Abstract
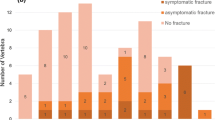
Vertebral compression fracture (VCF) occurs after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for spine metastasis. Recently, single fraction radiosurgery (sfSRS) is used more frequently. The aim of this study is to determine the clinical outcome of VCF after sfSRS. Spinal instability neoplastic score (SINS) criteria were used to retrospectively score 143 consecutive vertebral segments in 79 patients treated with SRS. Follow-up MRI, pain, and neurologic assessments obtained every 3–6 months. Pain also scored at 7, 14, and 30 days after sfSRS. Follow up was 16 ± 18 months ±SD, range 3–78. Long-term radiographic control occurred in 94 % of cases. Pain improvement resulted within 7 days in 100 % of cases with severe pain and sustained long-term in 95 %. VCF occurred in 21 % of segments: 30 % were de novo VCF. The overall 1 year fracture free probability (1yFFP) was 76 %. Pre-existing VCF resulted in higher probability to progress: 1yFFP 90 versus 60 %. Symptoms presented in 6 % of cases with de novo VCF and 39 % with progressive. The former were treated with vertebral augmentation (VA), the latter with open surgery. Surgery/VA prior to SRS did not change risk of progressive VCF. Univariate but not multivariate analysis identified histology (colorectal), pre-existing VCF, and pain (severe) as significant predictors of VCF. In conclusion, sfSRS compares favourably to SBRT for radiographic and pain control with similar VCF risk. Patients with pre-existing VCF have a higher probability to progress, become symptomatic, and require surgery. These results may help discussing risk and benefits with patients undergoing sfSRS for spinal metastasis and developing new treatment algorithms.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computer tomography
- CTV:
-
Clinical tumor volume
- EBRT:
-
External beam radiation
- FFP:
-
Fracture-free probability
- GTV:
-
Gross tumor volume
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- OAR:
-
Organs at risk
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- SBRT:
-
Stereotactic body radiation
- SINS:
-
Spine instability neoplastic score
- SRS:
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery
- sfSRS:
-
Single fraction stereotactic radiosurgery
- VA:
-
Vertebral augmentation
- VAS:
-
Visual analogue score
- VCF:
-
Vertebral compression fracture
References
Faul CM, Flickinger JC (1995) The use of radiation in the management of spinal metastases. J Neurooncol 23:149–161
Gerszten PC, Burton SA, Ozhasoglu C et al (2007) Single fraction radiosurgery for spine metastases: clinical experience in 500 cases from a single institution. Spine 32(2):193–199
Patchell R, Tibbs P, Regine W et al (2005) Direct decompressive surgical resection in the treatment of spinal cord compression caused by metastatic cancer: a randomized trial. Lancet 366:643–648
Bilsky M, Laufer I, Burch S (2009) Shifting paradigms in the treatment of metastatic spine disease. Spine 34(22):S101–S107
Sahgal A, Atenafu EG, Chao S et al (2013) Vertebral compression fracture after spine stereotactic body radiotherapy: a multi-Institutional analysis with a focus on radiation dose and spine instability neoplastic score. J Clin Oncol 31:3426–3431
Gerszten P (2014) Spine metastases: from radiotherapy, surgery, to radiosurgery. Neurosurg Online 61:16–25
Ryu S, Pugh SL, Gerszten PC et al (2014) RTOG 0631 phase 2/3 study of image guided stereotactic radiosurgery for localized (1–3) spine metastases: phase 2 results. Pract Radiat Oncol 4(2):76–81
Fisher CG, DiPaola CP, Ryken TC et al (2010) A novel classification system for spinal instability in neoplastic disease: an evidence-based approach and expert consensus from the Spine Oncology Study Group. Spine 35:E1221–E1229
Fisher CG, Versteeg AL, Schouten R et al (2014) Reliability of the spinal instability neoplastic scale among radiologists: an assessment of instability secondary to spinal metastases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 203(4):869–874
Fourney DR, Frangou EM, Ryken TC et al (2011) Spinal instability neoplastic score: and analysis of reliability and validity from the Spine Oncology Study Group. J Clin Oncol 29:3072–3077
Lee BH, Park JO, Kim HS et al (2014) Perioperative complication and surgical outcome in patients with spine metastases: retrospective 200-case series in a single institute. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 122:80–86
Al-Omair A, Smith R, Kiehl TR et al (2013) A radiation-induced vertebral compression fracture following spine stereotactic radiosurgery: clinicopathological correlation. J Neurosurg Spine 18(5):430–435
Chang-Seng E, Charissoux M, Larbi A et al (2014) Spinal metastasis in breast cancer: single center experience. World Neurosurg 82(6):1344–1350
Pan HY, Allen PK, Wang XS et al (2014) Incidence and predictive factors of pain flare after spine stereotactic body radiation therapy: secondary analysis of phase 1/2 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 90(4):870–876
Chiang A, Zeng L, Zhang L et al (2013) Pain flare is a common adverse event in steroid-naïve patients after spine stereotactic body radiation therapy: a prospective clinical trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86(4):638–642
Aj Clark, Lambon KR, Butowski NA et al (2012) Neurosurgical management and prognosis of patients with glioblastoma that progresses during bevacizumab treatment. Neurosurgery 70:361–370
Chang EL, Shiu AS, Mendel E et al (2007) Phase I/II study of stereotactic body radiotherapy for spinal metastasis and its pattern of failure. J Neurosurg Spine 7:151–160
Gagnon GJ, Nasr NM, Liano JJ, Molzahn I, Marsh D, McRae D et al (2009) Treatment of spinal tumors using cyberknife fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery: pain and quality-of-life assessment after treatment in 200 patients. Neurosurgery 64:297–307
Ryu S, Rock J, Rosenblum M et al (2004) Patterns of failure after single-dose radiosurgery for spinal metastasis. J Neurosurg 101:402–405
Yamada Y, Bilsky MH, Lovelock DM et al (2008) High-dose, single-fraction image-guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy for metastatic spinal lesions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71:484–490
Cox BW, Jackson A, Hunt M et al (2012) Esophageal toxicity from high-dose, single fraction paraspinal stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:e661–e662
Forquer JA, Fakiris AJ, Timmerman RD et al (2009) Brachial plexopathy from stereotactic body therapy in early stage NSCLC: dose-limiting toxicity in apical tumor sites. Radiother Oncol 93:408–413
Garg AK, Wang XS, Hiu AS et al (2011) Prospective evaluation of spinal reirradiation by using stereotactic body radiation therapy: the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center experience. Cancer 117:3509–3516
Grimm J, LaCouture T, Croce R et al (2012) Dose tolerance limits and dose volume histogram evaluation for stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 12:3368–3372
Gerszten P, Monaco E (2009) Complete percutaneous treatment of vertebral body tumors causing spinal compromise using transpedicular cavitation, cement augmentation, and radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 27:1–7
Gerszten P, Welch WC (2007) Combined percutaneous transpedicular tumor debulking and kyphoplasty for pathological compression fractures. Technical note. J Neurosurgical Spine 6:92–95
Rao PJ, Thayaparan GK, Fairhall JM et al (2014) Minimally invasive percutaneous fixation techniques for metastatic spinal disease. Orthop Surg 6(3):187–195
Rose PS, Laufer I, Boland PJ et al (2009) Risk of fracture after single fraction image-guided intensity-modulated radiation therapy to spinal metastases. J Clin Oncol 27:5075–5079
Boehling NS, Grosshans DR, Allen PK et al (2012) Vertebral compression fracture risk after stereotactic body radiotherapy for spinal metastases. J Neurosurg Spine 16(4):379–386
Cunha MVR, Al-Omair A, Atenafu EG et al (2012) Vertebral compression fracture (VCF) spine stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT): analysis of predictive factors. J Int Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:e343–e349
Sung SH, Chang UK (2014) Evaluation of risk factors for vertebral compression fracture after stereotactic radiosurgery in spinal tumor patients. Korean J Spine 11(3):103–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Germano, I.M., Carai, A., Pawha, P. et al. Clinical outcome of vertebral compression fracture after single fraction spine radiosurgery for spinal metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 33, 143–149 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9764-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9764-8