Abstract
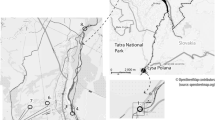
Microbial quality and physical–chemical properties of recreational spas were surveyed to investigate the health aspect of the spas’ water. A total of 195 samples were collected from pools and springs of the spas in five sites from Ardebil Province of Iran. The effects of an independent factor defined as ‘condition’ and its component sub-factors (i.e., sampling point, location, and sampling date) on microbial quality and physical–chemical properties of the spas were studied by applying path analysis. The influence of physical–chemical properties on microbial quality was also considered. The percentage of samples exceeding the ISIRI (Swimming pool water microbiological specifications (vol 9412), Institute of Standards and Industrial Research of Iran, Tehran, 2007) limits for Staphylococcus (spp.) was up to 55.8 in the springs and 87.8 in the pools, 58.1 and 99.2 for HPC, 90.7 and 97.8 for total coliform and fecal coliform, and 9.3 and 34.4 for Pseudomonas aeruginosa, respectively. There were significant differences between the pools and springs for both physical–chemical properties and microbial quality. From the path analysis, sampling point was the most effective sub-factor of ‘condition’ on both the physical–chemical properties and microbial quality. Among the physical–chemical properties, water color had the most enhancing or additive influence on microbial pollution, while EC indicated a reducing or subtractive effect.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmonem, A., El-Meleigi, M., & Al-Rokaibah, A. (1990). Chemical characteristics and bacterial contamination of groundwater in Buraydah, Saudi Arabia. Journal of King Saud University.
Anderson, H., & Cummings, D. (1999). Measuring the salinity of water: Department of Sustainability and Environment.
Barut, I., Erdogan, N., & Basak, E. (2004). Hydrogeochemical evaluation of Western Anatolian mineral waters. Environmental Geology, 45(4), 494–503.
Beauchamp, R. O., Bus, J. S., Popp, J. A., Boreiko, C. J., Andjelkovich, D. A., & Leber, P. (1984). A critical review of the literature on hydrogen sulfide toxicity. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 13(1), 25–97. doi:10.3109/10408448409029321.
Cimetiere, N., & De Laat, J. (2009). Henry’s law constant of N, N-dichloromethylamine: Application to the contamination of the atmosphere of indoor swimming pools. Chemosphere, 77(4), 465–470.
Dobaradaran, S., Bina, B., & Isfahani, B. N. (2006). The effect of some physical and chemical parameters on regrowth of aeromonas bacterium and heterotrophic bacteria in Isfahan drinking water system. Journal of Water and Wastewater, 17(1), 8–13.
Eaton, A. D., Franson, M. A. H., Association, A. P. H., Association, A. W. W., & Federation, W. E. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Esterman, A., Calder, I., Cameron, S., Roder, D., Walters, R., Christy, P., et al. (1987). Determinants of the microbiological characteristics of spa pools in South Australia. Water Research, 21(10), 1231–1235.
Fernandez-Luna, A., Burillo, P., Felipe, J. L., Gallardo, L., & Tamaral, F. M. (2013). Chlorine concentrations in the air of indoor swimming pools and their effects on swimming pool workers. Gaceta Sanitaria, 27(5), 411–417. doi:10.1016/j.gaceta.2013.02.002.
Germinario, C., Tafuri, S., Napoli, C., Martucci, V., Termite, S., Pedote, P., et al. (2012). An outbreak of pneumonia in a thermal water spa contaminated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An epidemiological and environmental concern. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 6(9), 1978–1984.
Hayashi, M. (2004). Temperature-electrical conductivity relation of water for environmental monitoring and geophysical data inversion. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 96(1–3), 119–128.
ISIRI. (2007). Swimming pool water microbiological specifications (Vol. 9412). Tehran: Institute of Standards and Industrial Research of Iran.
LeChevallier, M. W., Welch, N. J., & Smith, D. B. (1996). Full-scale studies of factors related to coliform regrowth in drinking water. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62(7), 2201–2211.
Leclerc, H., Mossel, D., Edberg, S., & Struijk, C. (2001). Advances in the bacteriology of the coliform group: Their suitability as markers of microbial water safety. Annual Reviews in Microbiology, 55(1), 201–234.
Liguori, G., Di Onofrio, V., Gallè, F., Liguori, R., Nastro, R. A., & Guida, M. (2014). Occurrence of Legionella spp. in thermal environments: Virulence factors and biofilm formation in isolates from a spa. Microchemical Journal, 112, 109–112.
Martins, M., Sato, M., Alves, M., Stoppe, N., Prado, V., & Sanchez, P. (1995). Assessment of microbiological quality for swimming pools in South America. Water Research, 29(10), 2417–2420.
Neghab, M., Gorgi, H., Baghapour, M., Rajaeefard, A., & Moemenbellah-Fard, M. (2006). Bacterial contamination of the swimming pools in Shiraz, Iran; Relationship to residual chlorine and other determinants. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 9(13), 2473–2477.
Nikaeen, M., Hatamzadeh, M., Dastjerdi, M. V., Hassanzadeh, A., Mosavi, Z., & Rafiei, M. (2010). An investigation on physical, chemical and microbial quality of Isfahan swimming pool waters based on standard indicators. Journal of Isfahan Medical School, 28(108), 346–356.
Papadopoulou, C., Economou, V., Sakkas, H., Gousia, P., Giannakopoulos, X., Dontorou, C., et al. (2008). Microbiological quality of indoor and outdoor swimming pools in Greece: Investigation of the antibiotic resistance of the bacterial isolates. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 211(3), 385–397.
Philpott, J. A., Woodburne, A., Philpott, O., Schaefer, W. B., & Mollohan, C. (1963). Swimming pool granuloma: A study of 290 cases. Archives of Dermatology, 88(2), 158–162.
Porter, J. D., Ragazzoni, H. P., Buchanon, J. D., Waskin, H. A., Juranek, D. D., & Parkin, W. E. (1988). Giardia transmission in a swimming pool. American Journal of Public Health, 78(6), 659–662.
Reis, M. A., Almeida, J. S., Lemos, P. C., & Carrondo, M. J. (1992). Effect of hydrogen sulfide on growth of sulfate reducing bacteria. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 40(5), 593–600.
Schoefer, Y., Zutavern, A., Brockow, I., Schäfer, T., Krämer, U., Schaaf, B., et al. (2008). Health risks of early swimming pool attendance. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 211(3), 367–373.
Shahriari, A., Naddafi, K., Younesuan, M., & Nabizadeh, R. (2011a). Microbial quality of swimming water in caspian sea coasts in golestan province. Health System Research, 6(2), 235–240.
Shahriari, A., Nafez, A., Norouzi, S., & Heidari, M. (2011b). Investigation of common microbial indicators in swimming pool of gorgan city. Journal of health and hygiene, 2(2), 17–26.
Shen, Q., Zhu, J., Cheng, L., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., & Xu, X. (2011). Enhanced algae removal by drinking water treatment of chlorination coupled with coagulation. Desalination, 271(1), 236–240.
Silva, A., Vieira, H., Martins, N., Granja, A., Vale, M., & Vale, F. (2010). Viral and bacterial contamination in recreational waters: A case study in the Lisbon bay area. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 108(3), 1023–1031.
Sukenik, S., Flusser, D., & Abu-Shakra, M. (1999). The role of spa therapy in various rheumatic diseases. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America, 25(4), 883–897.
Tanasković, I., Golobocanin, D., & Miljević, N. (2012). Multivariate statistical analysis of hydrochemical and radiological data of Serbian spa waters. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 112, 226–234.
Uyan, Z., Carraro, S., Piacentini, G., & Baraldi, E. (2009). Swimming pool, respiratory health, and childhood asthma: Should we change our beliefs? Pediatric Pulmonology, 44(1), 31–37.
Vikesland, P. J., Ozekin, K., & Valentine, R. L. (2001). Monochloramine decay in model and distribution system waters. Water Research, 35(7), 1766–1776.
WHO (2006a). Guidelines for safe recreational water environments. Vol 2: swimming pools and similar environments. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press.
WHO (2006b). Guidelines for safe recreational water environments (Vol. 2, Swimming pools). Geneva, Switzerland: WHO press.
Zwietering, M., De Koos, J., Hasenack, B., De Witt, J., & Van’t Riet, K. (1991). Modeling of bacterial growth as a function of temperature. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57(4), 1094–1101.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support of Ardabil University of Medical Sciences for this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fazlzadeh, M., Sadeghi, H., Bagheri, P. et al. Microbial quality and physical–chemical characteristics of thermal springs. Environ Geochem Health 38, 413–422 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9727-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9727-7