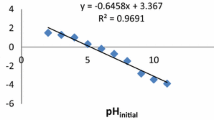
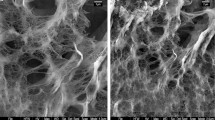
Abstract
The biosorption equilibrium isotherms of Ni(II) onto marine brown algae Lobophora variegata, which was chemically-modified by CaCl2 were studied and modeled. To predict the biosorption isotherms and to determine the characteristic parameters for process design, twenty-three one-, two-, three-, four- and five-parameter isotherm models were applied to experimental data. The interaction among biosorbed molecules is attractive and biosorption is carried out on energetically different sites and is an endothermic process. The five-parameter Fritz–Schluender model gives the most accurate fit with high regression coefficient, R 2 (0.9911–0.9975) and F-ratio (118.03–179.96), and low standard error, SE (0.0902–0.0.1556) and the residual or sum of square error, SSE (0.0012–0.1789) values to all experimental data in comparison to other models. The biosorption isotherm models fitted the experimental data in the order: Fritz–Schluender (five-parameter) > Freundlich (two-parameter) > Langmuir (two-parameter) > Khan (three-parameter) > Fritz–Schluender (four-parameter). The thermodynamic parameters such as ΔG 0, ΔH 0 and ΔS 0 have been determined, which indicates the sorption of Ni(II) onto L. variegata was spontaneous and endothermic in nature.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Constant in linear with intercept isotherm model
- a K :
-
Khan model exponent
- a R :
-
Radke-Prausnitz isotherm constant
- a RP :
-
Redlich-Peterson model constant (l mg−1)
- a S :
-
Sips isotherm constant
- A :
-
Fritz-Schluender four-parameter model constant
- A HJ :
-
Harkins–Jura model constant
- A KC :
-
Koble-Carrigan isotherm constant
- B :
-
Constant in linear with intercept isotherm model
- b K :
-
Khan isotherm constant
- b T :
-
Toth isotherm constant
- b Te :
-
Constant in Temkin sorption isotherm (J mol−1)
- B :
-
Constant in Dubinin-Radushkevich sorption model (mol2 kJ−2)
- B FS :
-
Constant in Fritz-Schluender four-parameter model
- B KC :
-
Koble-Carrigan isotherm constant
- C e :
-
Equilibrium concentration of sorbate in solution (mg l−1)
- E :
-
Polanyi potential (kJ mol−1)
- F :
-
Frukin model constant
- K F :
-
Freundlich isotherm constant (l g−1)
- K FG :
-
Fowler–Guggenheim equilibrium constant (l mg−1)
- K HE :
-
Henry’s law constant (l g−1)
- K L :
-
Langmuir isotherm equilibrium binding constant (l mg−1)
- K RP :
-
Redlich-Peterson isotherm constant (l g−1)
- K S :
-
Sips isotherm constant (l g−1)
- K T :
-
Temkin isotherm constant (l mg−1)
- M :
-
Number of experimental data points
- N :
-
Exponent in Freundlich isotherm
- n H :
-
Halsey isotherm constant
- n KC :
-
Koble-Carrigan model exponent
- n T :
-
Toth isotherm constant
- p :
-
Number of parameters in the sorption isotherm
- q e :
-
Amount of sorbate sorbed at equilibrium (mg g−1)
- q i :
-
Observed sorption capacity of batch experiment i
- q m :
-
Maximum sorption capacity (mg g−1)
- q t :
-
Amount of sorbate sorbed at time t (mg g−1)
- Q i :
-
Estimated sorption capacity of batch experiment i
- r R :
-
Radke-Prausnitz isotherm constant
- R :
-
Universal gas constant, 8.314 J mol−1 K−1
- R 2 :
-
Correlation coefficient
- R L :
-
Langmuir separation factor
- SE:
-
Standard error
- SSE:
-
Sum of squares error
- W FG :
-
The interaction energy between adsorbed molecules (kJ mol−1)
- Α :
-
Radke-Prausnitz isotherm constant
- α1 :
-
Fritz-Schluender five-parameter model sorption capacity (mg g−1)
- \( \alpha_{1}^{\prime } \) :
-
Fritz-Schluender five-parameter model constant
- α2 :
-
Fritz-Schluender five-parameter model constant
- αFS :
-
Fritz-Schluender four-parameter model exponent
- β:
-
Redlich-Peterson isotherm constant
- β1 :
-
Fritz-Schluender five-parameter model exponent
- β2 :
-
Fritz-Schluender five-parameter model exponent
- βFS :
-
Fritz-Schluender four-parameter model exponent
- γ:
-
Sips model exponent
- θ:
-
Surface coverage
- ΔG 0 :
-
Gibbs free energy change (kJ mol−1)
- ∆H 0 :
-
Enthalpy change (kJ mol−1)
- ∆S 0 :
-
Entropy change (kJ mol−1 K−1)
References
Ajmal M, Rao RAK, Ahmad R, Ahmad J (2000) Adsorption studies on citrus reticulate (fruit peel of orange): removal and recovery of Ni(II) from electroplating waste water. J Hazard Mater 79:17–131
Aksu Z (2001) Biosorption of reactive dyes by dried activated sludge: equilibrium and kinetic modelling. Biochem Eng J 7:79–84
Aksu A (2002) Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the batch biosorption of nickel(II) ions onto Chlorella. Process Biochem 38:89–99
Aksu Z, Kutsal TA (1991) Bioseparation process for removing lead(II) ions from waste water by using C. vulgaris. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 52:109–118
Basar CA (2006) Applicability of the various adsorption models of three dyes adsorption onto activated carbon prepared waste apricot. J Hazard Mater 135:232–241
Baudu M (1990) Etude des interactions solute-fibres de charbon actif. Application et regeneration, Ph. D. Thesis, Universite de Rennes I
Bhattacharyya D, Cheng CYR (1987) Activated carbon adsorption of heavy metals from single and multi-component systems. Environ Prog 6:110–118
Carrilho EN, Gilbert TR (2000) Assessing metal sorption on the marine algae Pilayella littoralis. J Environ Mon 2:410–415
Chen SG, Yang RT (1994) Theoretical basis for the potential theory adsorption isotherms. The Dubinin–Radushkevich and Dubinin–Astakhov equations. Langmuir 10:4244–4249
Chen Z, Ma W, Han M (2008) Biosorption of nickel and copper onto treated alga (Undaria pinnatifida): application of isotherm and kinetic models. J Hazard Mater 155:327–333
Chubar N, Carvalho JR, Correia MJN (2003) Cork biomass as biosorbent for Cu(II), Zn(II) and Ni(II). Colloid Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 230:57–65
Davis TA, Volesky B, Mucci A (2003) A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res 37:4311–4330
Dean JG, Bosqui FL, Lanouette KH (1972) Removing heavy metals from wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 6:518–522
Deng S, Ting Y-P (2005) Characterization of PEI-modified biomass and biosorption of Cu(II), Pb(II) and Ni(II). Water Res 39:2167–2177
Denkhaus E, Salniknow K (2002) Nickel essentiality toxicity, and carcinogenicity. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol 42:35–56
Donmez G, Aksu Z, Ozturk A, Kutsal T (1999) A comparative study on heavy metal biosorption characteristics of some algae. Process Biochem 34:885–892
Dubinin MM (1960) The potential theory of adsorption of gases and vapors for adsorbents with energetically non-uniform surface. Chem Rev 60:235–266
Eckenfelder WW (1989) Industrial water pollution control, 2nd edn. McGraw Hill, Singapore, pp 356–366
Elovich SY, Larinov OG (1962) Theory of adsorption from solutions of non electrolytes on solid (I) equation adsorption from solutions and the analysis of its simplest form (II) verification of the equation of adsorption isotherm from solutions. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Otd Khim Nauk 2:209–216
EPA (Environment Protection Agency) (1981) Control and treatment technology for the metal finishing industry—ion exchange USEPA EPA 625/-81-00, pp 4–10
Faust SD, Aly OM (1987) Adsorption processes for water treatment. Butterworth, Stoneham, pp 1–23
Fowler RH, Guggenheim EA (1939) Statistical thermodynamics. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 431–450
Freundlich HMF (1906) Uber die adsorption in lasugen. Z Phys Chem (Leipzig) 57:385–470
Fritz W, Schluender EU (1974) Simultaneous adsorption equilibria of organic solutes in dilute aqueous solution on activated carbon. Ceram Eng Sci Proc 29:1279–1282
Guo X, Zhang S, Shan X (2008) Adsorption of metal ions on lignin. J Hazard Mater 151:134–142
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Gajbe V (2005) Adsorption and desorption studies of a water soluble dye. Quinoline yellow, using waste materials. J Colloid Interf Sci 284:89–98
Ho YS (2004) Selection of optimum sorption isotherm. Carbon 42:2115–2116
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem Eng J 70:115–124
Holan ZR, Volesky B (1994) Biosorption of lead and nickel by biomass of marine algae. Biotechnol Bioeng 43:1001–1009
Kalyani S, Rao PS, Krishnaiah A (2004) Removal of Ni(II) from aqueous solutions using marine macroalgae as the sorbing biomass. Chemosphere 57:1225–1229
Khan AR, Ataullah R, Al-Haddad A (1997) Equilibrium adsorption studies of some aromatic pollutants from dilute aqueous solutions on activated carbon at different temperatures. J Colloid Interf Sci 194:154–165
Klimmek S, Stan HJ, Wilke A, Bunke G, Buchholz R (2001) Comparative analysis of the biosorption of cadmium, lead, nickel and zinc by algae. Environ Sci Technol 35:4283–4288
Koble RA, Carrigan TE (1952) Adsorption isotherms for pure hydrocarbons. Ind Eng Chem 44:383–387
Krishnani K, Meng X, Christodoulatos C, Boddu VM (2008) Biosorption mechanism of nine different heavy metals onto biomatrix from rice husk. J Hazard Mater 153:1222–1234
Kundu S, Gupta AK (2006) Arsenic adsorption onto iron oxide-coated cement (IOCC): regression analysis of equilibrium data with several isotherm models and their optimization. Chem Eng J 122:93–106
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295
Lau PS, Lee HY, Tsang CCK, Tam NFY, Wong YS (1999) Effect of metal interference, pH and temperature on Cu and Ni biosorption by Chlorella vulgaris and Chlorella miniata. Environ Technol 20:953–961
Lesage E, Mundia C, Rousseau DPL, Van de Moortel AMK, Du Laing G, Meers E, Tack FMG, De Pauw N, Verloo MG (2007) Sorption of Co, Cu, Ni and Zn from industrial effluents by the submerged aquatic macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum L. Ecol Eng 30:320–325
Leusch H, Volesky B (1995) Biosorption of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) by chemically reinforced biomass of marine algae. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 62:279–288
Malek A, Farooq S (1996) Comparison of isotherm models for hydrocarbon adsorption on activated carbon. AIChE J 42:3191–3201
Matheickal JT, Yu Q, Woodburn GM (1999) Biosorption of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by pre-treated biomass of marine algae Durvillaea potatorum. Water Res 33:335–342
Maurya NS, Mittal AK (2006) Applicability of equilibrium isotherm models for the biosorptive uptakes in comparison to activated carbon-based adsorption. J Environ Eng ASCE 132:1589–1599
McAnally SL, Benefield T, Reed RB (1984) Nickel removal from a synthetic nickel plating wastewater using sulphide and carbonate for precipitation and coprecipitation. Sep Sci Technol 19:191–217
Mehta SK, Gaur JP (2001) Characterization and optimization of Ni and Cu sorption from aqueous solution by Chlorella vulgaris. Ecol Eng 18:1–13
Nilsson R (1971) Removal of metals by chemical treatment of municipal wastewater. Water Res 5:51–61
O’Brien JA, Myers AL (1984) Physical adsorption of gases on heterogeneous surfaces series expansion of isotherms using central moments of the adsorption energy distribution. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 1(80):1467–1477
Ofer R, Yerachmiel A, Shmuel Y (2003) Marine macro algae as biosorbent for cadmium and nickel in water. Water Environ Res 75:246–253
Ozcan A, Oncu AE, Ozcan AS (2006) Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of acid blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto natural sepiolite. Coll Surf A 277:90–97
Ozer A, Gürbuz G, Çalimli A, Korbahti BK (2008) Investigation of nickel(II) biosorption on Enteromorpha prolifera: optimization using response surface analysis. J Hazard Mater 152:778–788
Peryasamy K, Namasivayam C (1995) Removal of nickel (II) from aqueous solution and nickel plating industry wastewater using an agricultural waste: peanut hulls. Waste Manag 15:63–68
Qi BC, Aldrich C (2008) Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions with tobacco dust. Bioresour Technol 99:5595–5601
Radke CJ, Prausnitz JM (1972) Adsorption of organic solutes from dilute aqueous solution of activated carbon. Ind Eng Chem Fund 11:445–451
Redlich O, Peterson DL (1959) A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem 63:1024–1026
Rengaraj S, Yeon J-W, Kim Y, Kim W-H (2007) Application of Mg-mesoporous alumina prepared by using magnesium stearate as a template for the removal of nickel: kinetics, isotherm, and error analysis. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:2834–2842
Sag Y, Aktay YA (2002) Comparative study for the sorption of Cu(II) ions by chitin and chitosan: application of equilibrium and mass transfer models. Sep Sci Technol 37:2801–2822
Sanchez A, Ballester A, Blazquez ML, Gonzalez F, Munoz J, Hammaini A (1999) Biosorption of copper and zinc by Cymodocea nodosa. FEMS Microbiol Rev 23:527–536
Sandau E, Sandau P, Pulz O (1996) Heavy metal sorption by microalgae. Acta Biotechnol 16:227–235
Saygideger S, Gulnaz O, Istifli ES, Yucel N (2005) Adsorption of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions by Lemna minor L.: effect of physicochemical environment. J Hazard Mater 126:96–104
Sekar M, Sakthi V, Rengaraj S (2004) Kinetics and equilibrium adsorption study of lead(II) onto activated carbon prepared from coconut shell. J Colloid Interf Sci 279:307–313
Sen Gupta B, Curran M, Hasan S, Ghosh TK (2009) Adsorption characteristics of Cu and Ni on Irish peat moss. J Environ Manag 90:954–960
Sheng PX, Ting YP, Chen JP, Hong L (2004) Sorption of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel by marine algal biomass: characterization of biosorption capacity and investigation of mechanisms. J Colloid Interf Sci 275:131–141
Sips R (1948) Structure of a catalyst surface. J Chem Phys 16:490–495
Temkin MJ, Pyzhev V (1940) Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta Physicochim URSS 12:217–225
Toth J (2000) Calculation of the BET-compatible surface area from any type I isotherms measured above the critical temperature. J Colloid Interf Sci 225:378–383
Tsezos M, Volesky B (1984) Recovery of uranium from biological adsorbents-desorption equilibrium. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:973–981
Tsui MTK, Cheung KC, Tam NFY, Wong MH (2006) A comparative study on metal sorption by brown seaweed. Chemosphere 65:51–57
Vadivelan K, Kumar VK (2005) Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J Collids Interf Sci 286:90–100
Vasconcelos HL, Favere VT, Gonçalves NS, Laranjeira MCM (2007) Chitosan modified with reactive blue 2 dye on adsorption equilibrium of Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions. React Functional Polym 67:1052–1060
Vijayaraghavan K, Jegan J, Palanivelu K, Velan M (2005) Biosorption of cobalt(II) and nickel(II) by seaweeds: batch and column studies. Sep Purif Technol 44:53–59
Vijayaraghavan K, Palanivelu K, Velan M (2006a) Treatment of nickel containing electroplating effluents with Sargassum wightii biomass. Process Biochem 41:853–859
Vijayaraghavan K, Padmesh TVN, Palanivelu K, Velan M (2006b) Biosorption of nickel(II) ions onto Sargassum wightii: application of two-parameter and three-parameter isotherm models. J Hazard Mater 133:304–308
Volesky B (1990) Biosorption of heavy metals. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton
Volesky B, Holan ZR (1995) Biosorption of heavy metals. Biotechnol Prog 11:235–250
Wang TC, Weissman JC, Ramesh G, Varadarajan R, Benemann JR (1996) Parameters for removal of toxic heavy metals by water milfoil (Myriophyllum spicatum). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 57:779–786
Wong JPK, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2000) Nickel biosorption by two Chlorella species, C. vulgaris (a commercial species) and C. miniata (a local isolate). Bioresour Technol 7:133–137
Xue B, Tong D, Sun Y (2001) Characterization of PVA-based magnetic affinity support for protein adsorption. Sep Sci Technol 36:2449–2461
Yang RT, Doong SJ (1985) Gas separation by pressure swing adsorption: a pore diffusion model for bulk separation. AIChE J 31:1829–1842
Yu O, Kaewsarn P (2000) Adsorption of Ni2+ from aqueous solutions by pretreated biomass of marine macroalga Durvillaea potatorum. Sep Sci Technol 35:689–701
Zafar MN, Nadeem R, Hanif MA (2007) Biosorptions of nickel from protonated rice bran. J Hazard Mater 143:478–485
Acknowledgments
The financial support received from CSIR (NWP 018) and from MoES to carry out the study is thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basha, S., Jaiswar, S. & Jha, B. On the biosorption, by brown seaweed, Lobophora variegata, of Ni(II) from aqueous solutions: equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Biodegradation 21, 661–680 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9333-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9333-4