Abstract
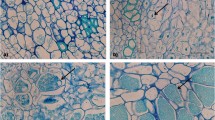
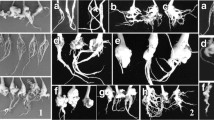
A commercial clubroot-resistant F1 cultivar of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. subsp. pekinensis), Kukai 70, is resistant to an isolate of populations of Plasmodiophora brassicae from Hagi (HG) city and is susceptible to another from Yamaguchi (YMG) city. The degree and frequency of primary and secondary cycle colonization by the isolates in the root hairs and root tissues of cv. Kukai 70 were compared. Seedlings of cv. Kukai 70 were grown in soils amended with inoculum of either HG or YMG and harvested 10 days after inoculation to observe the primary cycle (number of root-hair infections) and 20, 30, and 40 days after inoculation to observe of the secondary cycle (frequency of infected cells and degree of plasmodial development based on the number of nuclei in infected cells). Although more root hairs were infected in HG than in YMG, fewer cells in root tissues including the cortex and medullary rays were infected in HG than in YMG. In addition, YMG developed plasmodia with many nuclei and formed resting spores, whereas plasmodia remained immature with a small number of nuclei in HG and did not form resting spores even by 40 days after inoculation. These results suggest that suppression of plasmodial development during secondary colonization is associated with resistance mechanisms to HG in cv. Kukai 70. Starch did not accumulate (i.e., development of amyloplasts) in HG-infected cells. This may be involved in the suppression of secondary colonization of P. brassicae in the cultivar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HM Dekhuijzen (1979) ArticleTitleElectron microscopic studies on the root hairs and cortex of a susceptible and a resistant variety of Brassica campestris infected with Plasmodiophora brassicae Neth J Plant Pathol 85 1–17 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01976714
JS Karling (1968) The plasmodiophorales EditionNumber2nd edn. Hafner New York
NT Keen PH Williams (1969) ArticleTitleSynthesis and degradation of starch and lipids following infection of cabbage by Plasmodiophora brassicae Phytopathology 59 778–785 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF1MXksVKkurs%3D
P Kobelt J Siemens MD Sacristán (2000) ArticleTitleHistological characterization of the incompatible interaction between Arabidopsis thaliana and obligate biotrophic pathogen Plasmodiophora brassicae Mycol Res 104 220–225 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0953756299001781
TK Kroll GH Lacy LD Moore (1983) ArticleTitleA quantitative description of the colonization of susceptible and resistant radish plants by Plasmodiophora brassicae Phytopathol Z 108 97–105
Y Kuginuki H Yoshikawa M Hirai (1999) ArticleTitleVariation in virulence of Plasmodiophora brassicae in Japan tested with clubroot-resistant cultivars of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) Eur J Plant Pathol 105 327–332 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008705413127
M Morgner (1995) Mikroskopische Untersuchungen der Reaktion empfindlicher und resistenter Genotypen vershiedener Brassica-Arten gegenüber Plasmodiophora brassicae Wor Ph.D. Thesis, Free University of Berlin Berlin
G Samuel SD Garret (1945) ArticleTitleThe infected root hair count for estimating the activity of Plasmodiophora brassicae Woron. in the soil Ann Appl Biol 32 96–101 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1744-7348.1945.tb06767.x
WL Seaman JC Walker RH Larson (1963) ArticleTitleA new race of Plasmodiophora brassicae affecting Badger Shipper cabbage Phytopathology 53 1426–1429
AR Spurr (1969) ArticleTitleA low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy J Ultrastruct Res 26 31–43 Occurrence Handle4887011 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF1MXkvVahsLc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-5320(69)90033-1
S Tanaka M Negoro T Ota K Katumoto Y Nishi (1990) ArticleTitleClubroot of spring Chinese cabbage in Nagasaki Prefecture, Kyushu (in Japanese) Bull Fac Agric Yamaguchi Univ 38 33–45
S Tanaka Y Sakamoto K Kajima K Fujieda K Katumoto Y Nishi (1991) ArticleTitlePathogenicity of three isolates of clubroot fungus attacking clubroot-resistant cultivars of Chinese cabbage Bull Fac Agric Yamaguchi Univ 39 113–122
S Tanaka S Yoshihara S Ito M Kameya-Iwaki (1997) ArticleTitleThe influence of virulence of Plasmodiophora brassicae populations on epidemiology of Chinese cabbage clubroot and efficacy of fungicides (in Japanese) Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 63 183–187 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmsF2isbs%3D
S Tanaka S Fujiyama S Shigemori A Nakayama S Ito M Kameya-Iwaki (1998) ArticleTitlePathogenesis of isolates of Plasmodiophora brassicae from Japan (1). Race and pathogenicities in clubroot resistant cultivars (in Japanese) Kyushu Plant Prot Res 44 15–19
IC Tommerup DS Ingram (1971) ArticleTitleThe life cycle of Plasmodiophora brassicae Wor. in Brassica tissue cultures and in intact roots New Phytol 70 327–332 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1469-8137.1971.tb02531.x
PH Williams (1966) ArticleTitleA system for the determination of races of Plasmodiophora brassicae that infect cabbage and rutabaga Phytopathology 56 624–626
PH Williams NT Keen JO Strandberg SS McNabola (1968) ArticleTitleMetabolic synthesis and degradation during clubroot development in cabbage hypocotyls Phytopathology 58 921–928 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF1cXksV2rsLY%3D
H Yamagishi H Yoshikawa M Ashizawa K Hida S Yui (1986) ArticleTitleEffects of resistant plants as a catch crop on the reduction of resting spores of clubroot (Plasmodiophora brassicae Worn.) in soil J Japan Soc Hort Sci 54 460–466
H Yoshikawa (1981) Breeding for clubroot resistance in Chinese cabbage NS Teleker TD Griggs (Eds) Chinese cabbage AVRDC Tainan 405–413
H Yoshikawa M Ashizawa K Hida (1981) ArticleTitleStudies on the breeding of clubroot-resistance in cole crops. III. The 'insertion' screening method for clubroot resistance (in Japanese) Veg Crop Res Stn Jpn A8 1–21
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, S., Mido, H. & Ito, Si. Colonization by two isolates of Plasmodiophora brassicae with differing pathogenicity on a clubroot-resistant cultivar of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. subsp. pekinensis). J Gen Plant Pathol 72, 205–209 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-006-0276-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-006-0276-x