Abstract
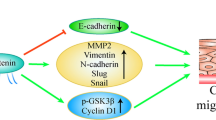
Lung cancer is the most common type of malignant tumor, but the molecular mechanisms for lung cancer progression remains to be elusive. Here, we demonstrated that FBP1 (Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase) was frequently down-regulated in lung cancer tissues and cells, and FBP1 down-regulation was associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Restored FBP1 expression inhibited glucose uptake and lactate production, but induced oxygen consumption. Restored FBP1 expression also inhibited lung cancer cells proliferation and invasion under hypoxia in vitro, and inhibited lung cancer growth in vivo. Moreover, we confirmed DNA methylation in the promoter contributed to the decrease of FBP1 expression in lung cancer cells. We identified Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) bond to FBP1 promoter to enhance DNA methylation in lung cancer cells. Our findings indicate that the down-regulation of FBP1 is a critical oncogenic event in lung cancer progression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Kumar MS, Armenteros-Monterroso E, East P, Chakravorty P, Matthews N, Winslow MM, Downward J (2014) HMGA2 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to promote lung cancer progression. Nature 505:212–217
Maione P, Rossi A, Sacco PC, Bareschino MA, Schettino C, Gridelli C (2010) Advances in chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Opin Pharm 11:2997–3007
Gonzalez de Castro D, Clarke PA, Al-Lazikani B, Workman P (2013) Personalized cancer medicine: molecular diagnostics, predictive biomarkers, and drug resistance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 93:252–259
Koppenol WH, Bounds PL, Dang CV (2011) Otto Warburg’s contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 11:325–337
Liu X, Wang X, Zhang J, Lam EK, Shin VY, Cheng AS, Yu J, Chan FK, Sung JJ, Jin HC (2010) Warburg effect revisited: an epigenetic link between glycolysis and gastric carcinogenesis. Oncogene 29:442–450
Chen M, Zhang J, Li N, Qian Z, Zhu M, Li Q, Zheng J, Wang X, Shi G (2011) Promoter hypermethylation mediated downregulation of FBP1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma and colon cancer. PLoS One 6:e25564
Dong C, Yuan T, Wu Y, Wang Y, Fan TW, Miriyala S, Lin Y, Yao J, Shi J, Kang T, Lorkiewicz P, St Clair D, Hung MC, Evers BM, Zhou BP (2013) Loss of FBP1 by Snail-mediated repression provides metabolic advantages in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Cell 23:316–331
Li MV, Chang B, Imamura M, Poungvarin N, Chan L (2006) Glucose-dependent transcriptional regulation by an evolutionarily conserved glucose-sensing module. Diabetes 55:1179–1189
Peterson CW, Stoltzman CA, Sighinolfi MP, Han KS, Ayer DE (2010) Glucose controls nuclear accumulation, promoter binding, and transcriptional activity of the MondoA-Mlx heterodimer. Mol Cell Biol 30:2887–2895
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Emery JL, Howat AJ, Variend S, Vawter GF (1988) Investigation of inborn errors of metabolism in unexpected infant deaths. Lancet 2:29–31
van Poelje PD, Potter SC, Chandramouli VC, Landau BR, Dang Q, Erion MD (2006) Inhibition of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase reduces excessive endogenous glucose production and attenuates hyperglycemia in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Diabetes 55:1747–1754
Li B, Qiu B, Lee DS, Walton ZE, Ochocki JD, Mathew LK, Mancuso A, Gade TP, Keith B, Nissim I, Simon MC (2014) Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase opposes renal carcinoma progression. Nature 513:251–255
Schmalhofer O, Brabletz S, Brabletz T (2009) E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and ZEB1 in malignant progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:151–166
Siebzehnrubl FA, Silver DJ, Tugertimur B, Deleyrolle LP, Siebzehnrubl D, Sarkisian MR, Devers KG, Yachnis AT, Kupper MD, Neal D, Nabilsi NH, Kladde MP, Suslov O, Brabletz S, Brabletz T, Reynolds BA, Steindler DA (2013) The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance. EMBO Mol Med 5:1196–1212
Zhang P, Wei Y, Wang L, Debeb BG, Yuan Y, Zhang J, Yuan J, Wang M, Chen D, Sun Y, Woodward WA, Liu Y, Dean DC, Liang H, Hu Y, Ang KK, Hung MC, Chen J, Ma L (2014) ATM-mediated stabilization of ZEB1 promotes DNA damage response and radioresistance through CHK1. Nat Cell Biol 16:864–875
Pipaon C, Real PJ, Fernandez-Luna JL (2005) Defective binding of transcriptional repressor ZEB via DNA methylation contributes to increased constitutive levels of p73 in Fanconi anemia cells. FEBS Lett 579:4610–4614
Aghdassi A, Sendler M, Guenther A, Mayerle J, Behn CO, Heidecke CD, Friess H, Büchler M, Evert M, Lerch MM, Weiss FU (2012) Recruitment of histone deacetylases HDAC1 and HDAC2 by the transcriptional repressor ZEB1 downregulates E-cadherin expression in pancreatic cancer. Gut 61:439–448
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, J., Xing, H. et al. Down-regulation of FBP1 by ZEB1-mediated repression confers to growth and invasion in lung cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 411, 331–340 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2595-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2595-8