDNF protein in the injured rat pup hippocampus 14 days after injury. BDNF mRNA levels decreased in both CCI and SHAM hippocampi relative to Naïve, suggesting that certain aspects of the experimental paradigm (such as craniotomy, anesthesia, and/or maternal separation) may decrease the expression of BDNF in the developing hippocampus. While BDNF is important for normal cognition, no inferences can be made regarding the cognitive impact of any of these factors. Such findings, however, suggest that meticulous attention to the experimental paradigm, and possible inclusion of a Naïve group, is warranted in studies of BDNF expression in the developing brain after TBI.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aid T, Kazantseva A, Piirsoo M, Palm K, Timmusk T (2007) Mouse and rat BDNF gene structure and expression revisited. J Neurosci Res 85:525–535
Aiguo W, Zhe Y, Gomez-Pinilla F (2010) Vitamin E protects against oxidative damage and learning disability after mild traumatic brain injury in rats. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 24:290–298
Aisa B, Elizalde N, Tordera R, Lasheras B, Del Rio J, Ramirez MJ (2009) Effects of neonatal stress on markers of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus: implications for spatial memory. Hippocampus 19:1222–1231
Altar CA, Cai N, Bliven T, Juhasz M, Conner JM, Acheson AL, Lindsay RM, Wiegand SJ (1997) Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain. Nature 389:856–860
Binder DK, Scharfman HE (2004) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Growth Factors 22:123–131
Cole JT, Yarnell A, Kean WS, Gold E, Lewis B, Ren M, McMullen DC, Jacobowitz DM, Pollard HB, O’Neill JT, Grunberg NE, Dalgard CL, Frank JA, Watson WD (2011) Craniotomy: true sham for traumatic brain injury, or a sham of a sham? J Neurotrauma 28:359–369
Cook JL, Marcheselli V, Alam J, Deininger PL, Bazan NG (1998) Simultaneous analysis of multiple gene expression patterns as a function of development, injury or senescence. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 3:1–6
Dixon CE, Kochanek PM, Yan HQ, Schiding JK, Griffith RG, Baum E, Marion DW, DeKosky ST (1999) One-year study of spatial memory performance, brain morphology, and cholinergic markers after moderate controlled cortical impact in rats. J Neurotrauma 16:109–122
Felderhoff-Mueser U, Sifringer M, Pesditschek S, Kuckuck H, Moysich A, Bittigau P, Ikonomidou C (2002) Pathways leading to apoptotic neurodegeneration following trauma to the developing rat brain. Neurobiol Dis 11:231–245
Gao X, Deng-Bryant Y, Cho W, Carrico KM, Hall ED, Chen J (2008) Selective death of newborn neurons in hippocampal dentate gyrus following moderate experimental traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Res 86:2258–2270
Griesbach GS, Hovda DA, Molteni R, Gomez-Pinilla F (2002) Alterations in BDNF and synapsin I within the occipital cortex and hippocampus after mild traumatic brain injury in the developing rat: reflections of injury-induced neuroplasticity. J Neurotrauma 19:803–814
Griesbach GS, Sutton RL, Hovda DA, Ying Z, Gomez-Pinilla F (2009) Controlled contusion injury alters molecular systems associated with cognitive performance. J Neurosci Res 87:795–805
Hamatake M, Miyazaki N, Sudo K, Matsuda M, Sadakata T, Furuya A, Ichisaka S, Hata Y, Nakagawa C, Nagata K, Furuichi T, Katoh-Semba R (2011) Phase advance of the light–dark cycle perturbs diurnal rhythms of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 protein levels, which reduces synaptophysin-positive presynaptic terminals in the cortex of juvenile rats. J Biol Chem 286:21478–21487
Hellmich HL, Garcia JM, Shimamura M, Shah SA, Avila MA, Uchida T, Parsley MA, Capra BA, Eidson KA, Kennedy DR, Winston JH, DeWitt DS, Prough DS (2005) Traumatic brain injury and hemorrhagic hypotension suppress neuroprotective gene expression in injured hippocampal neurons. Anesthesiology 102:806–814
Hicks RR, Martin VB, Zhang L, Seroogy KB (1999) Mild experimental brain injury differentially alters the expression of neurotrophin and neurotrophin receptor mRNAs in the hippocampus. Exp Neurol 160:469–478
Kikusui T, Ichikawa S, Mori Y (2009) Maternal deprivation by early weaning increases corticosterone and decreases hippocampal BDNF and neurogenesis in mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 34:762–772
Kim JK, Jeon SM, Lee KM, Park ES, Cho HJ (2007) Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat forebrain and upper brain stem during postnatal development: an immunohistochemical study. Neuroscience 146:1128–1136
Langlois JA, Rutland-Brown W, Wald MM (2006) The epidemiology and impact of traumatic brain injury: a brief overview. J Head Trauma Rehabil 21:375–378
Lessmann V (1998) Neurotrophin-dependent modulation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the mammalian CNS. Gen Pharmacol 31:667–674
Lindholm D, Castren E, Berzaghi M, Blochl A, Thoenen H (1994) Activity-dependent and hormonal regulation of neurotrophin mRNA levels in the brain–implications for neuronal plasticity. J Neurobiol 25:1362–1372
Liu D, Diorio J, Day JC, Francis DD, Meaney MJ (2000) Maternal care, hippocampal synaptogenesis and cognitive development in rats. Nature neuroscience 3:799–806
Liu Y, Fowler CD, Wang Z (2001) Ontogeny of brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression in the forebrain of prairie and montane voles. Brain research 127:51–61
Lu LX, Yon JH, Carter LB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2006) General anesthesia activates BDNF-dependent neuroapoptosis in the developing rat brain. Apoptosis 11:1603–1615
Matzilevich DA, Rall JM, Moore AN, Grill RJ, Dash PK (2002) High-density microarray analysis of hippocampal gene expression following experimental brain injury. J Neurosci Res 67:646–663
Ming Z, Knapp DJ, Mueller RA, Breese GR, Criswell HE (2001) Differential modulation of GABA- and NMDA-gated currents by ethanol and isoflurane in cultured rat cerebral cortical neurons. Brain Res 920:117–124
Oyesiku NM, Evans CO, Houston S, Darrell RS, Smith JS, Fulop ZL, Dixon CE, Stein DG (1999) Regional changes in the expression of neurotrophic factors and their receptors following acute traumatic brain injury in the adult rat brain. Brain Res 833:161–172
Palmer AM, Marion DW, Botscheller ML, Swedlow PE, Styren SD, DeKosky ST (1993) Traumatic brain injury-induced excitotoxicity assessed in a controlled cortical impact model. J Neurochem 61:2015–2024
Roceri M, Hendriks W, Racagni G, Ellenbroek BA, Riva MA (2002) Early maternal deprivation reduces the expression of BDNF and NMDA receptor subunits in rat hippocampus. Molecular psychiatry 7:609–616
Schober ME, Block B, Beachy JC, Statler KD, Giza CC, Lane RH (2010) Early and sustained increase in expression of hippocampal IGF-1, but not EPO, in a Developmental Rodent Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma.
Shah SA, Prough DS, Garcia JM, DeWitt DS, Hellmich HL (2006) Molecular correlates of age-specific responses to traumatic brain injury in mice. Exp Gerontol 41:1201–1205
Skoglosa Y, Lewen A, Takei N, Hillered L, Lindholm D (1999) Regulation of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide and its receptor type 1 after traumatic brain injury: comparison with brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the induction of neuronal cell death. Neuroscience 90:235–247
Smith DH, Chen XH, Pierce JE, Wolf JA, Trojanowski JQ, Graham DI, McIntosh TK (1997) Progressive atrophy and neuron death for one year following brain trauma in the rat. J Neurotrauma 14:715–727
Stansberg C, Vik-Mo AO, Holdhus R, Breilid H, Srebro B, Petersen K, Jorgensen HA, Jonassen I, Steen VM (2007) Gene expression profiles in rat brain disclose CNS signature genes and regional patterns of functional specialisation. BMC genomics 8:94
Wu A, Molteni R, Ying Z, Gomez-Pinilla F (2003) A saturated-fat diet aggravates the outcome of traumatic brain injury on hippocampal plasticity and cognitive function by reducing brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuroscience 119:365–375
Wu A, Ying Z, Gomez-Pinilla F (2006) Dietary curcumin counteracts the outcome of traumatic brain injury on oxidative stress, synaptic plasticity, and cognition. Exp Neurol 197:309–317
Yeates KO, Taylor HG, Wade SL, Drotar D, Stancin T, Minich N (2002) A prospective study of short- and long-term neuropsychological outcomes after traumatic brain injury in children. Neuropsychology 16:514–523
Yeates KO, Armstrong K, Janusz J, Taylor HG, Wade S, Stancin T, Drotar D (2005) Long-term attention problems in children with traumatic brain injury. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 44:574–584
Zafra F, Castren E, Thoenen H, Lindholm D (1991) Interplay between glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid transmitter systems in the physiological regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:10037–10041
Disclosure of Conflict Of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schober, M.E., Block, B., Requena, D.F. et al. Developmental traumatic brain injury decreased brain derived neurotrophic factor expression late after injury. Metab Brain Dis 27, 167–173 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-012-9309-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-012-9309-7