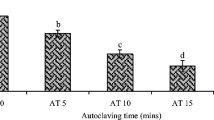
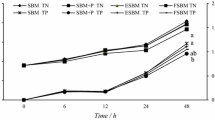
Abstract
Rainbow trout were fed a diet containing phytase-sprayed and phytase-pretreated soybean meal with different phytase levels. The single factor random block design was used to analyze the effects on rainbow trout of dietary phytase supplementation on growth performance, nutritional ingredient digestibility and nutrient excretion. After 90 days, the results showed that feed conversion ratio (FCR) and protein efficiency ratio (PER) were significantly improved and specific growth rate (SGR) was not affected by spraying phytase, but SGR, FCR and PER were not significantly improved by phytase pretreatment. A digestibility trial conducted after the feeding trial showed that apparent digestibility coefficient (ADC) of diet protein and minerals was increased with phytase supplementation. However, there was a negative effect of phytase on the ADC of lipid. The excretion experiment showed that the supplementation of phytase resulted in decreased nutrient excretion in feces, but lipid excretion was slightly increased with phytase supplementation. In addition, the results of P excretion and ADC of P analyzed by t-test showed that phytase pre-treatment method should be a more rational method than the spraying method. The results of SGR, ADC of P and P excretion analyzed by quadratic regression indicated that 2,000–3,000 U/kg levels by the spraying method could be a rational range of phytase supplementation, and about 1,000 U/kg should be an optimal level by the pretreatment method. Thus, use of phytase in rainbow trout feeds can have economic and environmental benefits.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- ADC:
-
Apparent digestibility coefficient
- SGR:
-
Specific growth rate
- FCR:
-
Feed conversion ratio
- PER:
-
Protein efficiency ratio
References
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International, 15th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International, 16th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington
Bergheim A, Aabel JP, Seymour EA (1991) Past and present approaches to aquaculture waste management in Norwegian net pen culture operations. In: Cowey CB, Cho CY (eds) Nutritional strategies and aquaculture waste. Proceedings of the first international symposium on nutritional strategies in management of aquaculture waste, 2–6 June 1990, Guelph, Canada. University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada, pp 117–136
Brown PB (1993) Comparison of fecal collection methods for determining P absorption in rainbow trout. In: Kaushik SJ, Luquet P (eds) Fish nutrition in practice, Biarritz (France), June 24–27, 1991. Ed. INRA, Paris 1993 (Les Colloques, no. 61), pp 443–447
Cain KD, Garling DL (1995) Pretreatment of soybean meal with phytase for salmonid diets to reduce P concentrations in hatchery effluents. Prog Fish-Cult 57:114–119
Cheng ZJ, Hardy RW (2002) Effect of microbial phytase on apparent nutrient digestibility of barley, canola meal, wheat and wheat middlings, measured in vivo using rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac Nutr 8:271–277
Cheng ZJ, Hardy RW (2003) Effects of extrusion and expelling processing, and microbial phytase supplementation on apparent digestibility coefficients of nutrients in full-fat soybeans for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 218:501–514
Cheryan M (1980) Phytic acid interactions in food systems. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 13:297–335
Fontainhas-Femandes A, Gomes E, Reis-Henriques MA, Coimbra J (1999) Replacement of fish meal by plant protein in the diet of Nile tilapia: digestibility and growth performance. Aquac Int 7:57–67
Forster I, Higgs DA, Dosanjh BS, Rowshandeli M, Parr J (1999) Potential for dietary phytase to improve the nutritive value of canola protein concentrate and decrease P output in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) held in 11°C fresh water. Aquaculture 179:109–125
Francis G, Makkar HPS, Becker K (2001) Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate ash feed ingredients and their effects in ash. Aquaculture 99:197–227
Helland SJ, Grisdale-Helland B, Nerland S (1996) A simple method for the measurement of daily feed intake of groups of fish in tanks. Aquaculture 139:157–163
Jackson LS, Li MH, Robinson EH (1996) Use of microbial phytase in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) diets to improve utilization of phytate P. J World Aquac Soc 27:309–313
Jahan P, Watanabe T, Kiron V, Satoh S (2003) Improved carp diets based on plant protein sources reduce environmental P loading. Fish Sci 69:219–225
Lall SP (1991) Digestibility, metabolism and excretion of dietary P in fish. In: Cowey CB, Cho CY (eds) Nutritional strategies and aquaculture waste. Proceedings of the first international symposium on nutritional strategies in management of aquaculture waste. University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada, pp 21–36
Lall SP (2002) The minerals. In: Halver JE, Hardy RW (eds) Fish nutrition. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 259–308
Lanari D, D’Agaro E, Turri C (1998) Use of nonlinear regression to evaluate the effects of phytase enzyme treatment of plant protein diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 161:345–356
Liu BL, Rafing A, Tzeng YM, Rob A (1998) The induction and characterization of phytase and beyond. Enzyme Microb Technol 22:415–424
Mabahinzireki GB, Dabrowski K, Lee KJ, EI-Saidy D, Wisner ER (2001) Growth, fed utilization and body composition of tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) fed with cottonseed meal-based diets in a recirculating system. Aquac Nutr 7:189–200
Masumoto T, Tamura B, Shimeno S (2001) Effects of phytase on bioavailability of P in soybean meal-based diets for Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Sci 67:1075–1080
National Research Council (1993) Nutrient requirements of fish. National Academic Press, Washington, DC
Oliva-Teles A, Pereira JP, Gouveia A, Gomes E (1998) Utilization of diets supplemented with microbial phytase by seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Aquat Living Resour 11:255–259
Papatryphon E, Howell RA, Soares JH Jr (1999) Growth and mineral absorption by striped bass (Morone saxatilis) fed a plant feedstuff based diet supplemented with phytase. J World Aquac Soc 30:161–173
Papatryphon E, Soares JH Jr (2001) The effect of phytase on apparent digestibility of four practical plant feedstuffs fed to striped bass (Morone saxatilis). Aquac Nutr 7:161–167
Powers Hughes K, Soares JH Jr (1998) Efficacy of phytase on P utilization in practical diets fed to striped bass (Morone saxatilis). Aquac Nutr 4:133–140
Riche M, Brown PB (1996) Availability of P from feedstuffs fed to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 142:269–282
Rodehutscord M (1996) Response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) growing from 50 to 200 g to supplements of dibasic sodium phosphate in a purified diet. J Nutr 126:324–331
Rodehutscord M, Pfeffer E (1995) Effects of supplemental microbial phytase on P digestibility and utilization in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Water Sci Technol 31:143–147
Sajjadi M, Carter CG (2004) Dietary phytase supplementation and the utilization of P by Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fed a canola-meal-based diet. Aquaculture 240:417–431
Schaefer A, Koppe WM, Meyer-Burgdorff KH, Gunther KD (1995) Effects of microbial phytase on utilization of native P by carp in a diet based on soybean meal. Water Sci Technol 31:149–155
Singh M, Krikorian AD (1982) Inhibition of trypsin activity in vitro by phytate. J Agric Food Chem 30:799–800
Slominski BA, Davie T, Nyachoti MC, Jones O (2007) Heat stability of endogenous and microbial phytase during feed pelleting. Livest Sci 109:244–246
Snedecor GW, Concbran WG (1978) Statistical methods, 6th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames
Spinelli J, Houle CR, Wekell JC (1983) The effect of phytates on the growth of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) fed purified diets containing varying quantities of Ca and Mg. Aquaculture 30:71–83
Storebakken T, Shearer KD, Roem AJ (1998) Availability of protein, P and other elements in fish meal, soy-protein concentrate and phytase-treated soy-protein-concentrate-based diets to Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 161:365–379
Sugiura SH, Dong FM, Hardy RW (1998) Effects of dietary supplements on the availability of minerals in fish meal; preliminary observations. Aquaculture 160:283–303
Sugiura SH, Gabaudan J, Dong FM, Hardy RW (2001) Dietary microbial phytase supplementation and the utilization of P, trace minerals and protein by rainbow trout [Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum)] fed soybean meal-based diets. Aquac Res 32:583–592
Teskeredzic Z, Higgs DA, Dosanjh BS, McBride JR, Hardy RW, Beames RM, Simell M, Vaara T, Bridges RB (1995) Assessment of unphytinized and dephytinized rapeseed protein concentrate as sources of dietary protein for juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 131:261–277
Vielma J, Lall SP, Koskela J, Schoner FJ, Mattila P (1998) Effects of dietary phytase and cholecalciferol on P bioavailability in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 163:309–323
Vielma J, Mäkinen T, Ekholm P, Koskela J (2000) Influence of dietary soy and phytase levels on performance and body composition of large rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and algal availability of P load. Aquaculture 183:349–362
Vielma J, Ruohonen K, Peisker M (2002) Dephytinization of two soy proteins increases P and protein utilization by rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 204:145–156
Vielma J, Ruohonen K, Gabaudan J, Vogel K (2004) Top-spraying soybean meal-based diets with phytase improves protein and mineral digestibilities but not lysine utilization in rainbow trout [Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum)]. Aquac Res 35:955–964
Wise A (1983) Dietary factors determining the biological activities of phytate. Nutr Abs Rev 53:791–807
Yan W, Reigh R, Xu Z (2002) Effects of fungal phytase on utilization of dietary protein and minerals, and dephosphorylation of phytic acid in the alimentary tract of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) fed an all-plant-protein diet. J World Aquac Soc 33:10–22
Yoo GY, Wang X, Choi S, Han K, Kang JC, Bai SC (2005) Dietary microbial phytase increased the P digestibility in juvenile Korean rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli) fed diets containing soybean meal. Aquaculture 243:315–322
Acknowledgements
The place of study was supported by Harbin Academy of Agricultural Sciences Fisheries Research Institute and the experiment was financially supported by grant # 2005AA6CN183 from Harbin Science and Technology Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Yang, YH., Han, ZZ. et al. Effects of phytase pretreatment of soybean meal and phytase-sprayed in diets on growth, apparent digestibility coefficient and nutrient excretion of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Aquacult Int 17, 143–157 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-008-9187-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-008-9187-5