Abstract
Purpose
To examine the effects of SRT2104, an SIRT1 activator, in optic nerve degeneration induced by TNF and to investigate whether it affects the autophagic status after induction of axonal degeneration.
Study design
Experimental.
Methods
Adult male Wistar rats received intravitreal injection of TNF alone, concomitant injection of SRT2104 and TNF, or injection of SRT2104 alone. The autophagic status in the optic nerve was evaluated to examine p62 and LC3-II expression by immunoblot analysis. The effect of SRT2104 on TNF-induced axon loss was determined by counting the number of axons.
Results
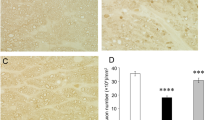
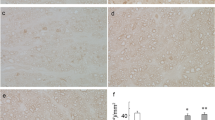
Intravitreal injection of SRT2104 showed a modest protective tendency in the 2-pmol-treated groups against TNF-induced axon loss, although the tendency was not significant on quantitative analysis. However, significant protective effects were found in the 20- or 200-pmol-treated groups. Injection of SRT2104 alone significantly decreased the p62 levels and increased the LC3-II levels as compared with the basal levels. Similarly, concomitant injection of SRT2104 and TNF significantly decreased the p62 levels and increased the LC3-II levels as compared with the TNF-treated group. Upregulation of SIRT1 expression was observed in the optic nerve after SRT2104 treatment.
Conclusion
The SIRT1 activator SRT2104 exerts axonal protection in TNF-induced optic nerve degeneration. This effect may be associated with upregulated autophagic status in the optic nerve.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menzies KJ, Singh K, Saleem A, Hood DA. Sirtuin 1-mediated effects of exercise and resveratrol on mitochondrial biogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:6968–79.
Shindler KS, Ventura E, Rex TS, Elliott P, Rostami A. SIRT1 activation confers neuroprotection in experimental optic neuritis. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:3602–9.
Zuo L, Khan RS, Lee V, Dine K, Wu W, Shindler KS. SIRT1 promotes RGC survival and delays loss of function following optic nerve crush. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54:5097–102.
Khan RS, Dine K, Das Sarma J, Shindler KS. SIRT1 activating compounds reduce oxidative stress mediated neuronal loss in viral induced CNS demyelinating disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2014;2:3.
Munemasa Y, Kitaoka Y. Autophagy in axonal degeneration in glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Prog Retina Eye Res. 2015;47:1–18.
Koch JC, Lingor P. The role of autophagy in axonal degeneration of the optic nerve. Exp Eye Res. 2016;144:81–9.
Russo R, Nucci C, Corasaniti MT, Bagetta G, Morrone LA. Autophagy dysregulation and the fate of retinal ganglion cells in glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Prog Brain Res. 2015;220:87–105.
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 2016;12:1–222.
Sase K, Kitaoka Y, Munemasa Y, Kojima K, Takagi H. Axonal protection by short-term hyperglycemia with involvement of autophagy in TNF-induced optic nerve degeneration. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:425.
Sase K, Kitaoka Y, Tsukahara C, Takagi H. Involvement of Beclin-1 in axonal protection by short-term hyperglycemia against TNF-induced optic nerve damage. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18:5455–60.
Kitaoka Y, Sase K, Tsukahara C, Kojima K, Shiono A, Kogo J, et al. Axonal protection by ripasudil, a rho kinase inhibitor, via modulating autophagy in TNF-induced optic nerve degeneration. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58:5056–64.
Lee IH, Cao L, Mostoslavsky R, Lombard DB, Liu J, Bruns NE, et al. A role for the NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 in the regulation of autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:3374–9.
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K. SIRT1: regulation of longevity via autophagy. Cell Signal. 2009;21:1356–60.
Morselli E, Maiuri MC, Markaki M, Megalou E, Pasparaki A, Palikaras K, et al. Caloric restriction and resveratrol promote longevity through the Sirtuin-1-dependent induction of autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2010;1:e10.
Wang P, Guan YF, Du H, Zhai QW, Su DF, Miao CY. Induction of autophagy contributes to the neuroprotection of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase in cerebral ischemia. Autophagy. 2012;8:77–87.
Tsukahara C, Sase K, Fujita N, Takagi H, Kitaoka Y. Axonal protection by tacrolimus with inhibition of NFATc1 in TNF-induced optic nerve degeneration. Neurochem Res. 2019;44:1726–35.
Oku H, Morishita S, Horie T, Nishikawa Y, Kida T, Mimura M, et al. Protective effect of P7C3 on retinal ganglion cells from optic nerve injury. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2017;61:195–203.
Zhang Y, Li H, Cao Y, Zhang M, Wei S. Sirtuin 1 regulates lipid metabolism associated with optic nerve regeneration. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12:6962–8.
Duan CM, Zhang JR, Wan TF, Wang Y, Chen HS, Liu L. SRT2104 attenuates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and imbalance between microglial M1 and M2 phenotypes in the mice. Behav Brain Res. 2020;378:112296.
Luo G, Jian Z, Zhu Y, Zhu Y, Chen B, Ma R, et al. Sirt1 promotes autophagy and inhibits apoptosis to protect cardiomyocytes from hypoxic stress. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43:2033–43.
Deng H, Mi MT. Resveratrol attenuates Aβ25-35 caused neurotoxicity by inducing autophagy through the TyrRS-PARP1-SIRT1 signaling pathway. Neurochem Res. 2016;41:2367–79.
Zhao H, Chen S, Gao K, Zhou Z, Wang C, Shen Z, et al. Resveratrol protects against spinal cord injury by activating autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis mediated by the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway. Neuroscience. 2017;348:241–51.
Wu H, Wu J, Zhou S, Huang W, Li Y, Zhang H, et al. SRT2104 attenuates diabetes-induced aortic endothelial dysfunction via inhibition of P53. J Endocrinol. 2018;237:1–14.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Kakenhi Grants-in-Aid (18K09427 to Y. K., 17K11469 to H.T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Y Kitaoka, None; K. Sase, None; C. Tsukahara, None; N. Fujita, None; N. Tokuda, None; J. Kogo, None; H. Takagi, None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Corresponding Author: Yasushi Kitaoka
About this article
Cite this article
Kitaoka, Y., Sase, K., Tsukahara, C. et al. Axonal protection by a small molecule SIRT1 activator, SRT2104, with alteration of autophagy in TNF-induced optic nerve degeneration. Jpn J Ophthalmol 64, 298–303 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-020-00731-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-020-00731-6