Abstract
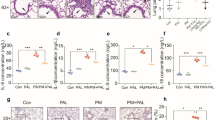
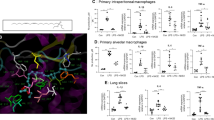
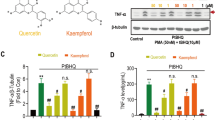
Macrophages play a critical role in mediating inflammatory processes; activated macrophages respond to endotoxin by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and IL-6. Ketamine, a widely used anesthetic agent, has unequivocally anti-inflammatory effects in vivo and in vitro. However, the detailed mechanisms for the anti-inflammatory effects of ketamine in microglia have not been elucidated yet. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of ketamine on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO), hydroxyl radical (·OH) production, and intracellular calcium accumulation in macrophages. Macrophages were pretreated with ketamine at the concentrations of 10, 100, and 1,000 μM 1 h before LPS stimulation. The production of NO and ·OH in the culture supernatant of macrophages was assayed by Griess Reagent Kit. LPS enhanced NO and ·OH production and provoked a significant intracellular calcium elevation. With the concentrations higher than 100 μM, ketamine inhibited LPS-induced NO and ·OH accumulation and intracellular calcium elevation. However, a low concentration of ketamine (10 μM) did not exert anti-inflammatory effects. These results suggest that intracellular calcium elevation is, at least, partially involved in the inhibitory effect of ketamine.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doherty, G.M., J.R. Lange, H.N. Langstein, H.R. Alexander, C.M. Buresh, and J.A. Norton. 1992. Evidence for IFN-gamma as a mediator of the lethality of endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Journal of Immunology 149: 1666–1670.
Nakagawa, S., Y. Arai, T. Kishida, N. Hiraoka, S. Tsuchida, H. Inoue, R. Sakai, O. Mazda, and T. Kubo. 2012. Lansoprazole inhibits nitric oxide and prostaglandin E(2) production in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Inflammation 35: 1062–1068.
Valledor, A.F., and M. Ricote. 2004. Nuclear receptor signaling in macrophages. Biochemical Pharmacology 67: 201–212.
Nathan, C.F. 1987. Neutrophil activation on biological surfaces. Massive secretion of hydrogen peroxide in response to products of macrophages and lymphocytes. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 80: 1550–1560.
Wu, G.J., T.L. Chen, Y.F. Ueng, and R.M. Chen. 2008. Ketamine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 gene expressions in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages through suppression of toll-like receptor 4-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation and activator protein-1 activation. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 228: 105–113.
Shimaoka, M., T. Iida, A. Ohara, N. Taenaka, T. Mashimo, T. Honda, and I. Yoshiya. 1996. Ketamine inhibits nitric oxide production in mouse-activated macrophage-like cells. British Journal of Anaesthesia 77: 238–242.
Gill, R., A. Tsung, and T. Billiar. 2010. Linking oxidative stress to inflammation: Toll-like receptors. Free Radical Biology & Medicine 48: 1121–1132.
Chang, Y., T.L. Chen, J.R. Sheu, and R.M. Chen. 2005. Suppressive effects of ketamine on macrophage functions. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 204: 27–35.
Sato, S., O. Takeuchi, T. Fujita, H. Tomizawa, K. Takeda, and S. Akira. 2002. A variety of microbial components induce tolerance to lipopolysaccharide by differentially affecting MyD88-dependent and -independent pathways. International Immunology 14: 783–791.
Reddy, D.B., and P. Reddanna. 2009. Chebulagic acid (CA) attenuates LPS-induced inflammation by suppressing NF-kappaB and MAPK activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 381: 112–117.
Gentile, C., M. Allegra, F. Angileri, A.M. Pintaudi, M.A. Livrea, and L. Tesoriere. 2012. Polymeric proanthocyanidins from Sicilian pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) nut extract inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in RAW 264.7 cells. European Journal of Nutrition 51: 353–363.
Sun, J., Z.Q. Zhou, R. Lv, W.Y. Li, and J.G. Xu. 2004. Ketamine inhibits LPS-induced calcium elevation and NF-kappa B activation in monocytes. Inflammation Research 53: 304–308.
White, P.F., W.L. Way, and A.J. Trevor. 1982. Ketamine—its pharmacology and therapeutic uses. Anesthesiology 56: 119–136.
Bourgoin, A., J. Albanese, N. Wereszczynski, M. Charbit, R. Vialet, and C. Martin. 2003. Safety of sedation with ketamine in severe head injury patients: comparison with sufentanil. Critical Care Medicine 31: 711–717.
Chen, T.L., C.C. Chang, Y.L. Lin, Y.F. Ueng, and R.M. Chen. 2009. Signal-transducing mechanisms of ketamine-caused inhibition of interleukin-1 beta gene expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophage-like Raw 264.7 cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 240: 15–25.
Chang, Y., J.J. Lee, C.Y. Hsieh, G. Hsiao, D.S. Chou, and J.R. Sheu. 2009. Inhibitory effects of ketamine on lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation. Mediators of Inflammation 2009: 705379.
Kawasaki, T., M. Ogata, C. Kawasaki, J. Ogata, Y. Inoue, and A. Shigematsu. 1999. Ketamine suppresses proinflammatory cytokine production in human whole blood in vitro. Anesthesia and Analgesia 89: 665–669.
Jiang, W., and D.S. Pisetsky. 2006. The role of IFN-alpha and nitric oxide in the release of HMGB1 by RAW 264.7 cells stimulated with polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid or lipopolysaccharide. Journal of Immunology 177: 3337–3343.
Chang, H.C., K.H. Lin, Y.T. Tai, J.T. Chen, and R.M. Chen. 2010. Lipoteichoic acid-induced TNF-alpha and IL-6 gene expressions and oxidative stress production in macrophages are suppressed by ketamine through downregulating Toll-like receptor 2-mediated activation oF ERK1/2 and NFkappaB. Shock 33: 485–492.
Scorrano, L., S.A. Oakes, J.T. Opferman, E.H. Cheng, M.D. Sorcinelli, T. Pozzan, and S.J. Korsmeyer. 2003. BAX and BAK regulation of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+: a control point for apoptosis. Science 300: 135–139.
Przygodzki, T., A. Sokal, and M. Bryszewska. 2005. Calcium ionophore A23187 action on cardiac myocytes is accompanied by enhanced production of reactive oxygen species. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1740: 481–488.
Jou, M.J., T.I. Peng, L.F. Hsu, S.B. Jou, R.J. Reiter, C.M. Yang, C.C. Chiao, Y.F. Lin, and C.C. Chen. 2010. Visualization of melatonin's multiple mitochondrial levels of protection against mitochondrial Ca(2+)-mediated permeability transition and beyond in rat brain astrocytes. Journal of Pineal Research 48: 20–38.
Petersen, A., R.F. Castilho, O. Hansson, T. Wieloch, and P. Brundin. 2000. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial permeability transition and activation of caspases in calcium ionophore A23187-induced death of cultured striatal neurons. Brain Research 857: 20–29.
Spentzas, T., R. Kudumula, C. Acuna, A.J. Talati, K.C. Ingram, F. Savorgnan, E.A. Meals, and B.K. English. 2011. Role of bacterial components in macrophage activation by the LAC and MW2 strains of community-associated, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Cellular Immunology 269: 46–53.
Spentzas, T., R.K. Shapley, C.A. Aguirre, E. Meals, L. Lazar, M.S. Rayburn, B.S. Walker, and B.K. English. 2011. Ketamine inhibits tumor necrosis factor secretion by RAW264.7 murine macrophages stimulated with antibiotic-exposed strains of community-associated, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Immunol 12: 11.
Helmke, R.J., V.F. German, and J.A. Mangos. 1989. A continuous alveolar macrophage cell line: comparisons with freshly derived alveolar macrophages. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology: Journal of the Tissue Culture Association 25: 44–48.
Aldakkak, M., D.F. Stowe, R.K. Dash, and A.K. Camara. 2012. Mitochondrial handling of excess Ca(2+) is substrate-dependent with implications for reactive oxygen species generation. Free Radical Biology & Medicine. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.09.020.
Stowe, D.F., and A.K. Camara. 2009. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in excitable cells: modulators of mitochondrial and cell function. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 11: 1373–1414.
Tsutsui, H., S. Kinugawa, and S. Matsushima. 2008. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial DNA damage in heart failure. Circulation Journal 72(Suppl A): A31–37.
D'Acquisto, F., M.J. May, and S. Ghosh. 2002. Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-B): an emerging theme in anti-inflammatory therapies. Molecular Interventions 2: 22–35.
Yu, Y., Z. Zhou, J. Xu, Z. Liu, and Y. Wang. 2002. Ketamine reduces NFkappaB activation and TNFalpha production in rat mononuclear cells induced by lipopolysaccharide in vitro. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science 32: 292–298.
Yildiz, H., I. Coskuner, E. Bulbuloglu, E. Silay, E.B. Kurutas, Z. Dogan, B. Kantarceken, H. Oksuz, N. Senoglu, M.F. Yuzbasioglu, A. Cetinkaya, and H. Ciralik. 2012. The protective effects of ketamine and propofol in obstructive jaundice: an experimental study. Bratislavské Lekárske Listy 113: 139–144.
Hou, L., and X. Wang. 2001. PKC and PKA, but not PKG mediate LPS-induced CGRP release and [Ca(2+)](i) elevation in DRG neurons of neonatal rats. Journal of Neuroscience Research 66: 592–600.
Jou, M.J., T.I. Peng, H.Y. Wu, and Y.H. Wei. 2005. Enhanced generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cybrids containing 4977-bp mitochondrial DNA deletion. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1042: 221–228.
Peng, T.I., P.R. Yu, J.Y. Chen, H.L. Wang, H.Y. Wu, Y.H. Wei, and M.J. Jou. 2006. Visualizing common deletion of mitochondrial DNA-augmented mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation and apoptosis upon oxidative stress. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1762: 241–255.
Jou, M.J., T.I. Peng, P.Z. Yu, S.B. Jou, R.J. Reiter, J.Y. Chen, H.Y. Wu, C.C. Chen, and L.F. Hsu. 2007. Melatonin protects against common deletion of mitochondrial DNA-augmented mitochondrial oxidative stress and apoptosis. Journal of Pineal Research 43: 389–403.
Grijalba, M.T., A.E. Vercesi, and S. Schreier. 1999. Ca2+−induced increased lipid packing and domain formation in submitochondrial particles. A possible early step in the mechanism of Ca2+−stimulated generation of reactive oxygen species by the respiratory chain. Biochemistry 38: 13279–13287.
Duan, Y., R.A. Gross, and S.S. Sheu. 2007. Ca2+−dependent generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species serves as a signal for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation during glutamate excitotoxicity. The Journal of Physiology 585: 741–758.
Li, C.Y., T.C. Chou, C.S. Wong, S.T. Ho, C.C. Wu, M.H. Yen, and Y.A. Ding. 1997. Ketamine inhibits nitric oxide synthase in lipopolysaccharide-treated rat alveolar macrophages. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 44: 989–995.
Weigand, M.A., H. Schmidt, Q. Zhao, K. Plaschke, E. Martin, and H.J. Bardenheuer. 2000. Ketamine modulates the stimulated adhesion molecule expression on human neutrophils in vitro. Anesthesia and Analgesia 90: 206–212.
Zhang, J., B. Jin, L. Li, E.R. Block, and J.M. Patel. 2005. Nitric oxide-induced persistent inhibition and nitrosylation of active site cysteine residues of mitochondrial cytochrome-c oxidase in lung endothelial cells. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology 288: C840–849.
Peng, T.I., and M.J. Jou. 2010. Oxidative stress caused by mitochondrial calcium overload. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1201: 183–188.
Grant, I.S., W.S. Nimmo, L.R. McNicol, and J.A. Clements. 1983. Ketamine disposition in children and adults. British Journal of Anaesthesia 55: 1107–1111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Feng, J., Zhu, P. et al. Ketamine Inhibits Calcium Elevation and Hydroxyl Radical and Nitric Oxide Production in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated NR8383 Alveolar Macrophages. Inflammation 36, 1094–1100 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9642-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9642-y