Abstract:
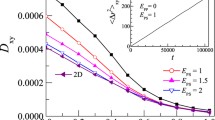
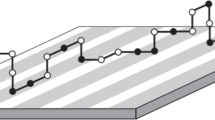
The adsorption of a single ideal polymer chain on energetically heterogeneous and rough surfaces is investigated using a variational procedure introduced by Garel and Orland (Phys. Rev. B 55, 226 (1997)). The mean polymer size is calculated perpendicular and parallel to the surface and is compared to the Gaussian conformation and to the results for polymers at flat and energetically homogeneous surfaces. The disorder-induced enhancement of adsorption is confirmed and is shown to be much more significant for a heterogeneous interaction strength than for spatial roughness. This difference also applies to the localization transition, where the polymer size becomes independent of the chain length. The localization criterion can be quantified, depending on an effective interaction strength and the length of the polymer chain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 October 1997 / Revised: 19 December 1997 / Accepted: 6 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huber, G., Vilgis, T. Polymer adsorption on heterogeneous surfaces. Eur. Phys. J. B 3, 217–223 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050306
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050306