Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to investigate the optic nerve’s elastic properties and optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) using shear-wave elastography (SWE) in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) compared to healthy individuals.
Methods
The study included 22 IIH patients and 15 healthy subjects. SWEs were performed on the optic nerve and ONSD, and optic nerve stiffness were measured.
Results
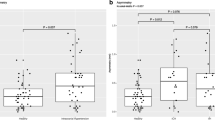
The patients with IIH demonstrated higher stiffness of the optic nerve compared with that of healthy volunteers (P < 0.001). The optic nerve sheath diameter of the optic nerve in the IIH group was significantly larger than that in the control group (P < 0.001). There was no correlation between the disease duration and SWE values in the Spearman correlation test.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that ONSD can be used as a follow-up method in the treatment of IIH. However, there was not any correlation between the disease duration and SWE-based stiffness measurement of the optic nerve.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IIH:
-
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- SWE:
-
Shear-wave elastography
- ONSD:
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter
- ICP:
-
Intracranial pressure
- US:
-
Ultrasonography
References
Wall M, George D (1991) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a perspective study of 50 patients. Brain 114:155–180
Digre KB, Nakamoto BK, Warner JE, Langeberg WJ, Baggaley SK, Katz BJ (2009) A comparison of idiopathic intracranial hypertension with and without papilledema. Headache 49:185–193
Helmke K, Hansen HC (1996) Fundamentals of transorbital sonographic evaluation of optic nerve sheath expansion under intracranial hypertension. I Experimental study. Pediatr Radiol 26(10):701–705
Hansen HC, Helmke K (1997) Validation of the optic nerve sheath response to changing cerebrospinal fluid pressure: ultrasound findings during intrathecal infusion tests. J Neurosurg 87(1):34–40
İnci E, Türkay R, Nalbant MO, Yenice MG, Tugcu V (2017) The value of shear wave elastography in the quantification ofcorpus cavernosum penis rigidity and its alteration with age. Eur J Radiol 89(4):106–110
İnal M, Tan S, Yumusak EM, Şahan MH, Alpua M, Örnek K (2017) Evaluation of the optic nerve using strain and shear wave elastography in patients with multiple sclerosis and healthy subjects. Med Ultrason 19:39–44
İnal M, Tan S, Demirkan S, Burulday V, Gündüz Ö, Örnek K (2017) Evaluation of optic nerve with strain andshear wave elastography in patients with Behçet’s disease and healthy subjects. Ultrasound Med Biol 43(7):1348–1354
Friedman DI, Jacobson DM (2002) Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology 59:1492–1495
Frisén L (1982) Swelling of the optic nerve head: a staging scheme. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:13–18
Munk PL, Vellet AD, Levin M, Lin DT, Collyer RT (1991) Sonography of the eye. Am J Roentgenol 157:1079–1086
Turkay R, Inci E, Bas D, Atar A (2018) Shear wave elastographic alterations in the kidney after extracorporeal schok wave lithotripsy. J Ultrasound Med 37(3):629–634
Palabıyık FB, İnci E, Türkay R, Bas D (2017) Evaluation of liver, kidney and spleen elasticity in heathy newborns and infants using shear wave elastography. J Ultrasound Med 36(10):2039–2045
Asal N, İnal M, Şahan MH, Say B (2020) Assessment of the optic nerve using strain and shear-wave elastography in patients with pseudotumour cerebri. Clin Radiol 75(8):629–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2020.03.038
Zha L, Chen KQ, Zheng XZ, Wu J (2017) The safety and feasibility of diagnostic acoustic radiation force impulse elastography used for eyes. A preliminary in vivo study. Med Ultrason 19(2):185–189. https://doi.org/10.11152/mu-996
Nusbaum DM, Wu SM, Frankfort BJ (2015) Elevated intracranial pressure causes optic nerve and retinal ganglion cell degeneration in mice. Exp Eye Res 136:38–44
Birnbaum FA, Johnson GM, Johnson LN, Jun B, Machan JT (2016) Increased prevalence of optic disc drusen after papilloedema from idiopathic intracranial hypertension: on the possible formation of optic disc drusen. Neuroophthalmology. 40(4):171–180
Gospe SM, Bhatti MT, El-Dairi MA (2016) Anatomic and visual function outcomes in paediatric idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Br J Ophthalmol 100:505–509
De Simone R, Ranieri A, Sansone M, Marano E, Russo CV, Saccà F, Bonavita V (2019) Dural sinus collapsibility, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, and the pathogenesis of chronic migraine. Neurol Sci 40(Suppl 1):59–70
Marzolİ SB, Cİasca P, Curone M et al (2013) Quantitative analysis of optic nerve damage in idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) at diagnosis. Neurol Sci 34:143–145
D’Amico D, Curone M, Erbetta A, Farago G, Bianchi-Marzoli S, Ciasca P, Bussone G, Chiapparini L (2014) Intracranial idiopathic hypertension: 1-year follow-up study. Neurol Sci 35(Suppl 1):177–179
Hayreh SS (1964) Pathogenesis of oedema of the optic disk (papilloedema), a preliminary report. Br J Ophthalmol 1964 48:522–543. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.48.10.522
Tamburrelli C, Salgarello T, Caputo CG, Giudiceandrea A, Scullica L (2000) Ultrasonographic evaluation of optic disc swelling: comparison with CSLO in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:2960–2966
Lochner P, Czosnyka M, Naldi A, Lyros E, Pelosi P, Mathur S, Fassbender K, Robba C (2019) Optic nerve sheath diameter: present and future perspectives for neurologists and critical care physicians. Neurol Sci 40:2447–2457
Chen Q, Chen W, Wang M, Sun X, Sha Y, Li Z, Tian G (2017) High-resolution transbulbar ultrasonography helping differentiate intracranial hypertension in bilateral optic disc oedema patients. Acta Ophthalmol 95(6):e481–e485. https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.13473
Corbett JJ, Savino PJ, Thompson HS, Kansu T, Schatz NJ, Orr LS, Hopson D (1982) Visual loss in pseudotumor cerebri. Follow-up of 57 patients from five to 41 years and a profile of 14 patients with permanent severe visual loss. Arch Neurol 39:461–474
Shah VA, Kardon RH, Lee AG, Corbett JJ (2008) Wall M (2008) Long-term follow-up of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: the Iowa experience. Neurology 70:634–640
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
None.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Informed consent
The study was performed according to the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments. Written informed consent was obtained from the participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(XLSX 18.3 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaya, F.S., Bayram, E. & İnci, E. Evaluating the optic nerve stiffness and optic nerve sheath diameter in idiopathic intracranial hypertension patients after the resolution of papilledema. Neurol Sci 42, 5165–5170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05208-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05208-z