Abstract
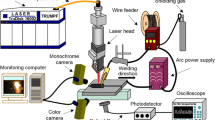
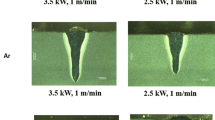
This work studied the effects of oxygen contamination in the argon shielding gases on weld microstructures and properties during laser welding of commercially pure titanium thin sheets. The experimental results, mainly analyzed by optical and scanning electron microscopy and mechanical testing, have indicated correlations between weld surface colour, weld microstructure and mechanical properties (strength, ductility, hardness). As the oxygen content increased, the weld surface colour changed from silver, straw to blue while the surface hardness continued to increase. On the other hand, with the increasing of oxygen content, the weld strength increased first and then decreased because the microstructure changed from mainly serrated alpha in welds made with pure argon shielding gas to mainly acicular and platelet alpha. Practical guidelines are also discussed, based on the study, to deal with shielding deficiencies in laser welding of titanium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASM Handbook, Propert. Select.: Nonferr. Alloys Spec.-Purp. Mater. 2 (1990) 586.
J. GEDOPT and E. DELARBRE, Proc. SPIE 4088 (2000) 264.
S. SHRIVASTAVA, Medical Device Materials, 8–10 September 2003, Anaheim CA, in Proceedings of the Materials and Processes for Medical Devices Conference, p. 417.
J. LIU, I. WATANABE, K. YOSHIDA and M. ATSUTA, Dental Mater. 18(2000) 143.
R. R. WANG and G. E. WELSCH J. Prosth. Dent. 74(5) (1995) 521.
J. C. BORLAND, Brit. Weld. J. February (1961) 61.
T. YAMAGISHI, M. ITO and Y. FUJIMURA, J. Prosth. Dent. 70(3) (1993) 264.
H. W. A. WISKOTT, T. DOUMAS, S.S. SCHERRER and U. C. BELSER, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 12 (2001) 719.
D. D. HARWIG, C. FOUNTAIN, W. ITTIWATTANA and H. CASTNER, Weld. J. Weld. Res. Nov. Suppl. (2000) 305s.
P. Y. Y. MAAK, The Effect of Air Contamination in the Argon Shielding Gas on the Mechanical Properties of Titanium Gas-Tungsten-Arc Welds, TR-282, Scientific Document Distribution Office (SDDO), Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River, Ontario, K0J 1J0, July 1984.
E. BIRO, D. C. WECKMAN and Y. ZHOU, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 33A (2002) 2019.
W. A. BAESLACK III and F. D. MULLINS, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1 (1982) 371.
J. TALKINGTON, D. HARWIG, H. CASTNER and G. MITCHELL, Weld. J. March (2000), 35.
K. K. MURTHY and S. SUNDARESAN, J. Mater. Sci. 33 (1998) 817.
Z. LIU and G. WELSCH, Metallu. Trans. A 19A (1988) 527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Xie, J. & Zhou, Y. Effects of oxygen contamination in the argon shielding gas in laser welding of commercially pure titanium thin sheet. J Mater Sci 40, 3437–3443 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-0447-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-0447-8