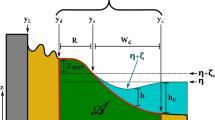
Abstract
Eleven-year long time series of monthly beach profile surveys and hourly incident wave conditions are analyzed for a macrotidal Low Tide Terrace beach. The lower intertidal zone of the beach has a pluriannual cycle, whereas the upper beach profile has a predominantly seasonal cycle. An equilibrium model is applied to study the variation of the contour elevation positions in the intertidal zone as a function of the wave energy, wave power, and water level. When forcing the model with wave energy, the predictive ability of the equilibrium model is around 60% in the upper intertidal zone but decreases to 40% in the lower intertidal zone. Using wave power increases the predictive ability up to 70% in both the upper and lower intertidal zones. However, changes around the inflection point are not well predicted. The equilibrium model is then extended to take into account the effects of the tide level. The initial results do not show an increase in the predictive capacity of the model, but do allow the model free parameters to represent more accurately the values expected in a macrotidal environment. This allows comparing the empirical model calibration in different tidal environment. The interpretation of the model free parameter variation across the intertidal zone highlights the behavior of the different zones along the intertidal beach profile. This contributes to a global interpretation of the four model parameters for beaches with different tidal ranges, and therefore to a global model applicable at a wide variety sites.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida LP, Almar R, Marchesiello P, Blenkinsopp C, Martins K, Sénéchal N, Floc’h F, Bergsma E, Benshila R, Caulet C, Biausque M, Duong TH, Le Thanh B, Nguyen TV (2018) Tide control on the swash dynamics of a steep beach with low-tide terrace. Mar Geol xx (accepted with minor revision)
Aubrey DG (1979) Seasonal patterns of onshore/offshore sediment movement. J Geophys Res Oceans 84 (C10):6347
Aubrey DG, Inman DL, Winant CD (1980) The statistical prediction of beach changes in southern California. J Geophys Res Oceans 85(C6):3264
Barth N, Wunsch C (1990) Oceanographic experiment design by simulated annealing. J Phys Oceanogr 20:1249
Blaise E, Suanez S, Stéphan P, Fichaut B, David L, Cuq V, Autret R, Houron J, Rouan M, Floc’h F et al (2015) Bilan des tempêtes de lÕhiver 2013–2014 sur la dynamique de recul du trait de côte en Bretagne. Géomorphologie: Relief, Processus, Environnement 21(3):267
Bruun P (1954) Coastal erosion and development of beach profiles. 44 (Technical Memorandum - U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Washington D. C.)
Castelle B, Marieu V, Bujan S, Ferreira S, Parisot JP, Capo S, Sénéchal N, Chouzenoux T (2014) Equilibrium shoreline modelling of a high-energy meso-macrotidal multiple-barred beach. Mar Geol 347:85
Castelle B, Dodet G, Masselink G, Scott T (2017) A new climate index controlling winter wave activity along the Atlantic coast of Europe: The West Europe Pressure Anomaly. Geophys Res Lett 44(3):1384
Caulet C, Floc’h F, Le Dantec N, Augereau E, Ardhuin F, Delacourt C (2017) Wave setup variations along a cross-shore profile of a sandy pocket beach, Porsmilin, Brittany, France. In: Coastal dynamics, copenhague, danemark, 12–16 juin
Davidson M, Turner I (2009) A behavioral template beach profile model for predicting seasonal to interannual shoreline evolution. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 114(F1):1:21
Davidson M, Lewis R, Turner I (2010) Forecasting seasonal to multi-year shoreline change. Coast Eng 57(6):620
Davidson M, Splinter K, Turner I (2013) A simple equilibrium model for predicting shoreline change. Coast Eng 73:191
Dean RG (1977) Equilibrium beach profiles: US Atlantic And Gulf coasts (Department of Civil Engineering and College of Marine Studies, University of Delaware)
Dean RG (1991) Equilibrium beach profiles: characteristics and applications. J Coast Res 7(1):53–84
Dehouck A, Dupuis H, Sénéchal N (2009) Pocket beach hydrodynamics: The example of four macrotidal beaches, Brittany, France. Mar Geol 266(1):1
Didier D, Bernatchez P, Augereau E, Caulet C, Dumont D, Bismuth E, Cormier L, Floc’h F, Delacourt C (2017) LiDAR validation of a video-derived beachface topography on a tidal flat. Remote Sens 9 (8):826
Floc’h F, Le Dantec N, Lemos C, Cancouët R, Sous D, Petitjean L, Bouchette F, Ardhuin F, Suanez S, Delacourt C (2016) Morphological response of a macrotidal embayed beach, Porsmilin, France. J Coast Res 75(sp1):373
Galvin C (1972) Wave breaking in shallow water. In: Meyer (ed) Waves on Beaches and Resulting Sediment Transport, pp 413–456
Gouirand I, Moron V (2003) Variability of the impact of El Niño–southern oscillation on sea-level pressure anomalies over the North Atlantic in January to March (1874–1996). Int J Climatol 23(13):1549
Guza R, Thornton EB (1982) Swash oscillations on a natural beach. J Geophys Res Oceans 87(C1):483
Hamon K (2014) Étude de la morphodynamique et du profil d’équilibre d’une plage de poche macrotidale. Master’s thesis, Laboratoire Géosciences Océan UMR6538 IUEM/UBO
Hansen JE, Barnard PL (2010) Sub-weekly to interannual variability of a high-energy shoreline. Coast Eng 57(11):959
Holman RA, Sallenger A (1985) Setup and swash on a natural beach. J Geophys Res Oceans 90(C1):945
Karunarathna H, Horrillo-Caraballo JM, Ranasinghe R, Short AD, Reeve DE (2012) An analysis of the cross-shore beach morphodynamics of a sandy and a composite gravel beach. Mar Geol 299:33
King B, Blackley M, Carr A, Hardcastle P (1990) Observations of wave-induced set-up on a natural beach. J Geophys Res Oceans 95(C12):22289
Kroon A, Masselink G (2002) Morphodynamics of intertidal bar morphology on a macrotidal beach under low-energy wave conditions, North Lincolnshire, England. Mar Geol 190(3-4): 591
Larson M, Capobianco M, Jansen H, Rózyński G, Southgate HN, Stive M, Wijnberg KM, Hulscher S (2003) Analysis and modeling of field data on coastal morphological evolution over yearly and decadal time scales. Part 1: Background and linear techniques. J Coast Res:760–775
Ludka B, Guza R, O’Reilly W, Yates M (2015) Field evidence of beach profile evolution toward equilibrium. J Geophys Res Oceans 120(11):7574
Masselink G, Short AD (1993) The effect of tide range on beach morphodynamics and morphology: a conceptual beach model. J Coast Res 9(3):785–800
Masselink G, Kroon A, Davidson-Arnott R (2006) Morphodynamics of intertidal bars in wave-dominated coastal settings’ review. Geomorphology 73(1-2):33
Masselink G, Castelle B, Scott T, Dodet G, Suanez S, Jackson D, Floc’h F (2016) Extreme wave activity during 2013/2014 winter and morphological impacts along the Atlantic coast of Europe. Geophys Res Lett 43(5):2135
Miles JR, Russell PE (2004) Dynamics of a reflective beach with a low tide terrace. Cont Shelf Res 24 (11):1219
Miller JK, Dean RG (2004) A simple new shoreline change model. Coast Eng 51(7):531
Price T, Ruessink B (2008) Morphodynamic zone variability on a microtidal barred beach. Mar Geol 251 (1-2):98
Qi H, Cai F, Lei G, Cao H, Shi F (2010) The response of three main beach types to tropical storms in South China. Mar Geol 275(1–4):244
Senechal N, Coco G, Bryan KR, Holman RA (2011) Wave runup during extreme storm conditions. J Geophys Res Oceans 116(C7):1:13
SHOM (1994) Courants de mare de la cte ouest de bretagne de goulven penmarch. Tech. rep. SHOM
Splinter KD, Turner IL, Davidson MA, Barnard P, Castelle B, Oltman-Shay J (2014) A generalized equilibrium model for predicting daily to interannual shoreline response. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 119(9):1936
Stive MJ, Aarninkhof SG, Hamm L, Hanson H, Larson M, Wijnberg KM, Nicholls RJ, Capobianco M (2002) Variability of shore and shoreline evolution. Coast Eng 47(2):211
Stockdon HF, Holman RA, Howd PA, Sallenger AH Jr (2006) Empirical parameterization of setup, swash, and runup. Coast Eng 53(7):573
Stocker T (2014) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis: Working Group I contribution to the Fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Suanez S, Cancouët R, Floc’h F, Blaise E, Ardhuin F, Filipot JF, Cariolet JM, Delacourt C (2015) Observations and predictions of wave runup, extreme water levels, and medium-term dune erosion during storm conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 3(3):674
Tolman HL (1991) A third-generation model for wind waves on slowly varying, unsteady, and inhomogeneous depths and currents. J Phys Oceanogr 21(6):782
Treguer P, Goberville E, Barrier N, L’Helguen S, Morin P, Bozec Y, Rimmelin-Maury P, Czamanski M, Grossteffan E, Cariou T et al (2014) Large and local-scale influences on physical and chemical characteristics of coastal waters of Western Europe during winter. J Mar Syst 139:79
Wright L, Short A, Green M (1985) Short-term changes in the morphodynamic states of beaches and surf zones: an empirical predictive model. Mar Geol 62(3-4):339
Yates M, Guza R, O’Reilly W (2009) Equilibrium shoreline response: Observations and modeling. J Geophys Res Oceans 114(C9):1:16
Yates M, Guza R, O’Reilly W, Hansen J, Barnard P (2011) Equilibrium shoreline response of a high wave energy beach. J Geophys Res Oceans 116(C4):1:13
Funding
This work was supported by the Labex-MER funded by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche under the program Investissements d’avenir with the reference ANR-10-LABX-19-01, the lab Géosciences Océan UMR6538 and the Pôle Image of IUEM. The long-term measurements were successively supported by the ANR COCORISCO (2010-CEPL-001-01), the SOERE trait de cte and the NSO Dynalit in the frame of the IR ILICO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Aart Kroon
This article is part of the Topical Collection on the 8th International conference on Coastal Dynamics, Helsingør, Denmark, 12–16 June 2017
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lemos, C., Floc’h, F., Yates, M. et al. Equilibrium modeling of the beach profile on a macrotidal embayed low tide terrace beach. Ocean Dynamics 68, 1207–1220 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-018-1185-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-018-1185-1