Abstract
Purpose
To prospectively investigate the long-term clinical outcomes of microendoscopic laminotomy (MEL) in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) with and without degenerative spondylolisthesis (DS).
Methods
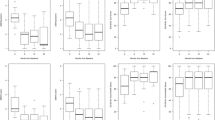
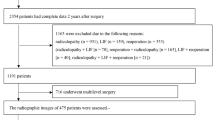
In total, 159 patients (mean age, 68 years) who had undergone MEL for single-level LSS at L4/5 at our institute were recruited and followed-up for 5 years. Patients with and without DS were assigned to the DS (n = 71) and control (n = 88) groups, respectively. In addition to slippage rate, Japanese orthopedic association (JOA), recovery rate, short-form 36 (SF-36), and Roland–Morris disability questionnaire (RDQ) values were evaluated preoperatively and 5 years postoperatively. All parameters were analyzed by Student’s t test, with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
Results
Of 159 patients, 12 were lost to follow-up (follow-up rate, 92.5 %); moreover, 15 patients were excluded because of death, cerebral infarction, dementia, or terminal cancer. Thus, 132 patients (DS group: 61, control group: 71) were finally examined. No significant differences were found in preoperative JOA, JOA recovery rate, RDQ, and SF-36 values between groups. The slippage rate in the DS group was 18.1 % preoperatively and 16.8 % at 5 years postoperatively (p > 0.05). There was no significant increase in instability in those with DS following MEL. Progressive spinal instability was noted in six patients (9.8 %) and five patients (7.0 %) in the DS and control groups, respectively (p > 0.05). Moreover, the success rate of MEL was good/excellent in 70 %, fair in 20 %, and poor in 10 % of patients in both groups.
Conclusion
MEL showed similar outcomes in patients with DS and in those without DS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amundsen T, Weber H, Nordal HJ, Magnaes B, Abdelnoor M, Lilleas F (2000) Lumbar spinal stenosis: conservative or surgical management? A prospective 10-year study. Spine 25:1424–1435
Athiviraham A, Yen D (2007) Is spinal stenosis better treated surgically or nonsurgically? Clin Orthop Relat Res 458:90–93
Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD et al (2007) Surgical versus nonsurgical treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. N Engl J Med 356:2257–2270
Perez-Cruet MJ, Foley KT, Isaacs RE, Rice-Wyllie L, Wellington R, Smith MM (2002) Microendoscopic lumbar discectomy: technical note. Neurosurgery 51:S129–S136
Khoo LT, Fessler RG (2002) Microendoscopic decompressive laminotomy for the treatment of lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery 51:S146–S154
Pao JL, Chen WC, Chen PQ (2009) Clinical outcomes of microendoscopic decompressive laminotomy for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J 18:672–678
Minamide A, Yoshida M, Yamada H, Nakagawa Y, Kawai M, Maio K, Hashizume H, Iwasaki H, Tsutsui S (2013) Endoscope-assisted spinal decompression surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: technical note. J Neurosurg Spine 19(6):664–671
Aebi M (2005) The adult scoliosis. Eur Spine J 14:925–948
Nakamura M, Miyamoto K, Shimizu K (2003) Validation of the Japanese version of the Roland–Morris disability questionnaire for Japanese patients with lumbar spinal diseases. Spine 28:2414–2418
Fukuhara S, Bito S, Green J, Hsiao A, Kurokawa K (1998) Translation, adaptation, and validation of the SF-36 for use in Japan. J Clin Epidemiol 51:1037–1044
Abumi K, Panjabi MM, Kramer KM, Duranceau J, Oxland T, Crisco JJ (1990) Biomechanical evaluation of lumbar spinal stability after graded facetectomies. Spine 15:1142–1147
Haher TR, O’Brien M, Dryer JW, Nucci R, Zipnick R (1994) The role of the lumbar facet joints in spinal stability. Identification of alternative paths of loading. Spine 19:2667–2670 (discussion 2671)
Bridwell KH, Sedgewick TA, O’Brien MF, Lenke LG, Baldus C (1993) The role of fusion and instrumentation in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 6:461–472
Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT (1991) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:802–808
Johnsson KE, Redlund-Johnell I, Udén A, Willner S (1989) Preoperative and postoperative instability in lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine 14:591–593
Kornblum MB, Fischgrund JS, Herkowitz HN, Abraham DA, Berkower DL, Ditkoff JS (2004) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Spine 29:726–733
Martin CR, Gruszczynski AT, Braunsfurth HA, Fallatah SM, O’Neil J, Wai EK (2007) The surgical management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a systematic review. Spine 32:1791–1798
Ghiselli G, Wang JC, Bhatia NN, Hsu WK, Dawson EG (2004) Adjacent segment degeneration in the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A:1497–1503
Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, Hoff JT, McGillicuddy JE (2004) Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine 29:1938–1944
Kauppila LI, Eustace S, Kiel DP, Felson DT, Wright AM (1998) Degenerative displacement of lumbar vertebrae. A 25-years follow-up study in Framingham. Spine 23:1868–1873
Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Morizono Y, Masuda A, Demirtas AM (1990) Natural history of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Pathogenesis and natural course of slippage. Spine 15:1204–1210
Bolesta MJ, Bohlman HH (1989) Degenerative spondylolisthesis. Instr Course Lec 38:157–165
Newman PH (1976) Stenosis of the lumbar spine in spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 115:116–121
Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Farfan HF (1982) Instability of the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res 165:110–123
Matsunaga S, Ijiri K, Hayashi K (2000) Nonsurgically managed patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis: a 10 to 18-year follow-up study. J Neurosurg 93:194–198
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings special in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minamide, A., Yoshida, M., Yamada, H. et al. Clinical outcomes after microendoscopic laminotomy for lumbar spinal stenosis: a 5-year follow-up study. Eur Spine J 24, 396–403 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3599-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3599-x