Abstract
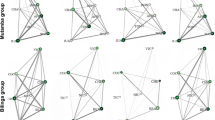
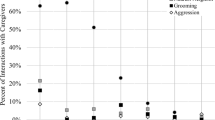
This study examined the anxiety levels and social interactions of two orphan and four mother-reared adolescent chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) in the Kasekela community at Gombe National Park, Tanzania. We used focal sampling in the field at Gombe to observe these adolescent individuals. Their social interactions and anxious behavior, measured as rough scratching, were recorded. The two orphans differed from others of a similar age by exhibiting higher levels of anxiety and lower levels of play. These results suggest that a mother’s absence, even in naturalistic conditions in which other members of the community are available to the orphan, may have long-lasting impact on an adolescent’s anxiety and its ability to engage in complex social interactions, such as play.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann J (1974) Observational study of behaviour: sampling methods. Behaviour 49:227–267
Aureli F, de Waal F (1997) Inhibition of social behavior in chimpanzees under high-density conditions. Am J Primatol 41:213–228
Baker KC (1996) Chimpanzees in single cages and small social groups: effects of housing on behavior. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci 35:71–74
Baker BL (2002) Habitat ecologique et liberts des primates: a case study of chimpanzee re-introduction in the republic of Congo. Re-introduction News No. 21, pp 16–18
Baker K, Aureli F (1997) Behavioural indicators of anxiety: an empirical test on chimpanzees. Behavior 137:1031–1050
Beck B (2010) Chimpanzee orphans: sanctuaries, reintroduction and cognition. In: Lonsdorf E, Ross SR, Matsuzawa T, Goodall J (eds) The mind of the chimpanzee: ecological and experimental perspectives. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 332–346
Bloomsmith M, Baker K, Ross S, Lambeth S (2005) Early rearing conditions and captive chimpanzee behavior: some surprising findings. In: Sackett G, Ruppenthal G (eds) Nursery rearing of nonhuman primates in the 21st century. Kluver Academic Publishers, New York, pp 289–312
Boesch C, Boesch-Achermann H (2000) The chimpanzees of the Taïforest: behavioural ecology and evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Boesch C, Bole ì C, Eckhardt N, Boesch H (2010) Altruism in forest chimpanzees: the case of adoption. PLoS ONE 5(1):e8901. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008901
Brent L, Lee DR, Eichberg JW (1991) Evaluation of chimpanzee enrichment enclosure. J Med Primatol 20:29–34
Carter J (2003) Orphan chimpanzees in West Africa: experiences and prospects for viability in chimpanzee rehabilitation. In: Kormos C, Boesch MI, Bakarr, Butynski T (eds) West African chimpanzees. Status survey and conservation action plan. Primate Specialist Group, IUCN. pp 157–168
Champoux M, Metz B, Suomi SJ (1989) Rehousing nonreproductive rhesus macaques with weanlings: I. Behavior of adults toward weanlings. Lab Primate Newslett 28(4):4. http://www.brown.edu/Research/Primate/lpn28-4.html#wean (retrieved March 12, 2012)
Clarke S, Juno C, Maple T (1982) Behavioral effects of a change in the physical environment: a pilot study of captive chimpanzees. Zoo Biol 1:371–380
Cordoni G, Palagi E (2011) Ontogenetic trajectories of chimpanzee social play: similarities with humans. PLoS ONE 6(11):e27344. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027344
Davila-Ross M, Allcock B, Thomas C, Bard KA (2011) Aping expressions? Chimpanzees produce distinct laugh types when responding to laughter of others. Emotion 11:1013–1020
Fagen R (1993) Primate juveniles and primate play. In: Pereira ME, Fairbanks LA (eds) Juvenile primates: life history, development, and behavior. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 183–196
Ferdowsian HR et al (2011) Signs of mood and anxiety disorders in chimpanzees. PLoS ONE 6(6):e19855. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019855
Goodall J (1986) The chimpanzees of Gombe: patterns of behavior. Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Goossens B, Setchell JM, Vidal C, Dilambaka E, Jamart A (2003) Successful reproduction in wild-released orphan chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes troglodytes). Primates 44:67–69
Harlow H, Suomi S (1971) Social recovery by isolation-reared monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 68:1534–1538
Hayaki H (1985) Social play of juvenile and adolescent chimpanzees in the Mahale mountains national park, Tanzania. Primates 26:343–360
Hicks T, Darby L, Hart J, Swinkels J, January N., Menken S (2010) Trade in orphans and bushmeat threatens one of the democratic republic of the Congo’s most important populations of eastern chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii). African Primates, North America. http://journals.sfu.ca/afrprims/index.php/AfricanPrimates/article/view/10 (retrieved March 12, 2012)
Howell S, Schwandt M, Fritz J, Marzke M, Murphy J, Young D (2006) Effects of early rearing history on growth. In: Sackett G, Ruppenthal G (eds) Nursery rearing of nonhuman primates in the 21st century. Kluver Academic Publishers, New York, pp 313–350
Humle T, Colin C, Laurans M, Raballand E (2011) Group release of sanctuary chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) in the Haut Niger National Park, Guinea, West Africa: ranging patterns and lessons so far. Int J Primatol 32:456–473
King N, Mellen J (1994) The effects of early experience on adult copulatory behavior in zoo-born chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). Zoo Biol 13:51–59
Leavens D, Aureli F, Hopkins W, Hyatt C (2001) Effects of cognitive challenge on self-directed behaviors by chimpanzees. Am J Primatol 55:1–14
Lutz CK, Mayer JS (2008) Self-injurious behavior: nonhuman primate models for the human condition. In: Abee C, Mansfield S, Moris T (eds) Primate models of children’s health and developmental disabilities. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 109–140
Mendoza-Granados D, Sommer V (1995) Play in chimpanzees of the Arnhem zoo: self-serving compromises. Primates 36:57–68
Menzel E (1964) Patterns of responsiveness in chimpanzees reared through infancy under conditions of environmental restriction. Psychol Forsch 27:337–365
Murray C, Eberly L, Pusey A (2006) Foraging strategies as a function of season and rank among wild female chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). Behav Ecol 17:1020–1028
Nash LT, Fritz J, Alford PA, Brent L (1999) Variables influencing the origins of diverse abnormal behaviors in a large sample of captive chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). Am J Primatol 48(1):15–29
Palagi E, Cordoni G, BorgogniniTarlirli SM (2004) Immediate and delayed benefits of play behaviour: new evidence from chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). Ethology 110:949–962
Pusey AE (1983) Mother-Offspring relationships in chimpanzees after weaning. Anim Behav 31:363–377
Pusey AE (1990) Behavioural changes at adolescence in chimpanzees. Behaviour 115:203–246
Pusey A, Williams J, Goodall J (1997) The influence of dominance rank on the reproductive success of female chimpanzees. Science 277:828–831. doi:10.1126/science.277.5327.828
Schino G, Trosi A, Perretta G, Monaco V (1991) Measuring anxiety in nonhuman primates: effect of lorazepam on macaque scratching. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 4:889–891
Schino G, Perreta G, Taglioni A, Monaco V, Trosi A (1996) Primate displacement activities as an ethopharmacological model of anxiety. Anxiety 2:186–191
Spijkerman R (1996) Effects of peer-only rearing in young chimpanzees: a comparison of social behavior development in peer and family groups. Utrecht University, Utrecht
Spijkerman RP, van Hooff J, Dienske H, Jens W (1997) Differences in subadult behaviors of chimpanzees living in peer groups and in a family group. Int J Primatol 18:439–454
Suomi S (1997) Early determinants of behaviour: evidence from primate studies. Br Med Bull 53:170–184
Tutin CEG et al (2001) Conservation biology framework for the release of wild-born orphaned chimpanzees into the Conkouati Reserve, Congo. Conserv Biol 15:1247–1257
van Ijzendoorn MH, Bard KA, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, Ivan K (2009) Enhancement of attachment and cognitive development of young nursery-reared chimpanzees in responsive versus standard care. Dev Psychobiol 51:173–185
Wobber T, Hare B (2011) Psychological health of orphan bonobos and chimpanzees in African sanctuaries. PLoS ONE 6:e17147. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017147
Yerkes R (1943) Chimpanzees: a laboratory colony. Yale university press; H, New Haven
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Milton and Ethel Harris Research Initiative (MEHRI), York University in collaboration with the Jane Goodall Institute, and the Jane Goodall Institute’s Center for Primate Studies (JGICPS), Duke University. We express appreciation to Jane Goodall and to Tanzania National Parks, the Tanzanian Wildlife Research Institute and the Tanzanian Commission for Science and Technology for their permission to conduct research at Gombe National Park. We are particularly grateful to S. Shanker and A. Pusey for their support and helpful advice, C. Murray for her assistance in the field, and J. Schumacher-Stankey for assistance at the JGICPS. Also for the helpful comments by Linda Brent and two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Botero, M., MacDonald, S.E. & Miller, R.S. Anxiety-related behavior of orphan chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) at Gombe National Park, Tanzania. Primates 54, 21–26 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10329-012-0327-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10329-012-0327-1