Abstract
Background
Emotional disorders and decrease in health-related quality of life (HRQoL) are well-documented sequelae of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). The aim of this study was to analyze the impact of emotional disorders on HRQoL in survivors of SAH.
Methods
This was a retrospective study enrolling 114 SAH-survivors at 1–10 years (mean 4,5 years) after the disease. Emotional State Questionnaire (EST-Q) was used to measure emotional health and the Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) was used to assess HRQoL of the patients.
Results
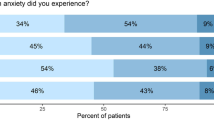
Most of the patients reported good recovery, but EST-Q results revealed high prevalence of emotional disorders after SAH. Almost half of the patients had higher than cut-off values indicating fatigue (47 %) and insomnia (46 %). About one third of SAH-patients had higher than cut-off scores demonstrating depression (30 %) and anxiety (31 %). The patients scored significantly lower in all scales of SF-36 as compared to age-matched general population. All EST-Q subscale results were significantly and negatively correlated with SF-36 scores. Fatigue was independently related to all SF-36 subscales and depression to most of the mental health component scores. Emotional symptoms alone were demonstrated to explain 23–47 % of the SF-36 subscale values, and more than half of the variance of mental health component score values were found to be explained by emotional disorders (53 %).
Conclusions
Emotional disorders are frequent after SAH and significantly associated with impairment of HRQOL. Proper and timely screening tests are important to reveal development of emotional problems and improve QoL for the SAH-patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khindi T, MacDonald RL, Schweizer TA (2010) Cognitive and functional outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 41:e519–e536
Aluoja A, Shlik J, Vasar V, Luuk K, Leinsalu M (1999) Development and psychometric properties of the Emotional State Questionnaire, a self-report questionnaire for depression and anxiety. Nord J Psychiatry 53:443–449
Aluoja A, Luuk K, Shlik J, Vasar V (2001) Assessment of depression and anxiety—psychometric properties of EST-Q, a new self-report instrument. 31st Congress of EABCT, Abstracts, p 81
Baisch SB, Schenk T, Noble AJ (2011) What is the cause of post-traumatic stress disorder following subarachnoid haemorrhage? Post-ictal events are key. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 153:913–922
Carter BS, Buckley D, Ferraro R, Rordorf G, Ogilvy CS (2000) Factors associated with reintegration to normal living after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 46:1326–1333
De Groot MH, Phillips SJ, Eskes GA (2003) Fatigue associated with stroke and other neurologic conditions: implications for stroke rehabilitation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 84:1714–1720
Fertl E, Killer M, Eder H, Linzmayer L, Richling B, Auff E (1999) Long-term functional effects of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage with special emphasis on the patient’s view. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141:571–577
Fontanella M, Perozzo P, Ursone R, Garbossa D, Bergui M (2003) Neuropsychological assessment after microsurgical clipping or endovascular treatment for anterior communicating artery aneurysm. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:867–872
Hedlund M, Ronne-Engström E, Carlsson M, Ekselius L (2010) Coping strategies, health-related quality of life and psychiatric history in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:1375–1382
Hunt WE, Hess RM (1968) Surgical risk as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 28:14–20
Kreitschmann-Andermahr I, Poll E, Hutter BO, Reineke A, Kristes S, Gilsbach JM, Saller B (2007) Quality of life and psychiatric sequelae following aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: does neuroendocrine dysfunction play a role? Clin Endocrinol 66:833–837
Kutlubaev MA, Barugh AJ, Mead GE (2012) Fatigue after subarachnoid haemorrhage: a systematic review. J Psychosom Res 72:305–310
Lai T, Kallikorm R, Salupere R, Kiivet R (2001) Health related quality of life in chronic diseases in Estonia (in Estonian). Eesti Arst 80:450–455
Lindberg M (1995) Quality of life after subarachnoid haemorrhage, and its relationship to impairments, disabilities and depression. Scand J Occup Ther 2:105–112
Matsi A, Oja L (2009) Estonian health interview survey 2006 tables. Tervise Arengu Instituut, Tallinn
McHorney CA, Ware JE Jr, Raczek AE (1993) The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36): II. Psychometric and clinical tests of validity in measuring physical and mental health constructs. Med Care 31:247–263
McHorney CA, Ware JE Jr, Lu JF, Sherbourne CD (1994) The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36): III. Tests of data quality, scaling assumptions, and reliability across diverse patient groups. Med Care 32:40–66
Meyer B, Ringel F, Winter Y, Spottke A, Gharevi N, Dams J, Balzer-Geldsetzer M, Mueller IK, Klockgether T, Schramm J, Urbach H, Dodel R (2010) Health-related quality of life in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis 30:423–431
Morris PG, Wilson JT, Dunn L (2004) Anxiety and depression after spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 54:47–52
Noble AJ, Baisch S, Mendelow AD, Allen L, Kane P, Schenk T (2008) Posttraumatic stress disorder explains reduced quality of life in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients in both the short and long term. Neurosurgery 63:1095–1104
Noble AJ, Schenk T (2010) Which variables help explain the poor health-related quality of life after subarachnoid hemorrhage? A meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 66:772–783
Ogden JA, Utley T, Mee EW (1997) Neurological and psychosocial outcome 4 to 7 years after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 41:25–34
Oöpik P, Aluoja A, Kalda R, Maaroos HI (2006) Screening for depression in primary care. Fam Pract 23:693–698
Passier PE, Post MW, van Zandvoort MJ, Rinkel GJ, Lindeman E, Visser-Meily JM (2011) Predicting fatigue 1 year after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurol 258:1091–1097
Passier PE, Visser-Meily JM, van Zandvoort MJ, Rinkel GJ, Lindeman E, Post MW (2012) Predictors of long-term health-related quality of life in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. NeuroRehabilitation 30:137–145
Passier PE, Visser-Meily JM, Rinkel GJ, Lindeman E, Post MW (2012) Determinants of health-related quality of life after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review. Qual Life Res. doi:10.1007/s11136-012-0236-1
Powell J, Kitchen N, Heslin J, Greenwood R (2002) Psychosocial outcomes at three and nine months after good neurological recovery from aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: predictors and prognosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72:772–781
Powell J, Kitchen N, Heslin J, Greenwood R (2004) Psychosocial outcomes at 18 months after good neurological recovery from aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1119–1124
Rinkel GJE, Algra A (2011) Long-term outcomes of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol 10:349–356
Scharbrodt W, Stein M, Schreiber V, Böker DK, Oertel MF (2009) The prediction of long-term outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage as measured by the short form-36 health survey. J Clin Neurosci 16:1409–1413
Schuiling WJ, Rinkel GJ, Walchenbach R, de Weerd AW (2005) Disorders of sleep and wake in patients after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 36:578–582
Taft C, Karlsson J, Sullivan M (2001) Do SF-36 summary component scores accurately summarize subscale scores? Qual Life Res 10:395–401
Van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJA, van Gijn J (1988) Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 19:604–607
Visser-Meily JM, Rhebergen ML, Rinkel GJ, van Zandvoort MJ, Post MW (2009) Long-term health-related quality of life after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: relationship with psychological symptoms and personality characteristics. Stroke 40:1526–1529
Wermer MJ, Kool H, Albrecht KW, Rinkel GJ (2007) Aneurysm screening after treatment for ruptured aneurysms study group. Subarachnoid hemorrhage treated with clipping: long-term effects on employment, relationships, personality, and mood. Neurosurgery 60:91–97
Wong GK, Poon WS, Boet R, Chan MT, Gin T, Ng SC, Zee BC (2011) Health-related quality of life after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: profile and clinical factors. Neurosurgery 68:1556–1561
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vetkas, A., Lepik, T., Eilat, T. et al. Emotional health and quality of life after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir 155, 1107–1114 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1683-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1683-3