Abstract
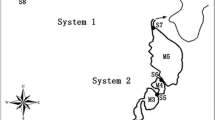
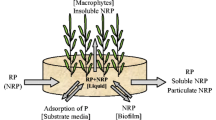
The present study offers several management strategies in order to improve the performance of a free water surface constructed wetland that treats mainly eutrophic water and which is also designed to improve and increase the biodiversity of habitat and wildlife. To attain these goals, it has been necessary to analyze the influence of certain operational parameters and environmental factors on the mass removal rates (MRRs) and the mass removal efficiencies (MREs), depending on if the objective is to maximize nutrient removal or to achieve low effluent concentrations. The system, referred to as FG, operated in a range of hydraulic loading rates (HLRs) from 7 to 58 m year−1 and removed phosphorus (P) and nitrogen (N) at an average rate of 7.15 g P m−2 year−1 and 60.07 g N m−2 year−1. P and N removal varied seasonally, mainly due to input concentrations (C in), but inlet mass loading and HLRs also strongly influenced MRRs. Based on these results, we propose to maintain a mean HLR of 58 m year−1 in winter and 25 m year−1 in summer to increase annual nutrient removal and thereby barely affecting pumping costs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FWSCWs:
-
Free water surface constructed wetlands
- FG:
-
The FWSCW studied
- MRRs:
-
Mass removal rates
- MREs:
-
Mass removal efficiencies
- HLRs:
-
Hydraulic loading rates
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- C in :
-
Input concentrations
- IML:
-
Inlet mass loading
- AV Lake:
-
l’Albufera de València Lake
- AVNP:
-
l’Albufera de València Natural Park
- CWs:
-
Constructed wetlands
- BP:
-
Barranco del Poyo
- DIN:
-
Dissolved inorganic nitrogen
- DIP:
-
Orthophosphates
- n-DIP:
-
Non-orthophosphate phosphorus
- DO:
-
Dissolved oxygen
References
APHA, 1991. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th ed. American Publish Health Association, Washington DC.
Brix, H., 1997. Do macrophytes play a role in constructed treatment wetlands? Water Science and Technology 35(5): 11–17.
CHJ, 2012. (Ed.). Memoria de investigación del Tancat de la Pipa. Technical report for the Spanish Water Authorities.
Comín, F. A., J. A. Romero, O. Hernández & M. Menéndez, 2001. Restoration of wetlands from abandoned rice fields for nutrient removal, and biological community and landscape diversity. Restoration Ecology 9(2): 201–208.
Cooke, G. D., E. B. Welch, S. A. Peterson & P. R. Newroth, 1993. Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs, 2nd ed. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL.
Coveney, M. F., D. L. Stites, E. F. Lowe, L. E. Battoe & R. Conrow, 2002. Nutrient removal from eutrophic lake water by wetland filtration. Ecological Engineering 19: 141–159.
Dunne, E. J., M. F. Coveney, E. R. Marzolf, V. R. Hoge, R. Conrow & R. Naleway, 2012. Efficacy of a large-scale constructed wetland to remove phosphorus and suspended solids from lake Apopka, Florida. Ecological Engineering 42: 90–100.
Dunne, E. J., M. F. Coveney, E. R. Marzolf, V. R. Hoge, R. Conrow, R. Naleway, E. F. Lowe, L. E. Battoe & P. W. Inglett, 2013. Nitrogen dynamics of a large-scale constructed wetland used to remove excess nitrogen from eutrophic lake water. Ecological Engineering 61: 224–234.
Dunne, E. J., M. F. Coveney, V. R. Hoge, R. Conrow, R. Naleway, E. F. Lowe, L. E. Battoe & Y. Wang, 2015. Phosphorus removal performance of a large-scale constructed treatment wetland receiving eutrophic lake water. Ecological Engineering 79: 132–142.
Fleming-Singer, M. S. & A. J. Horne, 2006. Balancing wildlife needs and nitrate removal in constructed wetlands: the case of the Irvine Ranch Water District’s San Joaquin Wildlife Sanctuary. Ecological Engineering 26: 147–166.
García, J., B. F. Green, T. Lundquist, R. Mujeriego, M. Hernández-Mariné & W. J. Oswald, 2006. Long term diurnal variations in contaminant removal in high rate ponds treating urban wastewater. Bioresource Technology 97: 1709–1715.
Gersberg, R. J., B. V. Elking, S. R. Lyong & C. R. Goldman, 1986. Role of aquatic plants in wastewater treatment by artificial wetlands. Water Research 20: 363–367.
Hernández-Crespo, C., N. Oliver, J. Bixquert, S. Gargallo & M. Martín, 2016. Comparison of three plants in a surface flow constructed wetland treating eutrophic water in a Mediterranean climate. Hydrobiologia 774: 183–192.
Hey, D. L., A. L. Kenimer & K. R. Barret, 1994. Water quality improvement by four experimental wetlands. Ecological Engineering 3: 381–397.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, J. P. Jensen, K. Havens, O. Anneville, L. Carvalho, M. F. Coveney, R. Deneke, M. T. Dokulil, B. Foy, D. Gerdeaux, S. E. Hampton, S. Hilt, K. Kangur, J. Kohler, E. Lammens, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Manca, R. Miracle, B. Moss, P. Noges, G. Persson, G. Phillips, R. Portielje, S. Romo, C. L. Schelske, D. Straile, I. Tatrai, E. Willén & M. Winder, 2005. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading – an analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshwater Biology 50: 1747–1771.
Jiang, C., X. Fan, G. Cui & Y. Zhang, 2007. Removal of agricultural non-point source pollutants by ditch wetlands: implications for lake eutrophication control. Hydrobiologia 581: 319–327.
Jing, S. R. & Y. F. Lin, 2004. Seasonal effect on ammonia nitrogen removal by constructed wetlands treating polluted river water in southern Taiwan. Environmental Pollution 127: 291–301.
Kadlec, R. H., 1999. The limits of phosphorus removal in wetlands. Wetlands Ecology and Management 7: 165–175.
Kadlec, R. H., 2006. Free surface wetlands for phosphorus removal: the position of the Everglades Nutrient Removal Project. Ecological Engineering 27: 361–379.
Kadlec, R. H. & R. L. Knight, 1996. Treatment Wetlands. CRC/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton FL: 893.
Kadlec, R. H. & K. R. Reddy, 2001. Temperature effects in treatment wetlands. Water Environment Research 73: 543–557.
Kadlec, R. H. & S. D. Wallace, 2009. Treatment Wetlands, 2nd ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Kadlec, R. H., S. B. Roy, R. K. Munson, S. Charlton & W. Brownlie, 2010. Water quality performance of treatment wetlands in the Imperial Valley, California. Ecological Engineering 36: 1093–1107.
Kadlec, R. H., J. S. Bays, L. E. Mokry, S. Andrews & M. R. Ernst, 2011. Performance analysis of the Richland-Chambers treatment wetlands. Ecological Engineering 37: 176–190.
Li, L., Y. Li, D. K. Biswas, Y. Nian & G. Jiang, 2008. Potential of constructed wetlands in treating the eutrophic water: evidence from Taihu Lake of China. Bioresource Technology 99: 1656–1663.
Mander, Ü., K. Lõhmus, S. Teiter, T. Mauring, K. Nurk & J. Augustin, 2008. Gaseous fluxes in the nitrogen and carbon budgets of subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment 404(2): 343–353.
Martín, M., N. Oliver, C. Hernández-Crespo, S. Gargallo & M. C. Regidor, 2013. The use of free water surface constructed wetland to treat the eutrophicated waters of lake L’Albufera de Valencia (Spain). Ecological Engineering 50: 52–61.
Mitsch, W. J. & J. G. Gosselink, 2000. Wetlands, 3rd ed. Wiley, New York.
Mitsch, W. J., B. Bernal, A. M. Nahlik, Ü. Mander, L. Zhang, C. J. Anderson, S. E. Jørgensen & H. Brix, 2013. Wetlands, carbon, and climate change. Landscape Ecology 28(4): 583–597.
Moustafa, M. Z., T. D. Fontaine, M. Guardo & R. T. James, 1998. The response of a freshwater wetland to long-term ‘low level’ nutrients loads: nutrients and water budget. Hydrobiologia 264: 41–53.
Nairn, R. W. & W. M. Mitsch, 2000. Phosphorus removal in created wetland ponds receiving river overflow. Ecological Engineering 14: 107–126.
Nichols, D. S., 1983. Capacity of natural wetlands to remove nutrients from wastewater. Water Pollution Control Federation 55(5): 495–505.
Phipps, R. G. & W. G. Crumpton, 1994. Factors affecting nitrogen loss in experimental wetlands with different hydrologic loads. Ecological Engineering 3: 399–408.
Phillips, G., A. Bramwell, J. Pitt, J. Stansfield & M. Perrow, 1999. Practical application of 25 years’ research into the management of shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 395(396): 61–76.
Picot, B., S. Moersidik, C. Casellas & J. Bontoux, 1993. Using diurnal variations in a high rate algal pond for management pattern. Water Science and Technology 28(10): 209–215.
Pomogyi, P., 1993. Nutrient retention by the Kis-Balaton Water Protection System. Hydrobiologia 251: 309–320.
Reddy, K. R., R. H. Kadlec, E. Flaig & P. M. Gale, 1999. Phosphorus retention in streams and wetlands: a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 29(1): 83–146.
Reilly, J. F., A. J. Horne & C. D. Miller, 2000. Nitrate removal from a drinking water supply with large free-surface constructed wetlands prior to groundwater recharge. Ecological Engineering 14: 33–47.
Richardson, C. J. & S. S. Quian, 1999. Long-term phosphorus assimilative capacity in freshwater wetlands: a new paradigm for sustaining ecosystem structure and function. Environmental Science and Technology 33(10): 1545–1551.
Rodrigo, M. A., M. Martín, C. Rojo, S. Gargallo, M. Segura & N. Oliver, 2013. The role of eutrophication reduction of two small man-made Mediterranean lagoons in the context of a broader remediation system: effects on water quality and plankton contribution. Ecological Engineering 61: 371–382.
Smith, V. H. & D. W. Schindler, 2009. Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends in Ecology and Evolution 24: 201–207.
Smith, V. H., G. D. Tilman & J. C. Nekola, 1999. Eutrophication: impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environmental Pollution 100: 179–196.
Søndergaard, M., J. P. Jensen & E. Jeppesen, 2003. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506–507: 135–145.
Sollie, S., H. Coops & J. T. A. Verhoeven, 2008. Natural and constructed littoral zones as nutrient traps in eutrophicated shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 605: 219–233.
Spieles, D. J. & W. J. Mitsch, 2000. The effects of season and hydrologic and chemical loading on nitrate retention in constructed wetlands: a comparison of low- and high-nutrient riverine systems. Ecological Engineering 14: 77–91.
Tang, X., S. Huang, M. Scholz & L. Jinzhong, 2009. Nutrient removal in pilot-scale constructed wetlands treating eutrophic river water: assessment of plants, intermittent artificial aeration and polyhedron hollow polypropylene balls. Water air Soil Pollution 197: 61–73.
Tanner, C. C., J. S. Clayton & M. P. Upsdell, 1995. Effect of loading rate and planting on treatment of dairy farm wastewaters in constructed wetlands – II. Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus. Water Research 29: 27–34.
Vymazal, J., 2007. Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment 380: 48–65.
Zamparas, M. & I. Zacharias, 2014. Restoration of eutrophic freshwater by managing internal nutrient loads. A review. Science of the Total Environmental 96: 551–562.
Acknowledgements
Núria Oliver acknowledges the scholarship provided by the Generalitat Valenciana, Spain (VALi + D PhD Program). The authors are also grateful to the Confederación Hidrográfica del Jucar (CHJ, MMARM) for the financial support of the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This manuscript has been prepared according to the ethical rules of Hydrobiologia and it has not been submitted to other journals.
Additional information
Handling editor: Pierluigi Viaroli
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliver, N., Martín, M., Gargallo, S. et al. Influence of operational parameters on nutrient removal from eutrophic water in a constructed wetland. Hydrobiologia 792, 105–120 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-3048-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-3048-4