Abstract
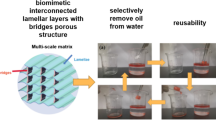
While cellulose nanofiber is advantageous for the preparation of porous materials with selective absorption, cellulose-based, hydrophilic-oleophobic aerogels are only prepared through complicated surface-modification. Herein, we report a facile one-pot fabrication of hydrophilic-oleophobic composite aerogels firstly through polycondensation of cellulose nanofiber and three silane coupling agents. The hydrophilic-oleophobic aerogels exhibited interconnected macroporous structures, robust compressive property (without failure at a high strain of 80%), excellent water resistance (without failure even at 100 °C, pH = 1 or pH = 12), the ability to selectively absorb water from oil–water mixtures, and excellent reusability (without significant decrease in hexadecane contact angle and absorption capacity after five absorption–regeneration cycles). The facile one-pot polycondensation and unique hydrophilicity-oleophobicity enabled the aerogels to be practical for removing water from oil–water mixtures.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen J et al (2017) Cellulose sponge with superhydrophilicity and high oleophobicity both in air and under water for efficient oil-water emulsion separation. Macromol Mater Eng 302:1700086
Cheng H, Gu B, Pennefather MP, Nguyen TX, Phan-Thien N, Duong HM (2017) Cotton aerogels and cotton-cellulose aerogels from environmental waste for oil spillage cleanup. Mater Des 130:452–458
Chhajed M, Yadav C, Agrawal AK, Maji PK (2019) Esterified superhydrophobic nanofibrillated cellulose based aerogel for oil spill treatment. Carbohydr Polym 226:115286
Chi H, Xu Z, Ma Y, Tang T, Zhang T, Zhao Y (2020) Multifunctional highly oleophobic and superhydrophilic fabric coatings prepared by facile photopolymerization. Adv Sustain Syst 4:2000049
Chu Z, Feng Y, Seeger S (2015) Oil/water separation with selective superantiwetting/superwetting surface materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:2328–2338
de Oliveira PB, Godinho M, Zattera AJ (2018) Oils sorption on hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogel obtained from the wood furniture industry waste. Cellulose 25:3105–3119
Durgadevi N, Swarnalatha V (2017) Polythiophene functionalized hydrophobic cellulose kitchen wipe sponge and cellulose fabric for effective oil–water separation. RSC Adv 7:34866–34874
He Z, Zhang X, Batchelor W (2016) Cellulose nanofibre aerogel filter with tuneable pore structure for oil/water separation and recovery. RSC Adv 6:21435–21438
He J, Zhao H, Li X, Su D, Zhang F, Ji H, Liu R (2018) Superelastic and superhydrophobic bacterial cellulose/silica aerogels with hierarchical cellular structure for oil absorption and recovery. J Hazard Mater 346:199–207
Huang H, Yu Y, Qing Y, Zhang X, Cui J, Wang H (2020) Ultralight industrial bamboo residue-derived holocellulose thermal insulation aerogels with hydrophobic and fire resistant properties. Materials 13:477
Ibrahim AS, Al-Salamah AA, El-Toni AM, Almaary KS, El-Tayeb MA, Elbadawi YB, Antranikian G (2016) Enhancement of alkaline protease activity and stability via covalent immobilization onto hollow core-mesoporous shell silica nanospheres. Int J Mol Sci 17:184
Laitinen O, Suopajärvi T, Österberg M, Liimatainen H (2017) Hydrophobic, superabsorbing aerogels from choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent pretreated and silylated cellulose nanofibrils for selective oil removal. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:25029–25037
Li Y, Zhang H, Fan M, Zhuang J, Chen L (2016) A robust salt-tolerant superoleophobic aerogel inspired by seaweed for efficient oil-water separation in marine environments. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:25394–25400
Li Y et al (2018a) Ester crosslinking enhanced hydrophilic cellulose nanofibrils aerogel. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:11979–11988
Li Z, Shao L, Hu W, Zheng T, Lu L, Cao Y, Chen Y (2018b) Excellent reusable chitosan/cellulose aerogel as an oil and organic solvent absorbent. Carbohydr Polym 191:183–190
Li Z, Zhong L, Zhang T, Qiu F, Yue X, Yang D (2019) Sustainable, flexible, and superhydrophobic functionalized cellulose aerogel for selective and versatile oil/water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:9984–9994
Lv Y, Li Q, Hou Y, Wang B, Zhang T (2019) Facile preparation of an asymmetric wettability janus cellulose membrane for switchable emulsions’ separation and antibacterial property. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:15002–15011
Ma Q, Cheng H, Fane AG, Wang R, Zhang H (2016) Recent development of advanced materials with special wettability for selective oil/water separation. Small 12:2186–2202
Mei Q, Tong B, Liang L, Lu M (2007) A novel way to prepare luminescent hybrid materials derived from 5-chloromehtyl-8-hydroxyquinoline and silylated monomer with coordination to aluminum ion. J Photoch Photobiol A 191:216–221
Rafieian F, Hosseini M, Jonoobi M, Yu Q (2018) Development of hydrophobic nanocellulose-based aerogel via chemical vapor deposition for oil separation for water treatment. Cellulose 25:4695–4710
Saleema N, Sarkar DK, Gallant D, Paynter RW, Chen XG (2011) Chemical nature of superhydrophobic aluminum alloy surfaces produced via a one-step process using fluoroalkyl-silane in a base medium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:4775–4581
Su C, Yang H, Song S, Lu B, Chen R (2017) A magnetic superhydrophilic/oleophobic sponge for continuous oil-water separation. Chem Eng J 309:366–373
Wang H, Chen Y, Dang B, Shen X, Jin C, Sun Q, Pei J (2018) Ultrafine Mn ferrite by anchoring in a cellulose framework for efficient toxic ions capture and fast water/oil separation. Carbohydr Polym 196:117–125
Xu Z, Zhao Y, Wang H, Wang X, Lin T (2015) A superamphiphobic coating with an ammonia-triggered transition to superhydrophilic and superoleophobic for oil-water separation. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:4527–4530
Xu Z, Zhou H, Tan S, Jiang X, Wu W, Shi J, Chen P (2018) Ultralight super-hydrophobic carbon aerogels based on cellulose nanofibers/poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide (CNFs/PVA/GO) for highly effective oil-water separation. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:508–519
Yang J, Xia Y, Xu P, Chen B (2018) Super-elastic and highly hydrophobic/superoleophilic sodium alginate/cellulose aerogel for oil/water separation. Cellulose 25:3533–3544
Zhang X, Wang H, Cai Z, Yan N, Liu M, Yu Y (2018) Highly compressible and hydrophobic anisotropic aerogels for selective oil/organic solvent absorption. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:332–340
Zhang T, Li X, Wang W, Xu Z, Zhao Y (2019a) Interface-initiated polymerization enables one-pot synthesis of hydrophilic and oleophobic foams through emulsion templating. Macromol Rapid Commun 40:1900288
Zhang X, Liu M, Wang H, Yan N, Cai Z, Yu Y (2019b) Ultralight, hydrophobic, anisotropic bamboo-derived cellulose nanofibrils aerogels with excellent shape recovery via freeze-casting. Carbohydr Polym 208:232–240
Zhou S, Liu P, Wang M, Zhao H, Yang J, Xu F (2016) Sustainable, reusable, and superhydrophobic aerogels from microfibrillated cellulose for highly effective oil/water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:6409–6416
Zhu Q, Chu Y, Wang Z, Chen N, Lin L, Liu F, Pan Q (2013) Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J Mater Chem A 1:5386–5393
Zhu Z, Fu S, Lucia LA (2019) A Fiber-aligned thermal-managed wood-based superhydrophobic aerogel for efficient oil recovery. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:16428–16439
Acknowledgements
Funding support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (51703149) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M651943) is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Zhang, T., Zhang, H. et al. One-pot fabrication of hydrophilic-oleophobic cellulose nanofiber-silane composite aerogels for selectively absorbing water from oil–water mixtures. Cellulose 28, 1443–1453 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03610-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03610-y