Abstract
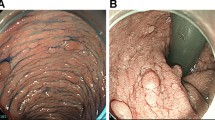
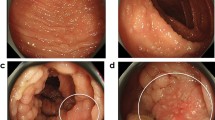
We report the clinical case of a patient who showed an “accelerated” form of polyposis, with development of major lesions within the first decade of life. The patient belongs to a familial adenomatous polyposis family—already described in 2001—featured by profuse polyposis at an early age of onset and desmoid tumors in the majority of affected individuals (of both sexes). The family was characterized by an uncommon mutation of the APC gene (c.4391_4700del310insCACCTACTGCTGAAA, previously defined as c.4394ins15del310) consisting in a large deletion of 310 bp at codon 1,464 with duplication of the breakpoint leading to a stop codon at position 1,575. The proband was affected by desmoids tumors at the age of 3 years. In the same year (2004) numerous polyps in the large bowel and a hepatoblastoma developed. After several months new desmoids appeared in the surgical scar. In 2010, at age 9, the patient was operated of total colectomy and endorectal pull-through of the small intestine owing to profuse colorectal adenomatosis. New desmoids developed in 2011 and 2012, and required chemotherapy. Further analysis of the APC gene in the proband revealed several polymorphisms. One of these (c.398A>G) had not been previously reported, nor was present in two other affected members of the family. The clinical case, and the practical implications for therapy, are discussed according to the most recent theories of colorectal cancer development. Long-term treatment with Cox-2 inhibitors might represent a good option for this patient.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galiatsatos P, Foulkes WD (2006) Familial adenomatous polyposis. Am J Gastroenterol 101(2):385–398
Mills SJ, Chapman PD, Burn J, Gunn A (1997) Endoscopic screening and surgery for familial adenomatous polyposis: dangerous delays. Br J Surg 84(1):74–77
Hughes LJ, Michels VV (1992) Risk of hepatoblastoma in familial adenomatous polyposis. Am J Med Genet 43(6):1023–1025
Lynch HT, Tinley ST, Lynch J, Vanderhoof J, Lemon SJ (1997) Familial adenomatous polyposis. Discovery of a family and its management in a Cancer Genetics Clinic. Cancer Suppl 80(3):614–620
Scott RJ (2003) Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and other polyposis syndromes. Hered Cancer Clin Pract 1(1):19–30
Kinney AY, Hicken B, Simonsen SE, Venne V, Lowstuter K, Balzotti J, Burt RW (2007) Colorectal cancer surveillance behaviors among members of typical and attenuated FAP families. Am J Gastroenterol 102(1):153–162
Ruttenberg D, Elliot MS, Bolding E (1991) Severe colonic dysplasia in a child with familial adenomatous polyposis. Int J Colorectal Dis 6(3):169–170
Lillehei CW, Leichtner A, Bousvaros A, Shamberger RC (2009) Restorative proctocolectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis in children. Dis Colon Rectum 52(9):1645–1649
De Ponz Leon M, Varesco L, Benatti P, Sassatelli R, Izzo P, Scarano MI, Rossi GB, Di Gregorio C, Gismondi V, Percesepe A, de Rosa M, Roncucci L (2001) Phenotype-genotype correlations in an extended family with adenomatosis coli and an unusual APC gene mutation. Dis Colon Rectum 44(11):1597–1604
Gismondi V, Bafico A, Biticchi R, Pedemonte S, Di Pietri S, Ponz de Leon M, Groden J, Varesco L. 310 basepair APC deletion with duplication of breakpoint (4394ins15del310) in an Italian polyposis patient. Hum Mutat. 1998;Suppl 1:S220-2. (No abstract available)
Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA Jr (2013) Kinzler KW. Cancer genome landscapes. Science. 339(6127):1546–1558. doi:10.1126/science.1235122. (Review)
LOVD-Leiden Open Variation Database (Colon Cancer Gene Variant Database) http://132.229.137.16/LOVD2/colon_cancer/variants.php?select_db=MSH2&action=view_all&order=Variant/Remarks,ASC&hide_col&show_col&limit=25
Fokkema IF, den Dunnen JT, Taschner PE (2005) LOVD: easy creation of a locus-specific sequence variation database using an “LSDB-in-a-box” approach. Hum Mutat 26(2):63–68
Pezzi A, Roncucci L, Benatti P, Sassatelli R, Varesco L, Di Gregorio C, Venesio T, Pedroni M, Maffei S, Reggiani Bonetti L, Borsi E, Ferrari M, Martella P, Rossi G, Ponz De Leon M (2009) Relative role of APC and MUTYH mutations in the pathogenesis of familial adenomatous polyposis. Scand J Gastroenterol 44(9):1092–1100
Pastrello C, Pin E, Marroni F, Bedin C, Fornasarig M, Tibiletti MG, Oliani C, Ponz De Leon M, Urso ED, Della Puppa L, Agostini M, Viel A (2011) Integrated analysis of unclassified variants in mismatch repair genes. Genet Med 13(2):115–124
Soave F (1964) Hirschsprung’s disease: a new surgical technique. Arch Dis Child 39:116–124
Boley S (1968) An endorectal pull-through operation with primary anastomosis for Hirschsprung’s disease. Surg Gynecol Obstet 127:353–357
Goss KH, Groden J (2000) Biology of the adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor. J Clin Oncol 18(9):1967–1979. (Review)
Talseth-Palmer BA, Brenne IS, Ashton KA, Evans TJ, McPhillips M, Groombridge C, Suchy J, Kurzawski G, Spigelman A, Lubinski J, Scott RJ (2011) Colorectal cancer susceptibility loci on chromosome 8q23.3 and 11q23.1 as modifiers for disease expression in Lynch syndrome. J Med Genet 48(4):279–284. doi:10.1136/jmg.2010.079962
Morak M, Koehler U, Schackert HK, Steinke V, Royer-Pokora B, Schulmann K, Kloor M, Höchter W, Weingart J, Keiling C, Massdorf T, Holinski-Feder E (2011) German HNPCC consortium. Biallelic MLH1 SNP cDNA expression or constitutional promoter methylation can hide genomic rearrangements causing Lynch syndrome. J Med Genet 48(8):513–519. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100050
Poynter JN, Figueiredo JC, Conti DV, Kennedy K, Gallinger S, Siegmund KD, Casey G, Thibodeau SN, Jenkins MA, Hopper JL, Byrnes GB, Baron JA, Goode EL, Tiirikainen M, Lindor N, Grove J, Newcomb P, Jass J, Young J, Potter JD, Haile RW, Duggan DJ, Le Marchand L, Colon CFR (2007) Variants on 9p24 and 8q24 are associated with risk of colorectal cancer: results from the Colon Cancer Family Registry. Cancer Res 67(23):11128–11132
Lynch HT, Lynch PM, Lanspa SJ, Snyder CL, Lynch JF, Boland CR (2009) Review of the Lynch syndrome: history, molecular genetics, screening, differential diagnosis, and medicolegal ramifications. Clin Genet 76(1):1–18. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2009.01230.x. (Review)
Levine AJ, Chang A, Dittmer D, Notterman DA, Silver A, Thorn K, Welsh D, Wu M (1994) The p53 tumor suppressor gene. J Lab Clin Med 123(6):817–823. (Review. No abstract available)
Church J, Burke C, McGannon E, Pastean O, Clark B (2003) Risk of rectal cancer in patients after colectomy and ileorectal anastomosis for familial adenomatous polyposis: a function of available surgical options. Dis Colon Rectum 46(9):1175–1181
Wallace MH, Phillips RK (1998) Upper gastrointestinal disease in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg 85(6):742–750. (Review)
Lynch PM, Ayers GD, Hawk E, Richmond E, Eagle C, Woloj M, Church J, Hasson H, Patterson S, Half E, Burke CA (2010) The safety and efficacy of celecoxib in children with familial adenomatous polyposis. Am J Gastroenterol 105(6):1437–1443. doi:10.1038/ajg.2009
Phillips RK, Wallace MH, Lynch PM, Hawk E, Gordon GB, Saunders BP, Wakabayashi N, Shen Y, Zimmerman S, Godio L, Rodrigues-Bigas M, Su LK, Sherman J, Kelloff G, Levin B, Steinbach G, FAP Study Group (2002) A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study of celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, on duodenal polyposis in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 50(6):857–860
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponz de Leon, M., Bianchini, M.A., Reggiani-Bonetti, L. et al. An unusual case of familial adenomatous polyposis with very early symptom occurrence. Familial Cancer 13, 375–380 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10689-014-9718-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10689-014-9718-3