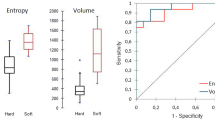
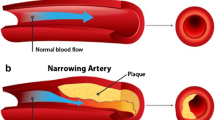
Abstract
Severe atherosclerosis disease in carotid arteries causes stenosis which in turn leads to stroke. Machine learning systems have been previously developed for plaque wall risk assessment using morphology-based characterization. The fundamental assumption in such systems is the extraction of the grayscale features of the plaque region. Even though these systems have the ability to perform risk stratification, they lack the ability to achieve higher performance due their inability to select and retain dominant features. This paper introduces a polling-based principal component analysis (PCA) strategy embedded in the machine learning framework to select and retain dominant features, resulting in superior performance. This leads to more stability and reliability. The automated system uses offline image data along with the ground truth labels to generate the parameters, which are then used to transform the online grayscale features to predict the risk of stroke. A set of sixteen grayscale plaque features is computed. Utilizing the cross-validation protocol (K = 10), and the PCA cutoff of 0.995, the machine learning system is able to achieve an accuracy of 98.55 and 98.83%corresponding to the carotidfar wall and near wall plaques, respectively. The corresponding reliability of the system was 94.56 and 95.63%, respectively. The automated system was validated against the manual risk assessment system and the precision of merit for same cross-validation settings and PCA cutoffs are 98.28 and 93.92%for the far and the near wall, respectively.PCA-embedded morphology-based plaque characterization shows a powerful strategy for risk assessment and can be adapted in clinical settings.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stroke statistics: Internet Stroke Center available at: http://www.strokecenter.org/patients/about-stroke/stroke-statistics/
WHO CVD available at http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/
Ross, R., Cell biology of atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Phys. 57(1):791–804, 1995.
Narula, J., Nakano, M., Virmani, R., Kolodgie, F.D., Petersen, R., Newcomb, R., Malik, S., Fuster, V., and Finn, A.V., Histopathologic characteristics of atherosclerotic coronary disease and implications of the findings for the invasive and noninvasive detection of vulnerable plaques. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 12. 61(10):1041–1051, 2013.
Suri J. S., Kathuria C., Molinari F. (Editors), Atherosclerosis disease management. Springer Science & Business Media, NewYork, 2011.
Saba, L., Tallapally, N., Gao, H., Molinari, F., Anzidei, M., Piga, M., Sanfilippo, R., and Suri, J.S., Semiautomated and automated algorithms for analysis of the carotid artery wall on computed tomography and sonography a correlation study. J. Ultrasound Med. 32(4):665–674, 2013b.
Prabhakaran, D., Jeemon, P., and Roy, A., Cardiovascular diseases in India current epidemiology and future directions. Circulation. 133(16):1605–1620, 2016.
Naim, C., Douziech, M., Therasse, E., Robillard, P., Giroux, M.F., Arsenault, F., Cloutier, G., and Soulez, G., Vulnerable atherosclerotic carotid plaque evaluation by ultrasound, computed tomography angiography, and magnetic resonance imaging: an overview. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 65(3):275–286, 2014.
Saba, L., and Suri, J.S. (Eds.), Multi-detector CT imaging: principles, head, neck, and vascular systems. Vol. 1. Boca Raton, Florida, CRC Press, 2014.
Saba, L., Sanches, J.M., Pedro, L.M., and Suri, J.S., Multi-modality atherosclerosis imaging and diagnosis. Springer, New York, 2015.
Sanches J. M., Laine A. F., Suri J. S., (Editors), Ultrasound imaging: advances and applications, Springer, NewYork, 2015.
Picano, E., and Paterni, M., Ultrasound tissue characterization of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16:10121–10133, 2015.
Sharma, A.M., Gupta, A., Kumar, P.K., Rajan, J., Saba, L., Nobutaka, I., Laird, J.R., Nicolades, A., and Suri, J.S., A review on carotid ultrasound atherosclerotic tissue characterization and stroke risk stratification in machine learning framework. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 17(9):55, 2015.
Mohebali, J., Romero, J.M., Hannon, K.M., Jaff, M.R., Cambria, R.P., and LaMuraglia, G.M., Acoustic shadowing impairs accurate characterization of stenosis in carotid ultrasound examinations. J. Vasc. Surg. 62(5):1236–1244, 2015.
Libby, P., Paul, M., Ridker, P.M., and Hansson, G.K., Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature. 473:317–325, 2011.
Patel, A.K., Suri, H.S., Singh, J., Kumar, D., Shafique, S., Nicolaides, A., Jain, S.K., Saba, L., Gupta, A., Laird, J.R., Giannopoulos, A., and Suri, J.S., A review on atherosclerotic biology, wall stiffness, physics of elasticity, and its ultrasound-based measurement. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 18(12):83, 2016.
Gupta, A., Kesavabhotla, K., Baradaran, H., Kamel, H., Pandya, A., Giambrone, A.E., Wright, D., Pain, K.J., Mtui, E.E., Suri, J.S., Sanelli, P.C., and Mushlin, A.I., Plaqueecholucencyandstrokeriskinasymptomaticcarotid stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 46(1):91–97, 2015.
Naim, C., Cloutier, G., Mercure, E., Destrempes, F., Zid, Q., El-Abyad, W., Lanthier, S., Giroux, M.F., and Soulez, G., Characterisation of carotid plaques with ultrasound elastography: feasibility and correlation with high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. European Soc. Radiol. 23(7):2030–2041, 2013.
Silver, F.L., Mackey, A., Clark, W.M., Brooks, W., Timaran, C.H., Chiu, D., Goldstein, L.B., Meschia, J.F., Ferguson, R.D., Moore, W.S., and Howard, G., Safety of stenting and endarterectomy by symptomatic status in the carotid revascularization endarterectomy versus stenting trial (CREST). Stroke. 42(3):675–680, 2011.
Bots, M.L., Baldassarre, D., Simon, A., de Groot, E., O'Leary, D.H., Riley, W., and Grobbee, D.E., Carotid intima-media thickness and coronary atherosclerosis: weak or strong relations? Eur. Heart J. 28(4):398–406, 2007.
Eigenbrodt, M.L., Sukhija, R., Rose, K.M., Tracy, R.E., Couper, D.J., Ewans, G.W., Bursac, Z., and Mehta, J.L., Common carotid artery wall thickness and external diameter as predictors of prevalent and incident cardiac events in a large population study. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound. 5:1–11, 2007.
Mirek, A.M., and Wolińska-Welcz, A., Is the lumen diameter of peripheral arteries a good marker of the extent of coronary atherosclerosis? Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 71(8):810–817, 2012.
Acharya, U.R., Faust, O., Sree, S.V., Molinari, F., Saba, L., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., An accurate and generalized approach to plaque characterization in 346 carotid ultrasound scans. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 61(4):0018–9456, 2012a.
Acharya, U.R., Faust, O., Alvin, A.P., Sree, S.V., Molinari, F., Saba, L., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., Symptomatic vs. asymptomatic plaque classification in carotid ultrasound. J. Med. Syst. 36(3):1861–1871, 2012b.
Acharya, U.R., Rama Krishnan, M.M., Sree, S.V., Sanches, J., Shafique, S., Nicolaides, A., Pedro, L.M., and Suri, J.S., Plaque tissue characterization and classification in ultrasound carotid scans: A paradigm for vascular feature amalgamation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 62(2):392–400, 2012c.
Acharya, U.R., Rama Krishnan, M.M., Sree, S.V., Afonso, D., Sanches, J., Shafique, S., Nicolaides, A., Pedro, L.M., Fernandes, F.J., and Suri, J.S., Atherosclerotic plaque tissue characterization in 2D ultrasound longitudinal carotid scans for automated classification: a paradigm for stroke risk assessment. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 51(5):513–523, 2013a.
Acharya, U.R., Faust, O., Sree, S.V., Alvin, A.P.C., Krishnamurthi, G., José, C.R., Sanches, J., and Suri, J.S., Understanding symptomatology of atherosclerotic plaque by image-based tissue characterization. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 110(1):66–75, 2013b.
Araki, T., Ikeda, N., Shukla, D., Jain, P.K., Londhe, N.D., Shrivastava, V.K., Banchhor, S.K., Saba, L., Nicolaides, A., Shafique, S., Laird, J.R., and Suri, J.S., PCA-based polling strategy in machine learning framework for coronary artery disease risk assessment in intravascular ultrasound: a link between carotid and coronary grayscale plaque morphology. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 128:137–158, 2016a.
Suri J.S., Yuan C., Wilson, D.L. editors, plaque imaging: pixel to molecular level IOS Press, Amsterdam, 2005.
Delsanto, S., Molinari, F., Giustetto, P., Liboni, W., Badalamenti, S., and Suri, J.S., Characterization of a completely user-independent algorithm for carotid artery segmentation in 2-D ultrasound images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 56(4):1265–1274, 2007.
Saba, L., Tadashi, A., Krishna Kumar, P., Jeny Rajan, D., Lavra, F., Ikeda, N., Sharma, A.M., Shoaib, S., Nicolaides, A., Laird, J.L., Gupta, A., and Suri, J.S., Carotid inter-adventitial diameter is more strongly related to plaque score compared to lumen diameter: an automated and first ultrasound study in Japanese diabetic cohort. J. Clin. Ultrasound. 44(4):210–220, 2016a.
Molinari, F., Zeng, G., and Suri, J.S., Intima-media thickness: setting a standard for completely automated method for ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control (IEEE UFFC). 57(5):1112–1124, 2010a.
Molinari, F., et al., Hypothesis validation of far-wall brightness in carotid-artery ultrasound for feature-based IMT measurement using a combination of level-set segmentation and registration. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 61(4):1054–1063, 2012a.
Molinari, F., Constantinos, P., Zeng, G., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., Completely automated multi-resolution edge snapper (“CAMES”) – a new technique for an accurate carotid ultrasound IMT measurement: clinical validation and benchmarking on a multi-institutional database. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(3):1211–1222, 2012b.
Molinari, F., Zeng, G., and Suri, J.S., An integrated approach to computer-based automated tracing and its validation for 200 common carotid arterial wall ultrasound images a new technique. J. Ultrasound Med. 29(3):399–418, 2010b.
Molinari, F., Zeng, G., and Suri, J.S., A state of the art review on intima–media thickness (IMT) measurement and wall segmentation techniques for carotid ultrasound. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 100(3):201–221, 2010c.
Molinari, F., Meiburger, K.M., Saba, L., Acharya, U.R., Ledda, G., Zeng, G., Ho, S.Y.S., Ahujae, A.T., Ho, S.C., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., Ultrasound IMT measurement on a multi-ethnic and multi-institutional database: our review and experience using four fully automated and one semi-automated methods. Comput. Methods Program. Biomed. 108(3):946–960, 2012c.
Molinari, F., Meiburger, K.M., Saba, L., Zeng, G., Acharya, U.R., Ledda, M., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., Fully automated dual snake formulation for carotid intima-media thickness measurement: a new approach. J. Ultrasound Med. 31(7):1123–1136, 2012d.
Molinari, F., Meiburger, K.M., Saba, L., Acharya, U.R., Ledda, M., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., Constrained snake vs. conventional snake for carotid ultrasound automated IMT measurements on multi-center data sets. Ultrasonics. 52(7):949–961, 2012e.
Molinari, F., Meiburger, K.M., Zeng, G., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., CAUDLES-EF: carotid automated ultrasound double line extraction system using edge flow. J. Ultrasound Imaging. 24(6):129–162, 2012f.
Molinari, F., Meiburger, K.M., Zeng, G., Acharya, U.R., Liboni, W., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., Carotid artery recognition system: a comparison of three automated paradigms for ultrasound images. Med. Phys. 39(1):378–391, 2012g.
Araki, T., Kumar, A.M., Krishna Kumar, P., Gupta, A., Saba, L., Rajan, J., Lavra, F., Sharma, A.M., Shafique, S., Nicolaides, A., and Laird, J.R., Ultrasound-based automated carotid lumen diameter/stenosis measurement and its validation system. Journal for Vascular Ultrasound. 40(3):120–134, 2016b.
Kumar K. P., Araki, T., Rajan, J., Saba, L., Lavra, F., Ikeda, N., Sharma, A. M., Shafique, S., Nicolaides, A., Laird, J. R., Gupta, A., Suri, J. S., Accurate lumen diameter measurement in curved vessels in carotid ultrasound: an iterative scale-space and spatial transformation approach", has been accepted for publication in, Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017; To Appear.
Mahalingam, A., Gawandalkar, U.U., Kini, G., Buradi, A., Araki, T., Ikeda, N., Nicolaides, A., Laird, J.R., Saba, L., and Suri, J.S., Numerical analysis of the effect of turbulence transition on the hemodynamic parameters in human coronary arteries. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 6(3):208, 2016.
Araki, T., Kumar, P.K., Suri, H.S., Ikeda, N., Gupta, A., Saba, L., Rajan, J., Lavra, F., Sharma, A.M., Shafique, S., and Nicolaides, A., Two automated techniques for carotid lumen diameter measurement: regional versus boundary approaches. J. Med. Syst. 40(7):1–19, 2016c.
Shrivastava, V.K., Londhe, N.D., Sonawane, R.S., and Suri, J.S., Reliable and accurate psoriasis disease classification in dermatology images using comprehensive feature space in machine learning paradigm. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(15):6184–6195, 2015a.
Shrivastava, V.K., Londhe, N.D., Sonawane, R.S., and Suri, J.S., Exploring the color feature power for psoriasis risk stratification and classification: a data mining paradigm. Comput. Biol. Med. 65:54–68, 2015b.
Shrivastava, V.K., Londhe, N.D., Sonawane, R.S., and Suri, J.S., A novel approach to multiclass psoriasis disease risk stratification: Machine learning paradigm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 28:27–40, 2016a.
Araki, T., Jain, P.K., Suri, H.S., Londhe, N.D., Ikeda, N., El-Baz, A., Shrivastava, V.K., Saba, L., Nicolaides, A., Shafique, S., Laird, J.R., Gupta, A., and Suri, J.S., Stroke risk stratification and its validation using ultrasonic Echolucent Carotid Wall plaque morphology: a machine learning paradigm. Comput. Biol. Med. 80:77–96, 2017.
Kalyan, K., Jakhia, B., Lele, R.D., Joshi, M., and Chowdhary, A., Artificial neural network application in the diagnosis of disease conditions with liver ultrasound images. Adv. Bioinforma.:708279–708279, 2014.
Soh, L.K., and Tsatsoulis, C., Texture analysis of SAR sea ice imagery using gray level co-occurrence matrices. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 37(2):780–795, 1999.
Tang, X., Texture information in run-length matrices. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 7(11):1602–1609, 1998.
Mandelbrot, B.B., The fractal geometry of nature. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, 1983.
Vapnik, V., Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York, 1998.
Kohavi, R., A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. Int. Joint Conf. Artif. Intell. 14(2):1137–1143, 1995.
Muller, K.R., Mika, S., Ratsch, G., Tsuda, K., and Scholkopf, B., An introduction to kernel based learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 12(2):181–201, 2001.
Song F., Guo Z. and Mei D., Feature selection using principalcomponent analysis, in: IEEE International Conference on System Science, Engineering Design and Manufacturing Informatization (ICSEM). 1:27–30, 2010.
Shrivastava, V.K., Londhe, N.D., Sonawane, R.S., and Suri, J.S., Reliability analysis of psoriasis decision support system in principal component analysis framework. Data Knowl. Eng. 106:1–17, 2016b.
Illuminati, G., Ricco, J.B., Caliò, F., Pacilè, M.A., Miraldi, F., Frati, G., Macrina, F., and Toscano, M., Short-term results of a randomized trial examining timing of carotid endarterectomy in patients with severe asymptomatic unilateral carotid stenosis undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. J. Vasc. Surg. 54(4):993–999, 2011.
Saba, L., Than, J.C., Noor, N.M., Rijal, O.M., Kassim, R.M., Yunus, A., Ng, C.R., and Suri, J.S., Inter-observer variability analysis of automatic lung delineation in normal and disease patients. J. Med. Syst. 40(6):1–8, 2016b.
Araki, T., Ikeda, N., Shukla, D., Londhe, N.D., Shrivastava, V.K., Banchhor, S.K., Saba, L., Nicolaides, A., Shafique, S., Laird, J.R., and Suri, J.S., A new method for IVUS-based coronary artery disease risk stratification: a link between coronary & carotid ultrasound plaque burdens. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 124:161–179, 2016d.
Araki, T., Banchhor, S.K., Londhe, N.D., Ikeda, N., Radeva, P., Shukla, D., Saba, L., Balestrieri, A., Nicolaides, A., Shafique, S., Laird, J.R., and Suri, J.S., Reliable and accurate calcium volume measurement in coronary artery using intravascular ultrasound videos. J. Med. Syst. 40(3):1–20, 2016e.
Noor, N.M., Than, J.C., Rijal, O.M., Kassim, R.M., Yunus, A., Zeki, A.A., Anzidei, M., Saba, L., and Suri, J.S., Automatic lung segmentation using control feedback system: morphology and texture paradigm. J. Med. Syst. 39(3):1–18, 2015.
Saba, L., Lippo, R.S., Tallapally, N., Molinari, F., Montisci, R., Mallarini, G., and Suri, J.S., Evaluation of carotid wall thickness by using computed tomography and semiautomated ultrasonographic software. J. Vasc. Ultrasound. 35(3):136–142, 2011.
Saba, L., Gao, H., Acharya, U.R., Sannia, S., Ledda, G., and Suri, J.S., Analysis of carotid artery plaque and wall boundaries on CT images by using a semi-automatic method based on level set model. Neuroradiology. 54(11):1207–1214, 2012.
Saba, L., Molinari, F., Meiburger, K.M., Acharya, U.R., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., Inter-and intra-observer variability analysis of completely automated cIMT measurement software (Athero edge™) and its benchmarking against commercial ultrasound scanner and expert readers. Comput. Biol. Med. 43(9):1261–1272, 2013a.
Saba, L., Ikeda, N., Deidda, M., Araki, T., Molinari, F., Meiburger, K.M., Acharya, U.R., Nagashima, Y., Mercuro, G., Nakano, M., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., Association of automated carotid IMT measurement and HbA1c in Japanese patients with coronary artery disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 100(3):348–353, 2013c.
Acharya U R, Sree S V, Rama Krishnan MM, Molinari F, Saba L, Sin Yee Stella Ho, Ahuja AT, Suzanne C. Ho, Nicolaides A and Suri J S 2012d Atherosclerotic risk stratification strategy for carotid arteries using texture-based features. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 38(6) 899–915
Pedro, L.M., Sanches, J.M., Seabra, J., Suri, J.S., Fernandes, E., and Fernandes, J., Asymptomatic carotid disease--a new tool for assessing neurological risk. Echocardiography. 31(3):353–361, 2014.
Acharya, U.R., Sree, S.V., Molinari, F., Saba, L., Nicolaides, A., and Suri, J.S., An automated technique for carotid far wall classification using grayscale features and wall thickness variability. J. Clin. Ultrasound. 43(5):302–311, 2015.
Acharya, U.R., Sree, S.V., Rama Krishnan, M.M., Saba, L., Gao, H., Mallarini, G., and Suri, J.S., Computed tomography carotid wall plaque characterization using a combination of discrete wavelet transform and texture features: a pilot study. J. Eng. Med. 227(6):643, 2013c.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Image & Signal Processing
Appendices
Appendix 1: Experimental results
Appendix 2: Grayscale features
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saba, L., Jain, P.K., Suri, H.S. et al. Plaque Tissue Morphology-Based Stroke Risk Stratification Using Carotid Ultrasound: A Polling-Based PCA Learning Paradigm. J Med Syst 41, 98 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-017-0745-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-017-0745-0