Abstract
Introduction
To our knowledge, thoracolumbar burst fractures with a neurological deficit treated with posterior decompression and interlaminar fusion have never been reported. Our study was to assess the outcome of posterior decompression and interlaminar fusion in treating thoracolumbar burst fractures with a neurological deficit.
Materials and methods
Forty-one patients suffering from thoracolumbar burst fractures with a neurological deficit were included this study. All patients were treated with posterior decompression, interlaminar fusion and short-segment fixation of the vertebrae above and below the fracture level and the fractured vertebrae.
Results
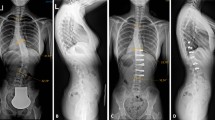
All patients were followed up for at least 24 months after surgery. Operative time and blood loss averaged 72 min and 325 ml, respectively. Thirty-eight patients with incomplete neurological lesions improved, by at least one American Spine Injury Association grade, whereas no neurological deterioration was observed in any case. Overall sagittal alignment improved from an average preoperative 22.4°–4.6° kyphosis at the final follow-up observation. The anterior vertebral body height ratio improved from 0.61 before surgery to 0.90 after surgery, whereas posterior vertebral body height ratio improved from 0.90 to 0.95. Spinal canal encroachment was reduced from an average 61.5% before surgery to 8.7% after surgery. Interlaminar radiological fusion was achieved within 6–8 months after surgery. No instrumentation failure was found in any patients.
Conclusion
Posterior decompression, interlaminar fusion with posterior short-segment fixation provided excellent immediate reduction for traumatic segmental kyphosis and significant spinal canal clearance, and restored vertebral body height in the fracture level in patients with a thoracolumbar burst fracture and associated neurological deficit.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denis F (1983) The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine 8:817–831
Marco RA, Kushwaha VP (2009) Thoracolumbar burst fractures treated with posterior decompression and pedicle screw instrumentation supplemented with balloon-assisted vertebroplasty and calcium phosphate reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:20–28
Dai LY, Jiang LS, Jiang SD (2009) Posterior short-segment fixation with or without fusion for thoracolumbar burst fractures. A five to seven-year prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:1033–1041
Dai LY, Jiang LS, Jiang SD (2009) Anterior-only stabilization using plating with bone structural autograft versus titanium mesh cages for two- or three-column thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective randomized study. Spine 34:1429–1435
Tezer M, Erturer RE, Ozturk C, Ozturk I, Kuzgun U (2005) Conservative treatment of fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. Int Orthop 29:78–82
Wood K, Buttermann G, Mehbod A, Garvey T, Jhanjee R, Sechriest V, Butterman G (2003) Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of a thoracolumbar burst fracture without neurological deficit. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A:773–781
Tezeren G, Kuru I (2005) Posterior fixation of thoracolumbar burst fracture: short-segment pedicle fixation versus long-segment instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech 18:485–488
Alanay A, Acaroglu E, Yazici M, Oznur A, Surat A (2001) Short-segment pedicle instrumentation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: does transpedicular intracorporeal grafting prevent early failure? Spine 26:213–217
Cho DY, Lee WY, Sheu PC (2003) Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures with polymethyl methacrylate vertebroplasty and short-segment pedicle screw fixation. Neurosurgery 53:1354–1360
Kramer DL, Rodgers WB, Mansfield FL (1995) Transpedicular instrumentation and short-segment fusion of thoracolumbar fractures: a prospective study using a single instrumentation system. J Orthop Trauma 9:499–506
McCormack T, Karaikovic E, Gaines RW (1994) The load sharing classification of spine fractures. Spine 19:1741–1744
Guven O, Kocaoglu B, Bezer M, Aydin N, Nalbantoglu U (2009) The use of screw at the fracture level in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech 22:417–421
Magerl F, Aebi M, Gertzbein SD, Harms J, Nazarian S (1994) A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries. Eur Spine J 3:184–201
Korovessis PG, Baikousis A, Stamatakis M (1997) Use of the Texas Scottish Rite Hospital instrumentation in the treatment of thoracolumbar injuries. Spine 22:882–888
Chow GH, Nelson BJ, Gebhard JS, Brugman JL, Brown CW, Donaldson DH (1996) Functional outcome of thoracolumbar burst fractures managed with hyperextension casting or bracing and early mobilization. Spine 21:2170–2175
Alvine GF, Swain JM, Asher MA, Burton DC (2004) Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures with variable screw placement or Isola instrumentation and arthrodesis: case series and literature review. J Spinal Disord Tech 17:251–264
Chen JF, Lee ST (2004) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of thoracolumbar spine bursting fracture. Surg Neurol 62:494–500
de Peretti F, Hovorka I, Cambas PM, Nasr JM, Argenson C (1996) Short device fixation and early mobilization for burst fractures of the thoracolumbar junction. Eur Spine J 5:112–120
Kaneda K, Taneichi H, Abumi K, Hashimoto T, Satoh S, Fujiya M (1997) Anterior decompression and stabilization with the Kaneda device for thoracolumbar burst fractures associated with neurological deficits. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79:69–83
Sasso RC, Best NM, Reilly TM, McGuire RA Jr (2005) Anterior-only stabilization of three-column thoracolumbar injuries. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(Suppl):S7–S14
Wood KB, Bohn D, Mehbod A (2005) Anterior versus posterior treatment of stable thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficit: a prospective, randomized study. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(Suppl):S15–S23
Dai LY, Ding WG, Wang XY, Jiang LS, Jiang SD, Xu HZ (2009) Assessment of ligamentous injury in patients with thoracolumbar burst fractures using MRI. J Trauma 66:1610–1615
Briem D, Lehmann W, Ruecker AH, Windolf J, Rueger JM, Linhart W (2004) Factors influencing the quality of life after burst fractures of the thoracolumbar transition. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124:461–468
Muller U, Berlemann U, Sledge J, Schwarzenbach O (1999) Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficit by indirect reduction and posterior instrumentation: bisegmental stabilization with monosegmental fusion. Eur Spine J 8:284–289
Vaccaro AR, Rihn JA, Saravanja D, Anderson DG, Hilibrand AS, Albert TJ, Fehlings MG, Morrison W, Flanders AE, France JC, Arnold P, Anderson PA, Friel B, Malfair D, Street J, Kwon B, Paquette S, Boyd M, Dvorak MF, Fisher C (2009) Injury of the posterior ligamentous complex of the thoracolumbar spine: a prospective evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging. Spine 34:E841–E847
Li KC, Hsieh CH, Lee CY, Chen TH (2005) Transpedicle body augmenter: a further step in treating burst fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:119–125
McLain RF, Sparling E, Benson DR (1993) Early failure of short-segment pedicle instrumentation for thoracolumbar fractures. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75:162–167
Parker JW, Lane JR, Karaikovic EE, Gaines RW (2000) Successful short-segment instrumentation and fusion for thoracolumbar spine fractures: a consecutive 41/2-year series. Spine 25:1157–1170
Mahar A, Kim C, Wedemeyer M, Mitsunaga L, Odell T, Johnson B, Garfin S (2007) Short-segment fixation of lumbar burst fractures using pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture. Spine 32:1503–1507
Reinhold M, Knop C, Beisse R, Audige L, Kandziora F, Pizanis A, Pranzl R, Gercek E, Schultheiss M, Weckbach A, Buhren V, Blauth M (2010) Operative treatment of 733 patients with acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries: comprehensive results from the second, prospective, internet-based multicenter study of the Spine Study Group of the German Association of Trauma Surgery. Eur Spine J 19:1657–1676
Aebi M, Etter C, Kehl T, Thalgott J (1987) Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with the internal spinal skeletal fixation system. Indications, techniques, and first results of treatment. Spine 12:544–551
Dick W, Kluger P, Magerl F, Woersdorfer O, Zach G (1985) A new device for internal fixation of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine fractures: the ‘fixateur interne’. Paraplegia 23:225–232
Daniaux H, Seykora P, Genelin A, Lang T, Kathrein A (1991) Application of posterior plating and modifications in thoracolumbar spine injuries. Indication, techniques, and results. Spine 16:S125–S133
Ebelke DK, Asher MA, Neff JR, Kraker DP (1991) Survivorship analysis of VSP spine instrumentation in the treatment of thoracolumbar and lumbar burst fractures. Spine 16:S428–S432
Bernucci C, Maiello M, Silvestro C, Francaviglia N, Bragazzi R, Pau A, Viale GL (1994) Delayed worsening of the surgical correction of angular and axial deformity consequent to burst fractures of the thoracolumbar or lumbar spine. Surg Neurol 42:23–25
Crawford RJ, Askin GN (1994) Fixation of thoracolumbar fractures with the Dick fixator: the influence of transpedicular bone grafting. Eur Spine J 3:45–51
Hart DA, Archambault JM, Kydd A, Reno C, Frank CB, Herzog W (1998) Gender and neurogenic variables in tendon biology and repetitive motion disorders. Clin Orthop Relat Res 351:44–56
Speth MJ, Oner FC, Kadic MA, de Klerk LW, Verbout AJ (1995) Recurrent kyphosis after posterior stabilization of thoracolumbar fractures. 24 cases treated with a Dick internal fixator followed for 1.5–4 years. Acta Orthop Scand 66:406–410
Knop C, Fabian HF, Bastian L, Blauth M (2001) Late results of thoracolumbar fractures after posterior instrumentation and transpedicular bone grafting. Spine 26:88–99
Sjostrom L, Jakobsson O, Karlstrom G, Pech P (1992) Transpedicular bone grafts misplaced into the spinal canal. J Orthop Trauma 6:376–378
Tagil M, Johnsson R, Stromqvist B, Aspenberg P (1999) Incomplete incorporation of morselized and impacted autologous bone graft: a histological study in 4 intracorporally grafted lumbar fractures. Acta Orthop Scand 70:555–558
Marco RA, Meyer BC, Kushwaha VP (2010) Thoracolumbar burst fractures treated with posterior decompression and pedicle screw instrumentation supplemented with balloon-assisted vertebroplasty and calcium phosphate reconstruction. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(Suppl 1 Pt 1):67–76
Dai LY (2001) Remodeling of the spinal canal after thoracolumbar burst fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res (382):119–123
de Klerk LW, Fontijne WP, Stijnen T, Braakman R, Tanghe HL, van Linge B (1998) Spontaneous remodeling of the spinal canal after conservative management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine 23:1057–1060
Leferink VJ, Zimmerman KW, Veldhuis EF, ten Vergert EM, ten Duis HJ (2001) Thoracolumbar spinal fractures: radiological results of transpedicular fixation combined with transpedicular cancellous bone graft and posterior fusion in 183 patients. Eur Spine J 10:517–523
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (08411950100).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, CM., Wang, YR., Jiang, SD. et al. Thoracolumbar burst fractures with a neurological deficit treated with posterior decompression and interlaminar fusion. Eur Spine J 20, 2195–2201 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-1875-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-1875-6