Abstract
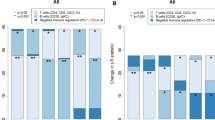
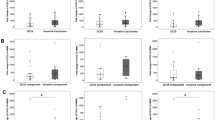
The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between expression of immune-related molecules such as STAT1, CD20, IL-8, IFN-γ, tumor genetic phenotype, and the clinical course of invasive breast cancer. We constructed tissue microarrays from the breast cancers of 727 patients and classified the cases as either luminal A, luminal B, HER-2, or triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) based on standard pathological and clinical classifications using genetic phenotype. Surrogate immunohistochemical stains (STAT1, CD20, IL-8, IFN-γ) and HER-2 FISH were performed on each microarray. Of the 727 patients cases, 303 (41.7 %) were luminal A, 169 (23.2 %) were luminal B, 71 (9.8 %) were HER2+, and 184 (25.3 %) were TNBC. The expression of STAT1 in tumor cells was higher in luminal-type cancers than in HER2+ and TNBC (P < 0.001), and the TNBC-type tumors showed the highest levels of stromal STAT1 expression (P < 0.001), stromal IL-8 expression (P = 0.005), and CD20 index (P < 0.001). Luminal A type tumors showed the lowest expression of these markers. The stromal IL-8 positivity was associated with shorter DFS and OS in ER positive group, HER-2 negative group, and luminal A group (P < 0.05). To conclude, the immune-related molecules, STAT1, IFN-γ, IL-8, and CD20 are differentially expressed and define particular molecular subtypes which correlate with genetically defined types of tumors. High expression of STAT1 in tumor cells is observed in luminal-type tumors, whereas stromal expression of STAT1, stromal IL-8, and IL-8 in tumor cells is the highest in TNBC-type tumors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752. doi:10.1038/35021093
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Eystein Lonning P, Borresen-Dale AL (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10869–10874. doi:10.1073/pnas.191367098
Desmedt C, Haibe-Kains B, Wirapati P, Buyse M, Larsimont D, Bontempi G, Delorenzi M, Piccart M, Sotiriou C (2008) Biological processes associated with breast cancer clinical outcome depend on the molecular subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 14:5158–5165. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-07-4756
Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD (2002) Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat Immunol 3:991–998. doi:10.1038/ni1102-991
Huang E, Cheng SH, Dressman H, Pittman J, Tsou MH, Horng CF, Bild A, Iversen ES, Liao M, Chen CM, West M, Nevins JR, Huang AT (2003) Gene expression predictors of breast cancer outcomes. Lancet 361:1590–1596. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(03)13308-9
Perou CM, Jeffrey SS, van de Rijn M, Rees CA, Eisen MB, Ross DT, Pergamenschikov A, Williams CF, Zhu SX, Lee JC, Lashkari D, Shalon D, Brown PO, Botstein D (1999) Distinctive gene expression patterns in human mammary epithelial cells and breast cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:9212–9217
Ihle JN (1996) STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell 84:331–334
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR (1994) Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264:1415–1421
Rody A, Karn T, Liedtke C, Pusztai L, Ruckhaeberle E, Hanker L, Gaetje R, Solbach C, Ahr A, Metzler D, Schmidt M, Muller V, Holtrich U, Kaufmann M (2011) A clinically relevant gene signature in triple negative and basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 13:R97. doi:10.1186/bcr3035
Ning Y, Manegold PC, Hong YK, Zhang W, Pohl A, Lurje G, Winder T, Yang D, LaBonte MJ, Wilson PM, Ladner RD, Lenz HJ (2011) Interleukin-8 is associated with proliferation, migration, angiogenesis and chemosensitivity in vitro and in vivo in colon cancer cell line models. Int J Cancer 128:2038–2049. doi:10.1002/ijc.25562
Alexe G, Dalgin GS, Scanfeld D, Tamayo P, Mesirov JP, DeLisi C, Harris L, Barnard N, Martel M, Levine AJ, Ganesan S, Bhanot G (2007) High expression of lymphocyte-associated genes in node-negative HER2+ breast cancers correlates with lower recurrence rates. Cancer Res 67:10669–10676. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-07-0539
Bertucci F, Finetti P, Cervera N, Charafe-Jauffret E, Mamessier E, Adelaide J, Debono S, Houvenaeghel G, Maraninchi D, Viens P, Charpin C, Jacquemier J, Birnbaum D (2006) Gene expression profiling shows medullary breast cancer is a subgroup of basal breast cancers. Cancer Res 66:4636–4644. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-06-0031
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Monville F, Finetti P, Adelaide J, Cervera N, Fekairi S, Xerri L, Jacquemier J, Birnbaum D, Bertucci F (2006) Gene expression profiling of breast cell lines identifies potential new basal markers. Oncogene 25:2273–2284. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209254
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, Fitzgibbons PL, Francis G, Goldstein NS, Hayes M, Hicks DG, Lester S, Love R, Mangu PB, McShane L, Miller K, Osborne CK, Paik S, Perlmutter J, Rhodes A, Sasano H, Schwartz JN, Sweep FC, Taube S, Torlakovic EE, Valenstein P, Viale G, Visscher D, Wheeler T, Williams RB, Wittliff JL, Wolff AC (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:2784–2795. doi:10.1200/jco.2009.25.6529
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, Dowsett M, Fitzgibbons PL, Hanna WM, Langer A, McShane LM, Paik S, Pegram MD, Perez EA, Press MF, Rhodes A, Sturgeon C, Taube SE, Tubbs R, Vance GH, van de Vijver M, Wheeler TM, Hayes DF (2007) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:118–145. doi:10.1200/jco.2006.09.2775
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ (2011) Strategies for subtypes–dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol 22:1736–1747. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr304
Muthuswamy SK, Muller WJ (1995) Direct and specific interaction of c-Src with Neu is involved in signaling by the epidermal growth factor receptor. Oncogene 11:271–279
Reissig D, Clement J, Sanger J, Berndt A, Kosmehl H, Bohmer FD (2001) Elevated activity and expression of Src-family kinases in human breast carcinoma tissue versus matched non-tumor tissue. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 127:226–230
Sheen-Chen SM, Huang CC, Tang RP, Yang CH, Chou FF, Eng HL (2007) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 in breast cancer: analysis with tissue microarray. Anticancer Res 27:2481–2486
Englert NA, Spink BC, Spink DC (2011) Persistent and non-persistent changes in gene expression result from long-term estrogen exposure of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 123:140–150. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.12.010
Teschendorff AE, Miremadi A, Pinder SE, Ellis IO, Caldas C (2007) An immune response gene expression module identifies a good prognosis subtype in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer. Genome Biol 8:R157. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-8-r157
Irshad S, Ellis P, Tutt A (2011) Molecular heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancer and its clinical implications. Curr Opin Oncol 23:566–577. doi:10.1097/CCO.0b013e32834bf8ae
Rody A, Holtrich U, Pusztai L, Liedtke C, Gaetje R, Ruckhaeberle E, Solbach C, Hanker L, Ahr A, Metzler D, Engels K, Karn T, Kaufmann M (2009) T-cell metagene predicts a favorable prognosis in estrogen receptor-negative and HER2-positive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res 11:R15. doi:10.1186/bcr2234
Zuccari DA, Leonel C, Castro R, Gelaleti GB, Jardim BV, Moscheta MG, Regiani VR, Ferreira LC, Lopes JR, Neto Dde S, Esteves JL (2012) An immunohistochemical study of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in breast cancer. Acta Histochem 114:571–576. doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2011.10.007
Yao C, Wang SM, Xie D, Wu HX, Chen DY, Lin Y (2006) The relationship between expression of interleukin-8 and prognosis of breast cancer. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 44:900–903
Waugh DJ, Wilson C (2008) The interleukin-8 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:6735–6741. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-07-4843
Yoshimura T, Matsushima K, Oppenheim JJ, Leonard EJ (1987) Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes: partial characterization and separation from interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol 139:788–793
Chen Y, Chen L, Li JY, Mukaida N, Wang Q, Yang C, Yin WJ, Zeng XH, Jin W, Shao ZM (2011) ERbeta and PEA3 co-activate IL-8 expression and promote the invasion of breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 11:497–511
Ju D, Sun D, Xiu L, Meng X, Zhang C, Wei P (2012) Interleukin-8 is associated with adhesion, migration and invasion in human gastric cancer SCG-7901 cells. Med Oncol 29:91–99. doi:10.1007/s12032-010-9780-0
Lin Y, Wang SM, Lu WM, Huang RP (2005) Effect of interleukin-8 in cell invasion and proliferation of human breast cancer. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 43:1541–1544
Welte G, Alt E, Devarajan E, Krishnappa S, Jotzu C, Song YH (2011) Interleukin-8 derived from local tissue-resident stromal cells promotes tumor cell invasion. Mol Carcinog. doi:10.1002/mc.20854
Turkson J (2004) STAT proteins as novel targets for cancer drug discovery. Expert Opin Ther Targets 8:409–422. doi:10.1517/14728222.8.5.409
Ginestier C, Liu S, Diebel ME, Korkaya H, Luo M, Brown M, Wicinski J, Cabaud O, Charafe-Jauffret E, Birnbaum D, Guan JL, Dontu G, Wicha MS (2010) CXCR1 blockade selectively targets human breast cancer stem cells in vitro and in xenografts. J Clin Invest 120:485–497. doi:10.1172/jci39397
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012R1A1A1002886).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J., Kim, D.H., Jung, W.H. et al. Differential expression of immune-related markers in breast cancer by molecular phenotypes. Breast Cancer Res Treat 137, 417–429 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2383-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2383-z