Abstract
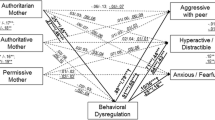
Mothers and fathers often adopt different approaches to raising their children, and the influence of different parenting styles on the development of behavioral problems may be different for boys and girls. Using data from 89 subjects, 42 boys and 47 girls, with a mean age of 62.8 months (SD = 3.3), the current study tested the influence of early negative maternal and paternal parenting styles on the development of boys’ and girls’ aggressive and behavioral problems. Parents, when children aged 5–6, completed the Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire, and when children aged 8–9, the child behavior checklist. Children were evaluated for aggressive behavior with peers using the Direct and Indirect Aggression Scale at age 8–9. Our results show that an authoritarian maternal style is positively associated with both children’s externalizing and internalizing problems while the combination of an authoritarian maternal style and a permissive paternal style was negatively associated with internalizing problems, but only in boys, and this type of family was positively associated with both types of aggressive behavior in girls and boys. Besides, the combination of a permissive maternal style and a permissive paternal style was positively related to girls’ (but not boys’) physical aggression.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for child behavior checklist/4–18 and 1991 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M. (1992). Manual for the child behavior checklist/2–3 and 1992 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. S. (1986). Manual for the teacher’s report form and teacher version of the child behavior profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont.
Akhter, N., Hanif, R., Tariq, N., & Atta, M. (2011). Parenting styles as predictors of externalizing and internalizing behavior problems among children. Pakistan Journal of Psychological Research, 26(1), 18–35.
Alizadeh, S., Talib, M. B. A., Abdullah, R., & Mansor, M. (2011). Relationship between parenting style and children’s behavior problems. Asian Social Science, 7(12), 195–200.
Antolín, L., Oliva, A., & Arranz, E. B. (2009). Contexto familiar y conducta antisocial infantil. Anuario de Psicología, 40(3), 313–327.
Barber, B. K. (1996). Parental psychological control: Revisiting a neglected construct. Child Development, 67, 3296–3319.
Baumrind, D. (1967). Child care practices anteceding three patterns of preschool behavior. Genetic Psychology Monographs, 75, 43–88.
Baumrind, D. (1973). The development of instrumental competence through socialization. In A. D. Pick (Ed.), Minnesota symposia on child psychology (Vol. 7, pp. 3–46). Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press.
Baumrind, D. (1989). Rearing competent children. In W. Damon (Ed.), Child development today and tomorrow (pp. 349–378). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Baumrind, D. (1991). Parenting styles and adolescent development. In R. Lerner, A. C. Peterson, & J. Brooks-Gunn (Eds.), The encyclopedia of adolescence (pp. 746–758). New York: Garland.
Baumrind, D. (1993). The average expectable environment is not good enough: A response to Scarr. Child Development, 64(5), 1299–1317.
Baumrind, D., Larzelere, R. E., & Owens, E. B. (2010). Effects of preschool parents’ power assertive patterns and practices on adolescent development. Parenting: Science and Practice, 10(3), 157–201.
Björkqvist, K., Lagerspetz, K. M. J., & Österman, K. (1992). The Direct and Indirect Aggression Scales. Vasa: Abo Akademi University.
Björkqvist, K., Österman, K., Lagerspetz, K. M. J., Landau, S. F., Caprara, G. V., & Fraczek, A. (2001). Aggression, victimization, and sociometric status: Findings from Finland, Israel, Italy and Poland. In J. M. Ramirez & D. S. Richardson (Eds.), Cross-cultural approaches to research on aggression and reconciliation (pp. 111–119). Huntington, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Bongers, I. L., Koot, H. M., van der Ende, J., & Verhulst, F. C. (2004). Developmental trajectories of externalizing behaviors in childhood and adolescence. Child Development, 75(5), 1523–1537.
Bornstein, M. H. (2006). Parenting science and practice. In K. A. Renninger & I. Sigel (Eds.), Child psychology in practice. Volume 4 of Handbook of Child Psychology (6th ed., pp. 893–949). Editors-in-chief: W. Damon & R. M. Lerner. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Broidy, L. M., Nagin, D. S., Tremblay, R. E., Bates, J. E., Brame, B., Dodge, K. A., et al. (2003). Developmental trajectories of childhood disruptive behaviors and adolescent delinquency: A six-site, cross-national study. Developmental Psychology, 39, 222–245.
Brumariu, L. E., & Kerns, K. A. (2010). Parent-child attachment and internalizing symptoms in childhood and adolescence: A review of empirical findings and future directions. Development and Psychopathology, 22, 177–203.
Calkins, S. D., Blandon, A. Y., Williford, A. P., & Keane, S. P. (2007). Biological, behavioral, and relational levels of resilience in the context of risk for early childhood behavior problems. Development and Psychopathology, 19, 675–700.
Campbell, S. B. (2002). Behavior problems in preschool children: Clinical and developmental issues (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
Campbell, S. B., Shaw, D. S., & Gilliom, M. (2000). Early externalizing behavior problems: Toddlers and preschoolers at risk for later maladjustment. Development and Psychopathology, 12(3), 467–488.
Casas, J. F., Weigel, S. M., Crick, N. R., Ostrov, J. M., Woods, K. E., Jansen Yeh, E. A., et al. (2006). Early parenting and children’s relational and physical aggression in the preschool and home contexts. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 27, 209–227.
Chao, R. K. (1994). Beyond parental control and authoritarian parenting style: Understanding Chinese parenting through the cultural notion of training. Child Development, 65, 1111–1119.
Chao, R. K. (2001). Extending research on the consequences of parenting style for Chinese Americans and European Americans. Child Development, 72, 1832–1843.
Crawford, N. A., Schrock, M., & Woodruff-Borden, J. (2011). Child internalizing symptoms: Contributions of child temperament, maternal negative affect, and family functioning. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 42(1), 53–64.
Cummings, E. M., Davies, P. T., & Campbell, S. (2000). Developmental psychopathology and family processes. New York: Guilford Press.
Deater-Deckard, K., & Dodge, K. A. (1997). Externalizing behavior problems and discipline revisited: Nonlinear effects and variation by culture, context, and gender. Psychological Inquiry, 8, 161–175.
Deater-Deckard, K., Dodge, K. A., Bates, J. E., & Pettit, G. S. (1998). Multiple risk factors in the development of externalizing behavior problems: Group and individual differences. Development and Psychopathology, 10, 469–493.
DiMaggio, R., & Zappulla, C. (2013). Mothering, fathering, and Italian adolescents’ problem behaviors and life satisfaction: Dimensional and typological approach. Journal of Child and Family Studies. doi:10.1007/s10826-013-9721-6.
Erath, S. A., El-Sheikh, M., & Cummings, E. M. (2009). Harsh parenting and child externalizing behavior: Skin conductance level reactivity as a moderator. Child Development, 80(2), 578–592.
Foster, E. M., Jones, D., & the Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (2006). Can a costly intervention be cost-effective? An analysis of violence prevention. Archives of General Psychiatry, 63, 1284–1291.
García, F., & Gracia, E. (2009). Is always authoritative the optimum parenting style? Evidence from Spanish families. Adolescence, 44(143), 101–131.
García Linares, M. C., Cerezo Rusillo, M. T., de la Torre Cruz, M. J., Carpio Fernández, M. D. L. V., & Casanova Arias, P. F. (2011). Parenting practices and internalizing and externalizing problems in Spanish adolescents. Psicothema, 23(4), 654–659.
Gazelle, H., & Ladd, G. W. (2003). Anxious solitude and peer exclusion: A diathesis-stress model of internalizing trajectories in childhood. Child Development, 74, 257–278.
Gershoff, E. T. (2002). Corporal punishment by parents and associated child behaviors and experiences: A meta-analytic and theoretical review. Psychological Bulletin, 128(4), 539–579.
Gilliom, M., & Shaw, D. S. (2004). Codevelopment of externalizing and internalizing problems in early childhood. Development and Psychopathology, 16, 313–333.
Heller, T. L., Baker, B. L., Henker, B., & Hinshaw, S. P. (1996). Externalizing behavior and cognitive functioning from preschool to first grade: Stability and predictors. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 25(4), 376–387.
Herz, L., & Gullone, E. (1999). The Relationship between self-esteem and parenting style. A cross-cultural comparison of Australian and Vietnamese Australian adolescents. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 30(6), 742–761.
Hoeve, M., Dubas, J. S., Gerris, J. R. M., van der Laan, P. H., & Smeenk, W. (2011). Maternal and paternal parenting styles: Unique and combined links to adolescent and early adult delinquency. Journal of Adolescence, 34, 813–827.
Holmbeck, G. N., Paikoff, R. L., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (1995). Parenting adolescents. In M. H. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of parenting. Volume 1. Children and parenting (pp. 91–118). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Jewell, J. D., Krohn, E. J., Scott, V. G., Carlton, M., & Meinz, E. (2008). The differential impact of mothers’ and fathers’ discipline on preschool children’s home and classroom behavior. North American Journal of Psychology, 10(1), 173–188.
Jewell, J. D., & Stark, K. D. (2003). Comparing the family environments of adolescents with conduct disorder and depression. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 12, 77–89.
Joosen, K. J., Mesman, J., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & van IJzendoorn, M. H. (2012). Maternal sensitivity to infants in various settings predicts harsh discipline in toddlerhood. Attachment and Human Development, 14(2), 101–117.
Kawabata, Y., Alink, L. R., Tseng, W. L., van IJzendoorn, M. H., & Crick, N. R. (2011). Maternal and paternal parenting styles associated with relational aggression in children and adolescents: A conceptual analysis and meta-analytic review. Developmental Review, 31(4), 240–278.
Keane, S. P., & Calkins, S. D. (2004). Predicting kindergarten peer social status from toddler and preschool problem behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 32, 409–423.
Kritzas, N., & Grobler, A. A. (2005). The relationship between perceived parenting styles and resilience during adolescence. Journal of Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 17(1), 1–12.
Lamborn, S. D., Mounts, N. S., Steinberg, L., & Dornbusch, S. M. (1991). Patterns of competence and adjustment among adolescents from authoritative, authoritarian, indulgent, and neglectful families. Child Development, 62, 1049–1065.
Leve, L. D., Kim, H. K., & Pears, K. C. (2005). Childhood temperament and family environment as predictors of internalizing and externalizing trajectories from ages 5 to 17. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33(5), 505–520.
Locke, L. M., & Prinz, R. J. (2002). Measurement of parental discipline and nurturance. Clinical Psychology Review, 22, 895–930.
Lorber, M. F., & Egeland, B. (2009). Infancy parenting and externalizing psychopathology from childhood through adulthood: Developmental trends. Developmental Psychology, 45(4), 909–912.
Maccoby, E. E., & Martin, J. A. (1983). Socialization in the context of the family: Parent-child interaction. In P. H. Mussen (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology (Vol. 4, pp. 1–101). Wiley: New York.
Martínez, I., & García, J. F. (2008). Internalization of values and self-esteem among Brazilian teenagers from authoritative, indulgent, authoritarian, and neglectful homes. Adolescence, 43(169), 13–29.
McCord, J. (1988). Parental behavior in the cycle of aggression. Psychiatry, 51(1), 14–23.
Mesman, J., Bongers, I. L., & Koot, H. M. (2001). Preschool developmental pathways to preadolescent internalizing and externalizing problems. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 42, 679–689.
Miner, J. L., & Clarke-Stewart, K. A. (2008). Trajectories of externalizing behavior from age 2 to age 9: Relations with gender, temperament, ethnicity, parenting, and rater. Developmental Psychology, 44, 771–786.
Musitu, G., & García, J. F. (2004). Consecuencias de la socialización familiar en la cultura española. Psicothema, 16(2), 288–293.
NICHD Early Child Care Research Network, & Arsenio, W. F. (2004). Trajectories of physical aggression from toddlerhood to middle childhood: Predictors, correlates, and outcomes. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 69, (no. 4, Serial No. 278).
Nigg, J. T., & Huang-Pollock, C. L. (2003). An early onset model of the role of executive functions and intelligence in conduct disorder delinquency. In B. B. Lahey, T. Moffitt, & A. Caspi (Eds.), The causes of conduct disorder and serious juvenile delinquency (pp. 227–253). New York: Guilford Press.
Odubote, B. A. (2008). Parenting style, race and delinquency: A comparative study of European American, African American and Nigerian families. Doctoral dissertation, University of Minnesota. http://proquest.umi.com.
Parke, R. D. (2002). Fathers and families. In M. H. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of parenting. Status and social conditions of parenting (2nd ed., Vol. 3, pp. 27–73). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Parke, R. D., & Buriel, R. (2006). Socialization in the family: Ethnic and ecological perspectives. In W. Damon, R. M. Lerner, & N. Eisenberg (Eds.), The handbook of child psychology. Social, emotional, and personality development (6th ed., Vol. 3, pp. 429–504). New York, NY: Wiley.
Paulussen-Hoogeboom, M. C., Stams, G. J. J., Hermanns, J., & Peetsma, T. T. (2007). Child negative emotionality and parenting from infancy to preschool: A meta-analytic review. Developmental Psychology, 43(2), 438.
Pereira, A. I., Canavarro, C., Cardoso, M. F., & Mendonça, D. (2009). Patterns of parental rearing styles and child behaviour problems among Portuguese school-aged children. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 18(4), 454–464.
Querido, J. G., Warner, T. D., & Eyberg, S. M. (2002). Parenting styles and child behavior in African-American families of preschool children. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 31, 272–277.
Raya, A. F., Pino, M. J., & Herruzo, J. (2009). La agresividad en la infancia: El estilo de crianza parental como factor relacionado. European Journal of Education and Psychology, 2(3), 211–222.
Rinaldi, C. M., & Howe, N. (2012). Mothers’ and fathers’ parenting styles and associations with toddlers’ externalizing, internalizing, and adaptive behaviors. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 27, 266–273.
Robinson, C. C., Mandelco, B., Olsen, S. F., & Hart, C. H. (1995). Authoritative, authoritarian, and permissive parenting practices. Development of a new measure. Psychological Reports, 77, 819–830.
Robinson, C. C., Mandelco, B., Olsen, S. F., & Hart, C. H. (2001). The parenting styles and dimensions questionnaire (PSQD). In B. F. Perlmutter, J. Touliatos, & G. W. Holden (Eds.), Handbook of family measurement techniques: Vol. 3. Instruments & Index (pp. 319–321). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Rodrigues, Y., Veiga, F., Fuentes, M. C., & García, F. (2013). Parenting and adolescents’ self-esteem: The Portuguese context. Journal of Psychodidactics. doi:10.1387/RevPsicodidact.6842.
Rose, A. J., & Rudolph, K. D. (2006). A review of sex differences in peer relationship processes: Potential trade-offs for the emotional and behavioral development of girls and boys. Psychological Bulletin, 132(1), 98–131.
Rubin, K. H., Stewart, S. L., & Chen, X. (1995). Parents of aggressive and withdrawn children. In M. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of Parenting: Vol. 1. Children and Parenting (pp. 225–284). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Russell, A., Aloa, V., Feder, T., Glover, A., Miller, H., & Palmer, G. (1998). Sex-based differences in parenting styles in a sample with preschool children. Australian Journal of Psychology, 50, 89–99.
Russell, A., Hart, C., Robinson, C., & Olsen, S. (2003). Children’s sociable and aggressive behavior with peers: A comparison of the U.S. and Australia, and contributions of temperament and parenting styles. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 27(1), 74–86.
Sandstrom, M. J. (2007). A link between mothers’ disciplinary strategies and children’s relational aggression. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 25, 399–407.
Simons, L. G., & Conger, R. D. (2007). Linking mother-father differences in parenting to a typology of family parenting styles and adolescent outcomes. Journal of Family Issues, 28(2), 212–241.
Snyder, J. R. (1998). Marital conflict and child adjustment: What about gender? Developmental Review, 18, 390–420.
Sommer, K. L. (2007). The relationship between parenting style, parental reading involvement, child behavior outcomes, child classroom competence and early childhood literacy. Master thesis, University of Oklahoma state. http://proquest.umi.com.
Steinberg, L., Blatt-Eisengart, I., & Cauffman, E. (2006). Patterns of competence and adjustment from authoritative, authoritarian, indulgent and neglectful homes: Replication in a sample of serious adolescent offenders. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 16, 47–58.
Steinberg, L., Lamborn, S., Darling, N., Mounts, N., & Dornbusch, S. M. (1994). Over-time changes in adjustment and competence among adolescents from authoritative, authoritarian, indulgent, and neglectful families. Child Development, 65, 754–770.
Steinberg, L., Mounts, N. S., Lamborn, S. D., & Dornbusch, S. M. (1991). Authoritative parenting and adolescent adjustment across varied ecological niches. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 1, 19–36.
Stocker, C. M., Burwell, R. A., & Briggs, M. L. (2002). Sibling conflict in middle childhood predicts children’s adjustment in early adolescence. Journal of Family Psychology, 16(1), 50–57.
Tur-Porcar, A., Mestre, V., Samper, P., & Malonda, E. (2012). Parenting and children’s aggression: Are there differences in the influence of the father and the mother? Psicothema, 24(2), 284–288.
Vaillancourt, T., Miller, J. T., Fagbemi, J., Cote, S., & Tremblay, R. E. (2007). Trajectories and predictors of indirect aggression: Results from a nationally representative sample of Canadian children aged 2–10. Aggressive Behavior, 33, 314–326.
Valles, N. L., & Knutson, J. F. (2008). Contingent responses of mothers and peers to indirect and direct aggression in preschool and school-aged children. Aggressive Behavior, 34(5), 497–510.
Wang, F., Christ, S. L., Mills-Koonce, W. R., Garrett-Peters, P., & Cox, M. J. (2013). Association between maternal sensitivity and externalizing behavior from preschool to preadolescence. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 34(2), 89–100.
Wenar, C., & Kerig, P. (2000). Developmental psychopathology: From infancy through adolescence (4th ed.). Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill.
Williams, L. R., Degnan, K. A., Perez-Edgar, K. E., Henderson, H. A., Rubin, K. H., Pine, D. S., et al. (2009). Impact of behavioral inhibition and parenting style on internalizing and externalizing problems from early childhood through adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37(8), 1063–1075.
Winsler, A., Madigan, A. L., & Aquilino, S. A. (2005). Correspondence between maternal and paternal parenting styles in early childhood. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 20(1), 1–12.
Wolfradt, U., Hempel, S., & Miles, J. N. V. (2003). Perceived parenting styles, depersonalisation, anxiety and coping behaviour in adolescents. Personality and Individual Differences, 34, 521–532.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Innovation (PSI2008-02958/PSIC; SEJ2007-62897), and funding provided by the Andalusian Regional Government’s Plan Andaluz de Investigación (PAI-2003/04, HUM-554) and by the Basque Country Government (GIC07/19-IT-238-07). We would like to express our gratitude to the teaching staff, parents and children of the participating schools; and to Ainhoa García, Aizpea Sorozabal and IñakiVerdier for helping us to collect the data. We thank Enrique Collado for his help in the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braza, P., Carreras, R., Muñoz, J.M. et al. Negative Maternal and Paternal Parenting Styles as Predictors of Children’s Behavioral Problems: Moderating Effects of the Child’s Sex. J Child Fam Stud 24, 847–856 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-013-9893-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-013-9893-0