Abstract
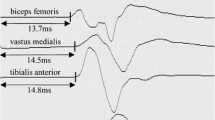
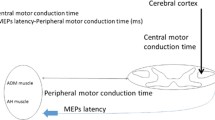
The pathogenesis of neurogenic claudication is thought to lie in relative ischemia of cauda equina roots during exercise. In this study we will evaluate the effect of the transient ischemia brought on by exercise on motor conduction in patients suffering from lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). We will also evaluate the sensitivity of motor evoked potentials (MEPs) in detecting motor conduction abnormalities before and after the onset of neurogenic claudication. Thirty patients with LSS and 19 healthy volunteers were enrolled in the study. All LSS patients had a history of neurogenic claudication and the diagnosis was confirmed with a CT myelogram. Both groups underwent a complete electrophysiological evaluation of the lower extremities. The motor evoked potential latency time (MEPLT) and the peripheral motor conduction time (PMCT) were measured. The subjects were asked to walk on a flat surface until their symptoms were reproduced. A new set of electrophysiological tests was then performed. Exercise did not produce claudication in any of the control group subjects. Twenty-seven patients did have claudication. The pre-exercise MEPLT and nerve conduction studies in the control group fell within the normal range. In the patient group, 19 patients had increased baseline values for MEPLT to at least one muscle. There was a significant difference between the MEPLT and the PMCT values measured before and after exercise in the patients with signs of neurological deficit. This difference was not found to be significant in patients without neurological deficits (t-test P < 0.05). It may be concluded that exercise increases the sensitivity of MEPs in detecting the roots under functional compression in LSS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 August 1998 Revised: 3 May 1999 Accepted: 14 July 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baramki, H., Steffen, T., Schondorf, R. et al. Motor conduction alterations in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis following the onset of neurogenic claudication. E Spine J 8, 411–416 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005860050196
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005860050196