Abstract
Background
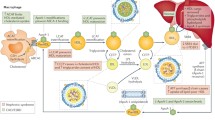
Chronic renal failure (CRF) is associated with hypertriglyceridemia and impaired clearance of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and chylomicrons which are largely due to lipoprotein lipase (LPL) deficiency/dysfunction. After its release from myocytes and adipocytes, LPL binds to the endothelium in the adjacent capillaries where it catalyzes hydrolysis of triglycerides in VLDL and chylomicrons. The novel endothelium-derived molecule, glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored binding protein 1 (GPIHBP1), plays a critical role in LPL metabolism and function by anchoring LPL to the endothelium and binding chylomicrons. GPIHBP1-deficient mice and humans exhibit severe hypertriglyceridemia and diminished heparin-releasable LPL, pointing to the critical role of GPIHBP1 in regulation of LPL activity. Given its central role in regulation of LPL activity and triglyceride metabolism, we explored the effect of chronic kidney disease (CKD) on GPIHBP1 expression.
Methods
Expression of GPIHBP1 and LPL were determined by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, Western blot and immunohistochemical analyses in the adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and myocardium of rats 12 weeks after 5/6 nephrectomy (CRF) or sham-operation (control).
Results
Compared to the controls, the CRF group exhibited severe hypertriglyceridemia, significant reduction of the skeletal muscle, myocardium and adipose tissue LPL mRNA and protein abundance. This was accompanied by parallel reductions of GPIHBP1 mRNA abundance and immunostaining in the tested tissues.
Conclusions
LPL deficiency in CKD is associated with and compounded by GPIHBP1 deficiency. Together these abnormalities contribute to impaired clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, diminished availability of lipid fuel for energy storage in adipocytes and energy production in myocytes and consequent hypertriglyceridemia, cachexia, muscle weakness and atherosclerosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaziri ND, Norris K. Lipid disorders and their relevance to outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2011;31(1–3):189–96.
Vaziri ND. Dyslipidemia of chronic renal failure: the nature, mechanisms and potential consequences. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;290:262–72.
Attman PO, Samuelsson O, Alaupovic P. Lipoprotein metabolism and renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993;21:573–92.
Vaziri ND. Causes of dysregulation of lipid metabolism in chronic renal failure. Semin Dial. 2009;22(6):644–51.
Vaziri ND, Navab M, Fogelman AM. HDL metabolism and activity in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6(5):287–96.
Shoji T, Nishizawa Y, Nishitani H, Yamakawa M, Morii H. Impaired metabolism of high density lipoprotein in uremic patients. Kidney Int. 1992;41:1653–61.
Catrran DC, Fenton SS, Wilson DR, Steiner G. Defective triglyceride removal in lipemia associated with peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85:29–33.
Horkko S, Huttunen K, Korhonen T, Kesaniemi YA. Decreased clearance of low-density lipoprotein in patients with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1994;45:561–70.
Weintraub M, Burstein A, Rassin T, Liron M, Ringel Y, Cabili S, Blum M, Peer G, Laina A. Severe defect in clearing postprandial chylomicron remnants in dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1992;42:1247–52.
Klin M, Smogorzewski M, Ni Z, Zhang G, Massry SG. Abnormalities in hepatic lipase in chronic renal failure: role of excess parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1996;97:2167–73.
Vaziri ND, Liang K. Down regulation of VLDL receptor expression in chronic experimental renal failure. Kidney Int. 1997;51:913–9.
Kim C, Vaziri ND. Downregulation of hepatic LDL receptor-related protein (LRP) in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1028–32.
Akmal M, Kasim SE, Soliman AR, Massry SG. Excess parathyroid hormone adversely affects lipid metabolism in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1990;37:854–8.
Vaziri ND, Liang K. Down-regulation of tissue lipoprotein lipase expression in experimental chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1996;50:1928–35.
Vaziri ND, Wang XQ, Liang K. Secondary hyperparathyroidism downregulates lipoprotein lipase expression in chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol (Renal Physiol). 1997;273(42):F925–30.
Sendak RA, Bensadoun A. Identification of a heparin-binding domain in the distal carboxyl-terminal region of lipoprotein lipase by site-directed mutagenesis. J Lipid Res. 1998;39:1310–5.
Chan MK, Persaud J, Varghese Z, Moorhead JF. Pathogenic role of post-heparin lipases in lipid abnormalities in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1984;25:812–8.
Goldberg IJ. Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis. J Lipid Res. 1996;37:693–707.
Parthasarathy N, Goldberg IJ, Sivaram P, Mulloy B, Flory DM, Wagner WD. Oligosaccharide sequences of endothelial cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan with affinity for lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:22391–6.
Young SB, Davies SJ, Fong LG, Gin P, Weinstein MM, Bensadoun A, Beigneux AP. GPIHBP1—an endothelial cell molecule required for the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2007;18:389–96.
Beigneux AP, Davies B, Gin P, Weinstein MM, Farber E, Qiao X, Peale P, Bunting S, Walzem RL, Wong JS, et al. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 plays a critical role in the lipolytic processing of chylomicrons. Cell Metab. 2007;5:279–91.
Beigneux AP, Davies BS, Bensadoun A, Fong LG, Young SG. GPIHBP1, a GPI-anchored protein required for the lipolytic processing of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 2009;50 Suppl:S57–62.
Véniant MM, Beigneux AP, Bensadoun A, Fong LG, Young SG. Lipoprotein size and susceptibility to atherosclerosis—insights from genetically modified mouse models. Curr Drug Targets. 2008;9:174–89.
Kim HJ, Moradi H, Yuan J, Norris K, Vaziri ND. Renal mass reduction results in accumulation of lipids and dysregulation of lipid regulatory proteins in the remnant kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009;296(6):F1297–306.
Kim HJ, Vaziri ND, Norris K, An WS, Quiroz Y, Rodriguez-Iturbe B. High-calorie diet with moderate protein restriction prevents cachexia and ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation and proteinuria in experimental chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2010;14(6):536–47.
Acknowledgment
This study was in part funded by the NIH Accelerating Excellence in Translational Science (AXIS) grant 5U54 RR026138-02 (10-11-KN-G0811C00-UCI).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare and warrant that the results presented in this paper have not been published previously in whole or part, except in abstract format.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Vaziri, N.D., Yuan, J., Ni, Z. et al. Lipoprotein lipase deficiency in chronic kidney disease is accompanied by down-regulation of endothelial GPIHBP1 expression. Clin Exp Nephrol 16, 238–243 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0549-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0549-3