Abstract
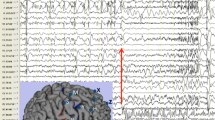
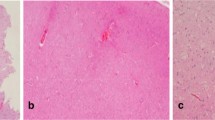
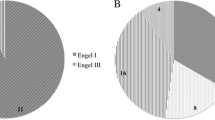
Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) type II is a major cause of drug-resistant epilepsy. In order to gain insight into the possible correlations between FCD II pathological pattern and different clinical characteristics (including clinical information, imaging characteristics and surgical outcomes), different clinicopathological characteristics in two types of FCD II were analyzed (especially in FCD IIb). The mean age of seizure onset and disease duration of 78 patients was 11.0 and 11.2 years, respectively. Patients with FCD type IIb had earlier seizure onset compared with those with FCD type IIa. Pathological subtype IIb was predominantly in frontal lobe and subtype IIa was predominantly seen in temporal. Type IIb demonstrated significantly more signal abnormalities in fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images and T2 images than Type IIa. The rate of satisfactory seizure outcome was 67.64 % in the FCD IIa group, while relative higher, 88.63 %, in the FCD IIb group. All these characteristics may assist in their earlier diagnosis and improve the predictability of surgical management.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engel J, Wiebe S, French J et al (2003) Practice parameter: temporal lobe and localized neocortical resections for epilepsy: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology, in association with the American Epilepsy Society and the American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Neurology 60:538–547
Te´llez-Zenteno JF, Dhar R, Wiebe S (2005) Long-term seizure outcomes following epilepsy surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain 128:1188–1198
Blumcke I, Thom M, Aronica E et al (2011) The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: a consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc task force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission. Epilepsia 52:158–174
Taylor DC, Falconer MA, Bruton CJ et al (1971) Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:369–387
Palmini A, Najm I, Avanzini G et al (2004) Terminology and classification of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology 62:S2–S8
Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD et al (2005) A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development. Neurology 65:1873–1887
Sisodiya SM (2004) Malformations of cortical development: burdens and insights from important causes of human epilepsy. Lancet Neurol 3:29–38
Aronica E, Ozbas-Gerceker F, Redeker S et al (2004) Expression and cellular distribution of high-and low-affinity neurotrophin receptors in malformations of cortical development. Acta Neuropathol 108:422–434
Ying Z, Gonzalez-Martinez J, Tilelli C et al (2005) Expression of neural stem cell surface marker CD133 in balloon cells of human focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia 46:1716–1723
Tassi L, Pasquier B, Minotti L et al (2001) Cortical dysplasia: electroclinical, imaging, and neuropathologic study of 13 patients. Epilepsia 42:1112–1123
Oh HS, Lee MC, Kim HS et al (2008) Pathophysiologic characteristics of balloon cells in cortical dysplasia. Childs Nerv Syst 24:175–183
Englund C, Folkerth RD, Born D et al (2005) Aberrant neuronal-glial differentiation in Taylor-type focal cortical dysp lasia (type II A/B). Acts Neuropathol 109:519–533
Tassi L, Garbelli R, Colombo N et al (2012) Electroclinical, MRI and surgical outcomes in 100 epileptic patients with type II FCD. Epileptic Disord 14:257–266
Colombo N, Tassi L, Deleo F et al (2012) Focal cortical dysplasia type IIa and IIb: MRI aspects in 118 cases proven by histopathology. Neuroradiology 54:1065–1077
Varotto G, Tassi L, Franceschetti S et al (2012) Epileptogenic networks of type II focal cortical dysplasia: a stereo-EEG study. Neuroimage 61:591–598
Lerner JT, Salamon N, Hauptman JS et al (2009) Assessment and surgical outcomes for mild type I and severe type II cortical dysplasia: a critical review and the UCLA experience. Epilepsia 50:1310–1335
Kim DW, Lee SK, Chu K et al (2009) Predictors of surgical outcome and pathologic considerations in focal cortical dysplasia. Neurology 72:211–216
Widdess-Walsh P, Jeha L, Nair D et al (2007) Subdural electrode analysis in focal cortical dysplasia: predictors of surgical outcome. Neurology 69:660–667
Fauser S, Bast T, Altenmuller DM et al (2008) Factors influencing surgical outcome in patients with focal cortical dysplasia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:103–105
Krsek P, Maton B, Korman B et al (2008) Different features of histopathological subtypes of pediatric focal cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol 63:758–769
Krsek P, Pieper T, Karlmeier A et al (2009) Different presurgical characteristics and seizure outcomes in children with focal conical dysplasia type I or II. Epilepsia 50:125–137
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Open Research Fund of the Beijing Key Lab of Epilepsy Research (Grant No. 2013DXBL03), Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant No.7122088), Capital health research and development of special (Grant No. 2011-1020-01), Joint Fund for basic and clinical research cooperation project of Capital Medical University (Grant No. 12JL87) and Beijing Postdoctoral Research Foundation (Grant No. 2013ZZ-22). We would like to thank Dr. Wei Zhang, Ruili Ma, Mingwang Zhu and Na Li for their helpful discussions and suggestions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no further financial or other conflicts of interest in relation to this research and its publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K. Yao, X. Mei contributed equally to this work and manuscript writing.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, K., Mei, X., Liu, X. et al. Clinical characteristics, pathological features and surgical outcomes of focal cortical dysplasia (FCD) type II: correlation with pathological subtypes. Neurol Sci 35, 1519–1526 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1782-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1782-9