Abstract
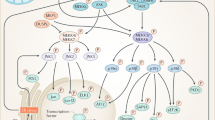
Obesity-induced low-grade inflammation (metaflammation) impairs insulin receptor signaling. This has been implicated in the development of insulin resistance. Insulin signaling in the target tissues is mediated by stress kinases such as p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, inhibitor of NF-kB kinase complex β (IKKβ), AMP-activated protein kinase, protein kinase C, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase, and RNA-activated protein kinase. Most of these kinases phosphorylate several key regulators in glucose homeostasis. The phosphorylation of serine residues in the insulin receptor and IRS-1 molecule results in diminished enzymatic activity in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway. This has been one of the key mechanisms observed in the tissues that are implicated in insulin resistance especially in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2-DM). Identifying the specific protein kinases involved in obesity-induced chronic inflammation may help in developing the targeted drug therapies to minimize the insulin resistance. This review is focused on the protein kinases involved in the inflammatory cascade and molecular mechanisms and their downstream targets with special reference to obesity-induced T2-DM.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teng K-T, Chang C-Y, Chang LF, Nesaretnam K (2014) Modulation of obesity-induced inflammation by dietary fats: mechanisms and clinical evidence. Nutr J 13:12. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-13-12
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM (2014) Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. JAMA 311:806–814. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.732
Kawasaki N, Asada R, Saito A et al (2012) Obesity-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes chronic inflammation in adipose tissue. Sci Rep 2:799. doi:10.1038/srep00799
Yang Y, Kim SC, Yu T et al (2014) Functional roles of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses. Mediators Inflamm 2014:352371. doi:10.1155/2014/352371
Nakamura T, Furuhashi M, Li P et al (2010) Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase links pathogen sensing with stress and metabolic homeostasis. Cell 140:338–348. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.001
Wieser V, Moschen AR, Tilg H (2013) Inflammation, cytokines and insulin resistance: a clinical perspective. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 61:119–125. doi:10.1007/s00005-012-0210-1
de Luca C, Olefsky JM (2008) Inflammation and insulin resistance. FEBS Lett 582:97–105. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.11.057
McArdle MA, Finucane OM, Connaughton RM et al (2013) Mechanisms of obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance: insights into the emerging role of nutritional strategies. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). doi:10.3389/fendo.2013.00052
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M et al (2003) Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 112:1796–1808. doi:10.1172/JCI200319246
Amano SU, Cohen JL, Vangala P et al (2014) Local proliferation of macrophages contributes to obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Cell Metab 19:162–171. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.11.017
Talukdar S, Oh DY, Bandyopadhyay G et al (2012) Neutrophils mediate insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet through secreted elastase. Nat Med 18:1407–1412. doi:10.1038/nm.2885
Eljaafari A, Robert M, Chehimi M et al (2015) Adipose tissue-derived stem cells from obese subjects contribute to inflammation and reduced insulin response in adipocytes through differential regulation of the Th1/Th17 balance and monocyte activation. Diabetes 64:2477–2488. doi:10.2337/db15-0162
Gerriets VA, MacIver NJ (2014) Role of T cells in malnutrition and obesity. Front Immunol 5:379. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00379
Fabbrini E, Cella M, McCartney SA et al (2013) Association between specific adipose tissue CD4+ T-cell populations and insulin resistance in obese individuals. Gastroenterology 145:366–374. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.010
McLaughlin T, Liu L-F, Lamendola C et al (2014) T-cell profile in adipose tissue is associated with insulin resistance and systemic inflammation in humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34:2637–2643. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304636
Priceman SJ, Kujawski M, Shen S et al (2013) Regulation of adipose tissue T cell subsets by Stat3 is crucial for diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:13079–13084. doi:10.1073/pnas.1311557110
DeFuria J, Belkina AC, Jagannathan-Bogdan M et al (2013) B cells promote inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes through regulation of T-cell function and an inflammatory cytokine profile. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:5133–5138. doi:10.1073/pnas.1215840110
Huh JY, Park YJ, Ham M, Kim JB (2014) Crosstalk between adipocytes and immune cells in adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysregulation in obesity. Mol Cells 37:365–371. doi:10.14348/molcells.2014.0074
Chen Y, Tian J, Tian X et al (2014) Adipose tissue dendritic cells enhances inflammation by prompting the generation of Th17 cells. PLoS ONE 9:e92450. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092450
Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L et al (2002) A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420:333–336. doi:10.1038/nature01137
Shoelson SE, Lee J, Yuan M (2003) Inflammation and the IKK β/I κB/NF-κB axis in obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27(Suppl 3):S49–S52. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802501
Itani SI, Ruderman NB, Schmieder F, Boden G (2002) Lipid-induced insulin resistance in human muscle is associated with changes in diacylglycerol, protein kinase C, and IκB-alpha. Diabetes 51:2005–2011
Lyons CL, Kennedy EB, Roche HM (2016) Metabolic inflammation-differential modulation by dietary constituents. Nutrients. doi:10.3390/nu8050247
Glass CK, Olefsky JM (2012) Inflammation and lipid signaling in the etiology of insulin resistance. Cell Metab 15:635–645. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.001
Lee DH, Shi J, Jeoung NH et al (2009) Targeted disruption of ROCK1 causes insulin resistance In vivo. J Biol Chem 284:11776–11780. doi:10.1074/jbc.C900014200
Lee S-H, Huang H, Choi K et al (2014) ROCK1 isoform-specific deletion reveals a role for diet-induced insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 306:E332–E343. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00619.2013
Carvalho-Filho MA, Carvalho BM, Oliveira AG et al (2012) Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase is a key modulator of insulin sensitivity in physiological conditions and in obesity in mice. Endocrinology 153:5261–5274. doi:10.1210/en.2012-1400
Li Y, Soos TJ, Li X et al (2004) Protein kinase C θ inhibits insulin signaling by phosphorylating IRS1 at Ser(1101). J Biol Chem 279:45304–45307. doi:10.1074/jbc.C400186200
Fazakerley DJ, Holman GD, Marley A et al (2010) Kinetic evidence for unique regulation of GLUT4 trafficking by insulin and AMP-activated protein kinase activators in L6 myotubes. J Biol Chem 285:1653–1660. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.051185
Ruderman NB, Carling D, Prentki M, Cacicedo JM (2013) AMPK, insulin resistance, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 123:2764–2772. doi:10.1172/JCI67227
Patterson H, Nibbs R, McInnes I, Siebert S (2014) Protein kinase inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Immunol 176:1–10. doi:10.1111/cei.12248
de Boer JF, Dikkers A, Jurdzinski A et al (2014) Mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 deficiency reduces insulin sensitivity in high-fat diet-fed mice. PLoS ONE 9:e106300. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0106300
Gual P, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Tanti J-F (2005) Positive and negative regulation of insulin signaling through IRS-1 phosphorylation. Biochimie 87:99–109. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2004.10.019
Carling D (2004) The AMP-activated protein kinase cascade—a unifying system for energy control. Trends Biochem Sci 29:18–24. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2003.11.005
Woods A, Vertommen D, Neumann D et al (2003) Identification of phosphorylation sites in AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) for upstream AMPK kinases and study of their roles by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 278:28434–28442. doi:10.1074/jbc.M303946200
Hawley SA, Boudeau J, Reid JL et al (2003) Complexes between the LKB1 tumor suppressor, STRAD α/β and MO25 α/β are upstream kinases in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. J Biol 2:28. doi:10.1186/1475-4924-2-28
Woods A, Dickerson K, Heath R et al (2005) Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-β acts upstream of AMP-activated protein kinase in mammalian cells. Cell Metab 2:21–33. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2005.06.005
Momcilovic M, Hong S-P, Carlson M (2006) Mammalian TAK1 activates Snf1 protein kinase in yeast and phosphorylates AMP-activated protein kinase in vitro. J Biol Chem 281:25336–25343. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604399200
Foretz M, Ancellin N, Andreelli F et al (2005) Short-term overexpression of a constitutively active form of AMP-activated protein kinase in the liver leads to mild hypoglycemia and fatty liver. Diabetes 54:1331–1339
Seo E, Park E-J, Joe Y et al (2009) Overexpression of AMPKα1 ameliorates fatty liver in hyperlipidemic diabetic rats. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 13:449–454. doi:10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.6.449
Ong KW, Hsu A, Tan BKH (2012) Chlorogenic acid stimulates glucose transport in skeletal muscle via AMPK activation: a contributor to the beneficial effects of coffee on diabetes. PLoS ONE 7:e32718. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032718
Richards SK, Parton LE, Leclerc I et al (2005) Over-expression of AMP-activated protein kinase impairs pancreatic {β}-cell function In vivo. J Endocrinol 187:225–235. doi:10.1677/joe.1.06413
Xie Z, Dong Y, Scholz R et al (2008) Phosphorylation of LKB1 at serine 428 by protein kinase C-zeta is required for metformin-enhanced activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial cells. Circulation 117:952–962. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.744490
Treebak JT, Glund S, Deshmukh A et al (2006) AMPK-mediated AS160 phosphorylation in skeletal muscle is dependent on AMPK catalytic and regulatory subunits. Diabetes 55:2051–2058. doi:10.2337/db06-0175
Lochhead PA, Salt IP, Walker KS et al (2000) 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside mimics the effects of insulin on the expression of the 2 key gluconeogenic genes PEPCK and glucose-6-phosphatase. Diabetes 49:896–903
Tao R, Gong J, Luo X et al (2010) AMPK exerts dual regulatory effects on the PI3K pathway. J Mol Signal 5:1. doi:10.1186/1750-2187-5-1
Park SH, Gammon SR, Knippers JD et al (2002) Phosphorylation-activity relationships of AMPK and acetyl-CoA carboxylase in muscle. J Appl Physiol 92:2475–2482. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00071.2002
Clarke PR, Hardie DG (1990) Regulation of HMG-CoA reductase: identification of the site phosphorylated by the AMP-activated protein kinase in vitro and in intact rat liver. EMBO J 9:2439–2446
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM et al (2011) AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab 13:376–388. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.03.009
Aw DKL, Sinha RA, Xie SY, Yen PM (2014) Differential AMPK phosphorylation by glucagon and metformin regulates insulin signaling in human hepatic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 447:569–573. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.031
Sag D, Carling D, Stout RD, Suttles J (2008) Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase promotes macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory functional phenotype. J Immunol 181:8633–8641
Jeong HW, Hsu KC, Lee J-W et al (2009) Berberine suppresses proinflammatory responses through AMPK activation in macrophages. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:E955–E964. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.90599.2008
Viollet B, Horman S, Leclerc J et al (2010) AMPK inhibition in health and disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 45:276–295. doi:10.3109/10409238.2010.488215
Steinberg GR, Michell BJ, van Denderen BJW et al (2006) Tumor necrosis factor α-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance involves suppression of AMP-kinase signaling. Cell Metab 4:465–474. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.11.005
Galic S, Fullerton MD, Schertzer JD et al (2011) Hematopoietic AMPK β1 reduces mouse adipose tissue macrophage inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. J Clin Invest 121:4903–4915. doi:10.1172/JCI58577
Khamzina L, Veilleux A, Bergeron S, Marette A (2005) Increased activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in liver and skeletal muscle of obese rats: possible involvement in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Endocrinology 146:1473–1481. doi:10.1210/en.2004-0921
Wang J, Yang X, Zhang J (2016) Bridges between mitochondrial oxidative stress, ER stress and mTOR signaling in pancreatic β cells. Cell Signal 28:1099–1104. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.05.007
Jiang H, Westerterp M, Wang C et al (2014) Macrophage mTORC1 disruption reduces inflammation and insulin resistance in obese mice. Diabetologia 57:2393–2404. doi:10.1007/s00125-014-3350-5
Zeng T, Zhou J, He L et al (2016) Blocking nuclear factor-κ B protects against diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice. PLoS ONE 11:e0149677. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0149677
Liu H-W, Wei C-C, Chen Y-J et al (2016) Flavanol-rich lychee fruit extract alleviates diet-induced insulin resistance via suppressing mTOR/SREBP-1 mediated lipogenesis in liver and restoring insulin signaling in skeletal muscle. Mol Nutr Food Res. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201501064
Iseli TJ, Turner N, Zeng X-Y et al (2013) Activation of AMPK by bitter melon triterpenoids involves CaMKKβ. PLoS ONE 8:e62309. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062309
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y et al (2001) Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest 108:1167–1174. doi:10.1172/JCI13505
Liu J, Zhang J, Lu J et al (2013) Astragalus polysaccharide stimulates glucose uptake in L6 myotubes through AMPK activation and AS160/TBC1D4 phosphorylation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:137–145. doi:10.1038/aps.2012.133
Fu X, Zhu M, Zhang S et al (2016) Obesity impairs skeletal muscle regeneration through inhibition of AMPK. Diabetes 65:188–200. doi:10.2337/db15-0647
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2012) NF-κB, the first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev 26:203–234. doi:10.1101/gad.183434.111
Hinz M, Arslan SÇ, Scheidereit C (2012) It takes two to tango: iκBs, the multifunctional partners of NF-κB. Immunol Rev 246:59–76. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01102.x
Reilly SM, Chiang S-H, Decker SJ et al (2013) An inhibitor of the protein kinases TBK1 and IKK-ɛ improves obesity-related metabolic dysfunctions in mice. Nat Med 19:313–321. doi:10.1038/nm.3082
Hu MC-T, Lee D-F, Xia W et al (2004) IκB kinase promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of forkhead FOXO3a. Cell 117:225–237
Gao Z, Hwang D, Bataille F et al (2002) Serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by inhibitor κB kinase complex. J Biol Chem 277:48115–48121. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209459200
Chiang S-H, Bazuine M, Lumeng CN et al (2009) The protein kinase IKKε regulates energy balance in obese mice. Cell 138:961–975. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.046
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N et al (2006) Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 116:1784–1792. doi:10.1172/JCI29126
Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR et al (2005) IKK-β links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med 11:191–198. doi:10.1038/nm1185
Wang X-A, Zhang R, She Z-G et al (2014) Interferon regulatory factor 3 constrains IKKβ/NF-κB signaling to alleviate hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Hepatology 59:870–885. doi:10.1002/hep.26751
Kamon J, Yamauchi T, Muto S et al (2004) A novel IKKβ inhibitor stimulates adiponectin levels and ameliorates obesity-linked insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323:242–248. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.083
Zhang X, Zhang G, Zhang H et al (2008) Hypothalamic IKKβ/NF-κB and ER stress link overnutrition to energy imbalance and obesity. Cell 135:61–73. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.043
Negi G, Sharma SS (2015) Inhibition of IκB kinase (IKK) protects against peripheral nerve dysfunction of experimental diabetes. Mol Neurobiol 51:591–598. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8784-8
Oguiza A, Recio C, Lazaro I et al (2015) Peptide-based inhibition of IκB kinase/nuclear factor-κB pathway protects against diabetes-associated nephropathy and atherosclerosis in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 58:1656–1667. doi:10.1007/s00125-015-3596-6
Röhl M, Pasparakis M, Baudler S et al (2004) Conditional disruption of IκB kinase 2 fails to prevent obesity-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 113:474–481. doi:10.1172/JCI18712
Eguchi J, Yan Q-W, Schones DE et al (2008) Interferon regulatory factors are transcriptional regulators of adipogenesis. Cell Metab 7:86–94. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2007.11.002
Weissmann L, Quaresma PGF, Santos AC et al (2014) IKKε is key to induction of insulin resistance in the hypothalamus, and its inhibition reverses obesity. Diabetes 63:3334–3345. doi:10.2337/db13-1817
Huang W, Bansode R, Mehta M, Mehta KD (2009) Loss of protein kinase Cβ function protects mice against diet-induced obesity and development of hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. Hepatology 49:1525–1536. doi:10.1002/hep.22815
Idris I, Donnelly R (2006) Protein kinase C β inhibition: a novel therapeutic strategy for diabetic microangiopathy. Diab Vasc Dis Res 3:172–178. doi:10.3132/dvdr.2006.026
Szendroedi J, Yoshimura T, Phielix E et al (2014) Role of diacylglycerol activation of PKCθ in lipid-induced muscle insulin resistance in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:9597–9602. doi:10.1073/pnas.1409229111
Guo K, Liu Y, Zhou H et al (2008) Involvement of protein kinase C β-extracellular signal-regulating kinase 1/2/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-heat shock protein 27 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility and invasion. Cancer Sci 99:486–496. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00702.x
Bansode RR, Huang W, Roy SK et al (2008) Protein kinase C deficiency increases fatty acid oxidation and reduces fat storage. J Biol Chem 283:231–236. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707268200
Qu X, Dang L, Seale JP (2003) Inhibitory effect of hypocrellin A on protein kinase C in liver and skeletal muscle of obese Zucker rats. Am J Chin Med 31:871–878. doi:10.1142/S0192415X03001624
Samuel VT, Liu Z-X, Wang A et al (2007) Inhibition of protein kinase Cε prevents hepatic insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest 117:739–745. doi:10.1172/JCI30400
Kumashiro N, Erion DM, Zhang D et al (2011) Cellular mechanism of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:16381–16385. doi:10.1073/pnas.1113359108
Ikeda Y, Olsen GS, Ziv E et al (2001) Cellular mechanism of nutritionally induced insulin resistance in Psammomys obesus: overexpression of protein kinase Cε in skeletal muscle precedes the onset of hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia. Diabetes 50:584–592
Brunetti A, Manfioletti G, Chiefari E et al (2001) Transcriptional regulation of human insulin receptor gene by the high-mobility group protein HMGI(Y). FASEB J 15:492–500. doi:10.1096/fj.00-0190com
Sgarra R, Maurizio E, Zammitti S et al (2009) Macroscopic differences in HMGA oncoproteins post-translational modifications: C-terminal phosphorylation of HMGA2 affects its DNA binding properties. J Proteome Res 8:2978–2989. doi:10.1021/pr900087r
Dasgupta S, Bhattacharya S, Maitra S et al (2011) Mechanism of lipid induced insulin resistance: activated PKCε is a key regulator. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:495–506. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.01.001
Oh Y-T, Chun KH, Park BD et al (2007) Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 by protein kinase CΔ-mediated phosphorylation. Apoptosis 12:1339–1347. doi:10.1007/s10495-007-0066-8
Cantley J, Boslem E, Laybutt DR et al (2011) Deletion of protein kinase Cδ in mice modulates stability of inflammatory genes and protects against cytokine-stimulated β cell death in vitro and In vivo. Diabetologia 54:380–389. doi:10.1007/s00125-010-1962-y
Mingo-Sion AM, Ferguson HA, Koller E et al (2005) PKCδ and mTOR interact to regulate stress and IGF-I induced IRS-1 Ser312 phosphorylation in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 91:259–269. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-0669-0
Ranta F, Leveringhaus J, Theilig D et al (2011) Protein kinase C delta (PKCδ) affects proliferation of insulin-secreting cells by promoting nuclear extrusion of the cell cycle inhibitor p21Cip1/WAF1. PLoS ONE 6:e28828. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028828
Patel NA, Song SS, Cooper DR (2006) PKCδ alternatively spliced isoforms modulate cellular apoptosis in retinoic acid-induced differentiation of human NT2 cells and mouse embryonic stem cells. Gene Expr 13:73–84
Apostolatos H, Apostolatos A, Vickers T et al (2010) Vitamin A metabolite, all-trans-retinoic acid, mediates alternative splicing of protein kinase C δVIII (PKCδVIII) isoform via splicing factor SC35. J Biol Chem 285:25987–25995. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.100735
Patel RS, Carter G, Cooper DR et al (2014) Transformer 2β homolog (Drosophila) (TRA2B) regulates protein kinase C δI (PKCδI) splice variant expression during 3T3L1 preadipocyte cell cycle. J Biol Chem 289:31662–31672. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.592337
Coulombe P, Meloche S (2007) Atypical mitogen-activated protein kinases: structure, regulation and functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1376–1387. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.11.001
Broom OJ, Widjaya B, Troelsen J et al (2009) Mitogen activated protein kinases: a role in inflammatory bowel disease? Clin Exp Immunol 158:272–280. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04033.x
Raman M, Chen W, Cobb MH (2007) Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene 26:3100–3112. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210392
Roth Flach RJ, Danai LV, DiStefano MT et al (2016) Protein kinase mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 (MAP4K4) promotes obesity-induced hyperinsulinemia. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M116.718932
Hu Y, Hou Z, Liu D, Yang X (2016) Tartary buckwheat flavonoids protect hepatic cells against high glucose-induced oxidative stress and insulin resistance via MAPK signaling pathways. Food Funct 7:1523–1536. doi:10.1039/c5fo01467k
Johnson GL, Lapadat R (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 298:1911–1912. doi:10.1126/science.1072682
Yoon S, Seger R (2006) The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors 24:21–44. doi:10.1080/02699050500284218
Arnette D, Gibson TB, Lawrence MC et al (2003) Regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 by glucose and peptide hormones in pancreatic β cells. J Biol Chem 278:32517–32525. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301174200
Gibson TB, Lawrence MC, Gibson CJ et al (2006) Inhibition of glucose-stimulated activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 by epinephrine in pancreatic β-cells. Diabetes 55:1066–1073
Lawrence MC, McGlynn K, Park B-H, Cobb MH (2005) ERK1/2-dependent activation of transcription factors required for acute and chronic effects of glucose on the insulin gene promoter. J Biol Chem 280:26751–26759. doi:10.1074/jbc.M503158200
Kotzka J, Lehr S, Roth G et al (2004) Insulin-activated Erk-mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 at serine residues 432 and 455 In vivo. J Biol Chem 279:22404–22411. doi:10.1074/jbc.M401198200
Zang K, Wang J, Dong M et al (2013) Brd2 inhibits adipogenesis via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. PLoS ONE 8:e78536. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078536
Liu H, Yu J, Xia T et al (2014) Hepatic serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated protein kinase 1 (SGK1) regulates insulin sensitivity in mice via extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Biochem J 464:281–289. doi:10.1042/BJ20141005
Hayashi M, Tapping RI, Chao TH et al (2001) BMK1 mediates growth factor-induced cell proliferation through direct cellular activation of serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase. J Biol Chem 276:8631–8634. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000838200
Regan CP, Li W, Boucher DM et al (2002) Erk5 null mice display multiple extraembryonic vascular and embryonic cardiovascular defects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9248–9253. doi:10.1073/pnas.142293999
Drew BA, Burow ME, Beckman BS (2012) MEK5/ERK5 pathway: the first fifteen years. Biochim Biophys Acta 1825:37–48. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2011.10.002
Zhu H, Guariglia S, Li W et al (2014) Role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 in adipocyte signaling. J Biol Chem 289:6311–6322. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.506584
Badshah II, Baines DL, Dockrell ME (2014) Erk5 is a mediator to TGFβ1-induced loss of phenotype and function in human podocytes. Front Pharmacol 5:71. doi:10.3389/fphar.2014.00071
Belgardt BF, Mauer J, Brüning JC (2010) Novel roles for JNK1 in metabolism. Aging (Albany NY) 2:621–626
Sabio G, Davis RJ (2010) cJun NH2-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1): roles in metabolic regulation of insulin resistance. Trends Biochem Sci 35:490–496. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2010.04.004
Hotamisligil GS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140:900–917. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.034
Hotamisligil GS (2008) Inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity and diabetes. Int J Obes (Lond) 32(Suppl 7):S52–S54. doi:10.1038/ijo.2008.238
Tsukumo DML, Carvalho-Filho MA, Carvalheira JBC et al (2007) Loss-of-function mutation in toll-like receptor 4 prevents diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56:1986–1998. doi:10.2337/db06-1595
Jaeschke A, Davis RJ (2007) Metabolic stress signaling mediated by mixed-lineage kinases. Mol Cell 27:498–508. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.07.008
Jaeschke A, Czech MP, Davis RJ (2004) An essential role of the JIP1 scaffold protein for JNK activation in adipose tissue. Genes Dev 18:1976–1980. doi:10.1101/gad.1216504
Kim WH, Lee JW, Gao B, Jung MH (2005) Synergistic activation of JNK/SAPK induced by TNF-α and IFN-γ: apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells via the p53 and ROS pathway. Cell Signal 17:1516–1532. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.03.020
Pal M, Wunderlich CM, Spohn G et al (2013) Alteration of JNK-1 signaling in skeletal muscle fails to affect glucose homeostasis and obesity-associated insulin resistance in mice. PLoS ONE 8:e54247. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054247
Sabio G, Das M, Mora A et al (2008) A stress signaling pathway in adipose tissue regulates hepatic insulin resistance. Science 322:1539–1543. doi:10.1126/science.1160794
Tuncman G, Hirosumi J, Solinas G et al (2006) Functional In vivo interactions between JNK1 and JNK2 isoforms in obesity and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10741–10746. doi:10.1073/pnas.0603509103
Han MS, Jung DY, Morel C et al (2013) JNK expression by macrophages promotes obesity-induced insulin resistance and inflammation. Science 339:218–222. doi:10.1126/science.1227568
Jaeschke A, Rincón M, Doran B et al (2005) Disruption of the Jnk2 (Mapk9) gene reduces destructive insulitis and diabetes in a mouse model of type I diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:6931–6935. doi:10.1073/pnas.0502143102
Abdelli S, Bonny C (2012) JNK3 maintains expression of the insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) in insulin-secreting cells: functional consequences for insulin signaling. PLoS ONE 7:e35997. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035997
Abdelli S, Papas KK, Mueller KR et al (2014) Regulation of the JNK3 signaling pathway during islet isolation: JNK3 and c-fos as new markers of islet quality for transplantation. PLoS ONE 9:e99796. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099796
Schindler JF, Monahan JB, Smith WG (2007) p38 pathway kinases as anti-inflammatory drug targets. J Dent Res 86:800–811
Thalhamer T, McGrath MA, Harnett MM (2008) MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47:409–414. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kem297
Dahan S, Roda G, Pinn D et al (2008) Epithelial: lamina propria lymphocyte interactions promote epithelial cell differentiation. Gastroenterology 134:192–203. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.10.022
McGee SL, Hargreaves M (2006) Exercise and skeletal muscle glucose transporter 4 expression: molecular mechanisms. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 33:395–399. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.2006.04362.x
Geiger PC, Wright DC, Han D-H, Holloszy JO (2005) Activation of p38 MAP kinase enhances sensitivity of muscle glucose transport to insulin. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E782–E788. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00477.2004
Liu S, Xu R, Gerin I et al (2014) SRA regulates adipogenesis by modulating p38/JNK phosphorylation and stimulating insulin receptor gene expression and downstream signaling. PLoS ONE 9:e95416. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095416
Pereira S, Yu WQ, Moore J et al (2016) Effect of a p38 MAPK inhibitor on FFA-induced hepatic insulin resistance In vivo. Nutr Diabetes 6:e210. doi:10.1038/nutd.2016.11
Makeeva N, Roomans GM, Welsh N (2007) Role of TAB 1 in nitric oxide-induced p38 activation in insulin-producing cells. Int J Biol Sci 3:71–76
Lee J, Sun C, Zhou Y et al (2011) p38 MAPK-mediated regulation of Xbp1s is crucial for glucose homeostasis. Nat Med 17:1251–1260. doi:10.1038/nm.2449
Sha H, Yang L, Liu M et al (2014) Adipocyte spliced form of X-box-binding protein 1 promotes adiponectin multimerization and systemic glucose homeostasis. Diabetes 63:867–879. doi:10.2337/db13-1067
Chun K-H, Choi K-D, Lee D-H et al (2011) In vivo activation of ROCK1 by insulin is impaired in skeletal muscle of humans with type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 300:E536–E542. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00538.2010
Copps KD, White MF (2012) Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2. Diabetologia 55:2565–2582. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2644-8
Soliman H, Nyamandi V, Garcia-Patino M et al (2015) Partial deletion of ROCK2 protects mice from high-fat diet-induced cardiac insulin resistance and contractile dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 309:H70–H81. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00664.2014
Song Y, Wan X, Gao L et al (2015) Activated PKR inhibits pancreatic β-cell proliferation through sumoylation-dependent stabilization of P53. Mol Immunol 68:341–349. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2015.09.007
Nakamura T, Arduini A, Baccaro B et al (2014) Small-molecule inhibitors of PKR improve glucose homeostasis in obese diabetic mice. Diabetes 63:526–534. doi:10.2337/db13-1019
Sud N, Rutledge AC, Pan K, Su Q (2016) Activation of the dsRNA-activated protein kinase PKR in mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammatory stress in metabolic syndrome. Curr Pharm Des 22:2697–2703
Sun Y, Connors KE, Yang D-Q (2007) AICAR induces phosphorylation of AMPK in an ATM-dependent, LKB1-independent manner. Mol Cell Biochem 306:239–245. doi:10.1007/s11010-007-9575-6
Mohankumar SK, Taylor CG, Siemens L, Zahradka P (2013) Activation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, AMP-activated kinase and Akt substrate-160 kDa by trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid mediates skeletal muscle glucose uptake. J Nutr Biochem 24:445–456. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.01.006
Svegliati-Baroni G, Saccomanno S, Rychlicki C et al (2011) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation stimulates hepatic lipid oxidation and restores hepatic signalling alteration induced by a high-fat diet in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int 31:1285–1297. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02462.x
Cool B, Zinker B, Chiou W et al (2006) Identification and characterization of a small molecule AMPK activator that treats key components of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab 3:403–416. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.05.005
Li Y-Y, Yu L-F, Zhang L-N et al (2013) Novel small-molecule AMPK activator orally exerts beneficial effects on diabetic db/db mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 273:325–334. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2013.09.006
Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJY et al (2012) SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab 15:675–690. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.003
Park K-G, Min A-K, Koh EH et al (2008) Alpha-lipoic acid decreases hepatic lipogenesis through adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent and AMPK-independent pathways. Hepatology 48:1477–1486. doi:10.1002/hep.22496
Park E, Wong V, Guan X et al (2007) Salicylate prevents hepatic insulin resistance caused by short-term elevation of free fatty acids In vivo. J Endocrinol 195:323–331. doi:10.1677/JOE-07-0005
Lu J, Wu D, Zheng Y et al (2011) Ursolic acid improves high fat diet-induced cognitive impairments by blocking endoplasmic reticulum stress and IκB kinase β/nuclear factor-κB-mediated inflammatory pathways in mice. Brain Behav Immun 25:1658–1667. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2011.06.009
Sajan MP, Nimal S, Mastorides S et al (2012) Correction of metabolic abnormalities in a rodent model of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes mellitus by inhibitors of hepatic protein kinase C-ι. Metabolism 61:459–469. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2011.12.008
Dias AS, Porawski M, Alonso M et al (2005) Quercetin decreases oxidative stress, NF-κB activation, and iNOS overexpression in liver of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Nutr 135:2299–2304
Ozaki K-I, Awazu M, Tamiya M et al (2016) Targeting the ERK signaling pathway as a potential treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00445.2015
Tesch GH, Ma FY, Han Y et al (2015) ASK1 inhibitor halts progression of diabetic nephropathy in Nos3-deficient mice. Diabetes 64:3903–3913. doi:10.2337/db15-0384
Cao H, Lu J, Du J et al (2015) TAK1 inhibition prevents the development of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. Sci Rep 5:14593. doi:10.1038/srep14593
Bargut TCL, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Aguila MB (2015) A high-fish-oil diet prevents adiposity and modulates white adipose tissue inflammation pathways in mice. J Nutr Biochem 26:960–969. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.04.002
Furuya DT, Poletto AC, Favaro RR et al (2010) Anti-inflammatory effect of atorvastatin ameliorates insulin resistance in monosodium glutamate-treated obese mice. Metabolism 59:395–399. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2009.08.011
Lee J, Hong S-W, Chae SW et al (2012) Exendin-4 improves steatohepatitis by increasing Sirt1 expression in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice. PLoS ONE 7:e31394. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031394
Steinberg GR, Kemp BE (2009) AMPK in health and disease. Physiol Rev 89:1025–1078. doi:10.1152/physrev.00011.2008
Moreno D, Knecht E, Viollet B, Sanz P (2008) A769662, a novel activator of AMP-activated protein kinase, inhibits non-proteolytic components of the 26S proteasome by an AMPK-independent mechanism. FEBS Lett 582:2650–2654. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.06.044
Pang T, Zhang Z-S, Gu M et al (2008) Small molecule antagonizes autoinhibition and activates AMP-activated protein kinase in cells. J Biol Chem 283:16051–16060. doi:10.1074/jbc.M710114200
Yu L-F, Li Y-Y, Su M-B et al (2013) Development of novel alkene oxindole derivatives as orally efficacious AMP-activated protein kinase activators. ACS Med Chem Lett 4:475–480. doi:10.1021/ml400028q
Komers R, Lindsley JN, Oyama TT et al (2007) Renal p38 MAP kinase activity in experimental diabetes. Lab Invest 87:548–558. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3700549
Du Y, Tang J, Li G et al (2010) Effects of p38 MAPK inhibition on early stages of diabetic retinopathy and sensory nerve function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:2158–2164. doi:10.1167/iovs.09-3674
Lim CT, Kola B, Korbonits M (2010) AMPK as a mediator of hormonal signalling. J Mol Endocrinol 44:87–97. doi:10.1677/JME-09-0063
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a research grant to Dr. Kalyana C Nandipati from the LB692 Nebraska Tobacco Settlement Funds to Creighton University, and by the research Grants R01HL116042 and R01HL128063 from the National Institutes of Health, USA to DK Agrawal. The content of this article is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have read the journal’s policy on disclosure of potential conflict of interest and declares no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandipati, K.C., Subramanian, S. & Agrawal, D.K. Protein kinases: mechanisms and downstream targets in inflammation-mediated obesity and insulin resistance. Mol Cell Biochem 426, 27–45 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2878-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2878-8