Abstract
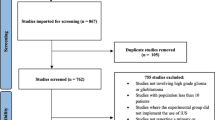
Intraoperative ultrasonography (iUS) is considered an accurate, safe, and cost-effective tool to estimate the extent of resection of both high-grade (HGG) and low-grade (DLGG) diffuse gliomas (DGs). However, it is currently missing an evidence-based assessment of iUS diagnostic accuracy in DGs surgery. The objective of review is to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic performance of iUS in detecting tumor residue after DGs resection. A comprehensive literature search for studies published through October 2018 was performed according to PRISMA-DTA and STARD 2015 guidelines, using the following algorithm: (“ultrasound” OR “ultrasonography” OR “ultra-so*” OR “echo*” OR “eco*”) AND (“brain” OR “nervous”) AND (“tumor” OR “tumour” OR “lesion” OR “mass” OR “glio*” OR “GBM”) AND (“surgery” OR “surgical” OR “microsurg*” OR “neurosurg*”). Pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios (LR+ and LR−), and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of iUS in DGs were calculated. A subgroup analysis for HGGs and DLGGs was also conducted. Thirteen studies were included in the systematic review (665 DGs). Ten articles (409 DGs) were selected for the meta-analysis with the following results: sensitivity 72.2%, specificity 93.5%, LR− 0.29, LR+ 3, and DOR 9.67. Heterogeneity among studies was non-significant. Subgroup analysis demonstrates a better diagnostic performance of iUS for DLGGs compared with HGGs. iUS is an effective technique in assessing DGs resection. No significant differences are seen regarding iUS modality and transducer characteristics. Its diagnostic performance is higher in DLGGs than HGGs and could be worsened by previous treatments, surgical artifacts, and small tumor residue volumes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altieri R, Melcarne A, Di Perna G, Specchia FMC, Fronda C, La Rocca G, Cofano F, Sabatino G, Pepa GMD, Olivi A, Ducati A, Garbossa D (2018) Intra-operative ultrasound: tips and tricks for making the most in neurosurgery. Surg Technol Int 33:353–360
Altieri R, Zenga F, Fontanella MM, Cofano F, Agnoletti A, Spena G, Crobeddu E, Fornaro R, Ducati A, Garbossa D (2015) Glioma surgery: technological advances to achieve a maximal safe resection. Surg Technol Int 27:297–302
Arlt F, Chalopin C, Müns A, Meixensberger J, Lindner D (2016) Intraoperative 3D contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS): a prospective study of 50 patients with brain tumours. Acta Neurochir 158:685–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2738-z
Attia J (2003) Moving beyond sensitivity and specificity: using likelihood ratios to help interpret diagnostic tests. Aust Prescr 26:11–13
Barbagallo GMV, Morrone A, Certo F (2018) Intraoperative computed tomography and awake craniotomy: a useful and safe combination in brain surgery. World Neurosurg 119:e159–e166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.07.078
Beiko J, Suki D, Hess KR, Fox BD, Cheung V, Cabral M, Shonka N, Gilbert MR, Sawaya R, Prabhu SS, Weinberg J, Lang FF, Aldape KD, Sulman EP, Rao G, McCutcheon IE, Cahill DP (2014) IDH1 mutant malignant astrocytomas are more amenable to surgical resection and have a survival benefit associated with maximal surgical resection. Neuro-Oncol 16:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not159
Brown TJ, Brennan MC, Li M, Church EW, Brandmeir NJ, Rakszawski KL, Patel AS, Rizk EB, Suki D, Sawaya R, Glantz M (2016) Association of the extent of resection with survival in glioblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 2:1460–1469. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.1373
Cenciarelli C, Marei HE, Zonfrillo M, Casalbore P, Felsani A, Giannetti S, Trevisi G, Althani A, Mangiola A (2017) The interference of Notch1 target Hes1 affects cell growth, differentiation and invasiveness of glioblastoma stem cells through modulation of multiple oncogenic targets. Oncotarget 8:17873–17886. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15013
Chaichana KL, Jusue-Torres I, Navarro-Ramirez R, Raza SM, Pascual-Gallego M, Ibrahim A, Hernandez-Hermann M, Gomez L, Ye X, Weingart JD, Olivi A, Blakeley J, Gallia GL, Lim M, Brem H, Quinones-Hinojosa A (2014) Establishing percent resection and residual volume thresholds affecting survival and recurrence for patients with newly diagnosed intracranial glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol 16:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not137
Coburger J, Scheuerle A, Kapapa T, Engelke J, Thal DR, Wirtz CR, König R (2015) Sensitivity and specificity of linear array intraoperative ultrasound in glioblastoma surgery: a comparative study with high field intraoperative MRI and conventional sector array ultrasound. Neurosurg Rev 38:499–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-015-0627-1
Cohen JF, Korevaar DA, Altman DG, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Hooft L, Irwig L, Levine D, Reitsma JB, de Vet HCW, Bossuyt PMM (2016) STARD 2015 guidelines for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies: explanation and elaboration. BMJ Open 6:e012799. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012799
Cordella R, Nava S, Prada F, Agnoletti A, Legnani F, Meco FD (2018) Ultrasound guided mini-invasive tailored approach and intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring: a synergistic strategy for the removal of tumors near the motor cortex. A preliminary experience. J Neurosurg Sci 62:255–264. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0390-5616.16.03565-7
Eljamel MS, Mahboob SO (2016) The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of intraoperative imaging in high-grade glioma resection; a comparative review of intraoperative ALA, fluorescein, ultrasound and MRI. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 16:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2016.07.012
Ellingson BM, Wen PY, Cloughesy TF (2018) Evidence and context of use for contrast enhancement as a surrogate of disease burden and treatment response in malignant glioma. Neuro-Oncol 20:457–471. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nox193
Esquenazi Y, Friedman E, Liu Z, Zhu J-J, Hsu S, Tandon N (2017) The survival advantage of “Supratotal” resection of glioblastoma using selective cortical mapping and the subpial technique. Neurosurgery 81:275–288. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyw174
Gerganov VM, Samii A, Giordano M, Samii M, Fahlbusch R (2011) Two-dimensional high-end ultrasound imaging compared to intraoperative MRI during resection of low-grade gliomas. J Clin Neurosci 18:669–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2010.08.017
Hadjipanayis CG, Widhalm G, Stummer W (2015) What is the surgical benefit of utilizing 5-ALA for fluorescence-guided surgery of malignant gliomas? Neurosurgery 77:663–673. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000929
Hammoud MA, Ligon BL, Elsouki R, Shi WM, Schomer DF, Sawaya R (1996) Use of intraoperative ultrasound for localizing tumors and determining the extent of resection: a comparative study with magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 84:737–741. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1996.84.5.0737
Jenkinson MD, Barone DG, Bryant A, Vale L, Bulbeck H, Lawrie TA, Hart MG, Watts C (2018) Intraoperative imaging technology to maximise extent of resection for glioma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD012788. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD012788.pub2
Kubben PL, Scholtes F, Schijns OEMG, Ter Laak-Poort MP, Teernstra OPM, Kessels AGH, van Overbeeke JJ, Martin DH, van Santbrink H (2014) Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging versus standard neuronavigation for the neurosurgical treatment of glioblastoma: a randomized controlled trial. Surg Neurol Int 5:70. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.132572
Lacroix M, Abi-Said D, Fourney DR, Gokaslan ZL, Shi W, DeMonte F, Lang FF, McCutcheon IE, Hassenbusch SJ, Holland E, Hess K, Michael C, Miller D, Sawaya R (2001) A multivariate analysis of 416 patients with glioblastoma multiforme: prognosis, extent of resection, and survival. J Neurosurg 95:190–198. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.95.2.0190
de Leeuw CN, Vogelbaum MA (2019) Supratotal resection in glioma: a systematic review. Neuro-Oncol 21:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy166
Lekht I, Brauner N, Bakhsheshian J, Chang K-E, Gulati M, Shiroishi MS, Grant EG, Christian E, Zada G (2016) Versatile utilization of real-time intraoperative contrast-enhanced ultrasound in cranial neurosurgery: technical note and retrospective case series. Neurosurg Focus 40:E6. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.11.FOCUS15570
Letteboer MMJ, Willems PWA, Viergever MA, Niessen WJ (2005) Brain shift estimation in image-guided neurosurgery using 3-D ultrasound. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52:268–276. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2004.840186
Mahboob S, McPhillips R, Qiu Z, Jiang Y, Meggs C, Schiavone G, Button T, Desmulliez M, Demore C, Cochran S, Eljamel S (2016) Intraoperative ultrasound-guided resection of gliomas: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 92:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.05.007
Majós C, Cos M, Castañer S, Gil M, Plans G, Lucas A, Bruna J, Aguilera C (2016) Early post-operative magnetic resonance imaging in glioblastoma: correlation among radiological findings and overall survival in 60 patients. Eur Radiol 26:1048–1055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3914-x
Mampre D, Ehresman J, Pinilla-Monsalve G, Osorio MAG, Olivi A, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Chaichana KL (2018) Extending the resection beyond the contrast-enhancement for glioblastoma: feasibility, efficacy, and outcomes. Br J Neurosurg 32:528–535. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688697.2018.1498450
Mangiola A, Saulnier N, De Bonis P, Orteschi D, Sica G, Lama G, Pettorini BL, Sabatino G, Zollino M, Lauriola L, Colabianchi A, Proietti G, Kovacs G, Maira G, Anile C (2013) Gene expression profile of glioblastoma peritumoral tissue: an ex vivo study. PLoS One 8:e57145. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057145
Mattei L, Prada F, Legnani FG, Perin A, Olivi A, DiMeco F (2016) Neurosurgical tools to extend tumor resection in hemispheric low-grade gliomas: conventional and contrast enhanced ultrasonography. Childs Nerv Syst 32:1907–1914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3186-z
McInnes MDF, Moher D, Thombs BD, McGrath TA, Bossuyt PM, the PRISMA-DTA Group, Clifford T, Cohen JF, Deeks JJ, Gatsonis C, Hooft L, Hunt HA, Hyde CJ, Korevaar DA, Leeflang MMG, Macaskill P, Reitsma JB, Rodin R, Rutjes AWS, Salameh J-P, Stevens A, Takwoingi Y, Tonelli M, Weeks L, Whiting P, Willis BH (2018) Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies: the PRISMA-DTA statement. JAMA 319:388–396. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.19163
Mert A, Kiesel B, Wöhrer A, Martínez-Moreno M, Minchev G, Furtner J, Knosp E, Wolfsberger S, Widhalm G (2015) Introduction of a standardized multimodality image protocol for navigation-guided surgery of suspected low-grade gliomas. Neurosurg Focus 38:E4. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.FOCUS14597
Moiyadi A, Shetty P, John R (2018) Non enhancing gliomas: does intraoperative ultrasound help improve resections? Ultrasonography. https://doi.org/10.14366/usg.18032
Moiyadi AV (2016) Intraoperative ultrasound technology in neuro-oncology practice-current role and future applications. World Neurosurg 93:81–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.05.083
Morin F, Courtecuisse H, Reinertsen I, Le Lann F, Palombi O, Payan Y, Chabanas M (2017) Brain-shift compensation using intraoperative ultrasound and constraint-based biomechanical simulation. Med Image Anal 40:133–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.06.003
Munkvold BKR, Jakola AS, Reinertsen I, Sagberg LM, Unsgård G, Solheim O (2018) The diagnostic properties of intraoperative ultrasound in glioma surgery and factors associated with gross total tumor resection. World Neurosurg 115:e129–e136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.03.208
Pallud J, Varlet P, Devaux B, Geha S, Badoual M, Deroulers C, Page P, Dezamis E, Daumas-Duport C, Roux F-X (2010) Diffuse low-grade oligodendrogliomas extend beyond MRI-defined abnormalities. Neurology 74:1724–1731. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e04264
Pino M, Imperato A, Musca I, Maugeri R, Giammalva G, Costantino G, Graziano F, Meli F, Francaviglia N, Iacopino D, Villa A (2018) New hope in brain glioma surgery: the role of intraoperative ultrasound. A Review Brain Sci 8:202. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8110202
Prada F, Bene MD, Fornaro R, Vetrano IG, Martegani A, Aiani L, Sconfienza LM, Mauri G, Solbiati L, Pollo B, DiMeco F (2016) Identification of residual tumor with intraoperative contrast-enhanced ultrasound during glioblastoma resection. Neurosurg Focus 40:E7. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.11.FOCUS15573
Prada F, Vitale V, Del Bene M, Boffano C, Sconfienza LM, Pinzi V, Mauri G, Solbiati L, Sakas G, Kolev V, D’Incerti L, DiMeco F (2017) Contrast-enhanced MR imaging versus contrast-enhanced US: a comparison in glioblastoma surgery by using intraoperative fusion imaging. Radiology 285:242–249. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017161206
Renner C, Lindner D, Schneider JP, Meixensberger J (2005) Evaluation of intra-operative ultrasound imaging in brain tumor resection: a prospective study. Neurol Res 27:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1179/016164105X40039
Renovanz M, Hickmann A-K, Henkel C, Nadji-Ohl M, Hopf N (2014) Navigated versus non-navigated intraoperative ultrasound: is there any impact on the extent of resection of high-grade gliomas? A retrospective clinical analysis. J Neurol Surg Part Cent Eur Neurosurg 75:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1356486
Riva M, Hennersperger C, Milletari F, Katouzian A, Pessina F, Gutierrez-Becker B, Castellano A, Navab N, Bello L (2017) 3D intra-operative ultrasound and MR image guidance: pursuing an ultrasound-based management of brainshift to enhance neuronavigation. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12:1711–1725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1578-5
Rygh OM, Selbekk T, Torp SH, Lydersen S, Hernes TAN, Unsgaard G (2008) Comparison of navigated 3D ultrasound findings with histopathology in subsequent phases of glioblastoma resection. Acta Neurochir 150:1033–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-008-0017-3
Sadeghi R, Treglia G (2017) Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of diagnostic studies: a practical guideline. Clin Transl Imaging 5:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-016-0219-2
Sanai N, Berger MS (2008) Glioma extent of resection and its impact on patient outcome. Neurosurgery 62:753–764; discussion 264-266. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000318159.21731.cf
Sastry R, Bi WL, Pieper S, Frisken S, Kapur T, Wells W, Golby AJ (2017) Applications of ultrasound in the resection of brain tumors: ultrasound in brain tumor resection. J Neuroimaging 27:5–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/jon.12382
Selbekk T, Jakola AS, Solheim O, Johansen TF, Lindseth F, Reinertsen I, Unsgård G (2013) Ultrasound imaging in neurosurgery: approaches to minimize surgically induced image artefacts for improved resection control. Acta Neurochir 155:973–980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1647-7
Senft C, Bink A, Franz K, Vatter H, Gasser T, Seifert V (2011) Intraoperative MRI guidance and extent of resection in glioma surgery: a randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 12:997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70196-6
Serra C, Stauffer A, Actor B, Burkhardt J-K, Ulrich N, Bernays R-L, Bozinov O (2012) Intraoperative high frequency ultrasound in intracerebral high-grade tumors. Ultraschall Med - Eur J Ultrasound 33:E306–E312. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1325369
Solheim O, Selbekk T, Jakola AS, Unsgård G (2010) Ultrasound-guided operations in unselected high-grade gliomas—overall results, impact of image quality and patient selection. Acta Neurochir 152:1873–1886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0731-5
Šteňo A, Hollý V, Mendel P, Šteňová V, Petričková Ľ, Timárová G, Jezberová M, Belan V, Rychlý B, Šurkala J, Šteňo J (2018) Navigated 3D–ultrasound versus conventional neuronavigation during awake resections of eloquent low-grade gliomas: a comparative study at a single institution. Acta Neurochir 160:331–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3377-8
Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, Wiestler OD, Zanella F, Reulen H-J, ALA-Glioma Study Group (2006) Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 7:392–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70665-9
Su X, Huang Q-F, Chen H-L, Chen J (2014) Fluorescence-guided resection of high-grade gliomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 11:451–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2014.08.001
Sweeney JF, Smith H, Taplin A, Perloff E, Adamo MA (2018) Efficacy of intraoperative ultrasonography in neurosurgical tumor resection. J Neurosurg Pediatr 21:504–510. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.11.PEDS17473
Toms SA, Lin W-C, Weil RJ, Johnson MD, Jansen ED, Mahadevan-Jansen A (2005) Intraoperative optical spectroscopy identifies infiltrating glioma margins with high sensitivity. Neurosurgery 57:382–391 discussion 382-391
Trevisi G, Roujeau T, Duffau H (2016) Awake surgery for hemispheric low-grade gliomas: oncological, functional and methodological differences between pediatric and adult populations. Childs Nerv Syst 32:1861–1874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3069-3
Ulrich NH, Burkhardt J-K, Serra C, Bernays R-L, Bozinov O (2012) Resection of pediatric intracerebral tumors with the aid of intraoperative real-time 3-D ultrasound. Childs Nerv Syst 28:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1571-1
Valdés PA, Jacobs V, Harris BT, Wilson BC, Leblond F, Paulsen KD, Roberts DW (2015) Quantitative fluorescence using 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX biomarker as a surgical adjunct in low-grade glioma surgery. J Neurosurg 123:771–780. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.12.JNS14391
Wesseling P, Capper D (2018) WHO 2016 classification of gliomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 44:139–150. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12432
Whiting PF, AWS R, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MMG, Sterne JAC, Bossuyt PMM, QUADAS-2 Group (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155:529–536. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009
Willems PWA, Taphoorn MJB, Burger H, Berkelbach van der Sprenkel JW, Tulleken CAF (2006) Effectiveness of neuronavigation in resecting solitary intracerebral contrast-enhancing tumors: a randomized controlled trial. J Neurosurg 104:360–368. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.104.3.360
Yordanova YN, Duffau H (2017) Supratotal resection of diffuse gliomas - an overview of its multifaceted implications. Neurochirurgie 63:243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuchi.2016.09.006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Due to the nature of the present study (literature review), no ethical approval was needed.
Informed consent
Due to the nature of the present study (literature review), no informed consent was obtained.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trevisi, G., Barbone, P., Treglia, G. et al. Reliability of intraoperative ultrasound in detecting tumor residual after brain diffuse glioma surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 43, 1221–1233 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01160-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01160-x