Abstract
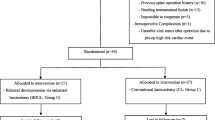
The aim of our study is to evaluate the results and effectiveness of bilateral decompression via a unilateral approach in the treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. We have conducted a prospective study to compare the midterm outcome of unilateral laminotomy with unilateral laminectomy. One hundred patients with 269 levels of lumbar stenosis without instability were randomized to two treatment groups: unilateral laminectomy (Group 1), and laminotomy (Group 2). Clinical outcomes were assessed with the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) and Short Form–36 Health Survey (SF-36). Spinal canal size was measured pre- and postoperatively. The spinal canal was increased to 4–6.1-fold (mean 5.1 ± SD 0.8-fold) the preoperative size in Group 1, and 3.3–5.9-fold (mean 4.7 ± SD 1.1-fold) the preoperative size in Group 2. The mean follow-up time was 5.4 years (range 4–7 years). The ODI scores decreased significantly in both early and late follow-up evaluations and the SF-36 scores demonstrated significant improvement in late follow-up results in our series. Analysis of clinical outcome showed no statistical differences between two groups. For degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis unilateral approaches allowed sufficient and safe decompression of the neural structures and adequate preservation of vertebral stability, resulted in a highly significant reduction of symptoms and disability, and improved health-related quality of life.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LSS:
-
Lumbar spinal stenosis
- ODI:
-
Oswestry disability index
- SF-36:
-
36-item short-form health survey
References
Adachi K, Futami T, Ebihara A, Yamaya T, Kasai N, Nakazawa T, et al (2003) Spinal canal enlargement procedure by restorative laminoplasty for the treatment of lumbar canal stenosis. Spine J 3(6):471–478
Adams MA, Hutton WC, Stott JR (1980) The resistance to flexion of the lumbar intervertebral joint. Spine 5(3):245–253
Adams MA, Hutton WC (1983) The mechanical function of the lumbar apophyseal joints. Spine 8(3):327–330
Airaksinen O, Herno A, Kaukanen E, Saari T, Sihvonen T, Suomalainen O (1996) Density of lumbar muscles 4 years after decompressive spinal surgery. Eur Spine J 5(3):193–197
Airaksinen O, Herno A, Turunen V, Saari T, Suomlainen O (1997) Surgical outcome of 438 patients treated surgically for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine 22(19):2278–2282
Aryanpur J, Ducker T (1990) Multilevel lumbar laminotomies: an alternative to laminectomy in the treatment of lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery 26(3):429–432 discussion 433
Askar Z, Wardlaw D, Choudhary S, Rege A (2003) A ligamentum flavum-preserving approach to the lumbar spinal canal. Spine 28(19):E385–E390
Cammisa FP Jr, Girardi FP, Sangani PK, Parvataneni HK, Cadag S, Sandhu HS (2000) Incidental durotomy in spine surgery. Spine 25(20):2663–2667
Deyo RA, Nachemson A, Mirza SK (2004) Spinal-fusion surgery-the case for restraint. N Engl J Med 350(7):722–726
diPiero CG, Helm GA, Shaffrey CI, Chadduck JB, Henson SL, Malik JM et al (1996) Treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis by extensive unilateral decompression and contralateral autolougs bone fusion: operative technique and results. J Nuerosurg 84(2):166–173
Epstein NE (1998) Decompression in the surgical management of degenerative spondylolisthesis: advantages of a conservative approach in 290 patients. J Spinal Disord 11(2):116–122 discussion 123
Epstein NE, Maldonado VC, Cusick JF (1998) Symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis. Surg Neurol 50(1):3–10
Fox MW, Onofrio BM, Hanssen AD (1996) Clinical outcomes and radiological instability following decompressive lumbar laminectomy for degenerative spinal stenosis: a comparison of patients undergoing concomitant arthrodesis versus decompression alone. J Neurosurg 85(5):793–802
Goel VK, Fromknecht SJ, Nishiyama K, Weinstein J, Liu YK (1985) The role of the lumbar spinal elements in flexion. Spine 10(6):516–523
Grob D, Humke T, Dvorak J (1995) Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Decompression with and without arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77(7):1036–1041
Guiot BH, Khoo LT, Fessler RG (2002) A minimally invasive technique for decompression of the lumbar spine. Spine 27(4):432–438
Haba K, Ikeda M, Soma M, Yamashima T (2005) Bilateral decompression of multilevel lumbar spinal stenosis through a unilateral approach. J Clinical Neurosci 12(2):169–171
Herno A, Saari T, Suomalainen O, Airaksinen O (1999) The degree of decompressive relief and its relation to clinical outcome in patients undergoing surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine 24(10):1010–1014
Herron LD, Mangelsdorf C (1991) Lumbar spinal stenosis: results of surgical treatment. J Spinal Disord 4(1):26–33
Hindle RJ, Pearcy MJ, Cross A (1990) Mechanical function of the human lumbar interspinous and supraspinous ligaments. J Biomed Eng 12(4):340–344
Hopp E, Tsou PM (1988) Postdecompression lumbar instability. Clin Orthop Relat Res 227:143–151
Javid MJ, Hadar EJ (1998) Long-term follow-up review of patients who underwent laminectomy for lumbar stenosis: a prospective study. J Neurosurg 89(1):1–7
Ji YC, Kim YB, Hwang SN, Park SW, Kwon JT, Min BK (2005) Efficacy of Unilateral Laminectomy for bilateral decompression in elderly lumbar spinal stenosis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 37:410–415
Johnsson KE, Willner S, Johnsson K (1986) Postoperative instability after decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine 11(2):107–110
Kalbarczyk A, Lukes A, Seiler RW (1998) Surgical treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis in the elderly. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140(7):637–641
Katz JN, Lipson SJ, Larson MG, McInnes JM, Fossel AH, Liang MH (1991) The outcome of decompressive laminectomy for degenerative lumbar stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73(6):809–816
Khoo LT, Fessler RG (2002) Microendoscopic decompressive laminotomy for the treatment of lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery 51(5 Suppl):S146–S154
Kleeman TJ, Hiscoe AC, Berg EE (2000) Patient outcomes after minimally destabilizing lumbar stenosis decompression: the “Port-Hole” technique. Spine 25(7):865–870
Lin PM (1982) Internal decompression for multiple levels of lumbar spinal stenosis: a technical note. Neurosurgery 11(4):546–549
Lipson SJ (2004) Spinal-fusion surgery-advances and concerns. N Engl J Med 350(7):643–644
Mackay DC, Wheelwright EF (1998) Unilateral fenestration in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. Br J Neurosurg 12(6):556–558
Mariconda M, Fava R, Gatto A, Longo C, Milano C (2002) Unilateral laminectomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis: a prospective comparative study with conservatively treated patients. J Spinal Disord Tech 15(1):39–46
Mayer TG, Vanharanta H, Gatchel RJ, Mooney V, Barnes D, Judge L, et al (1989) Comparison of CT scan muscle measurements and isokinetic trunk strength in postoperative patients. Spine 14(1):33–6
McCulloch JA (1991) Microsurgical spinal laminotomies in the adult spine: principles and practice. J.W. Frymoyer (ed) Raven Press, New York
Nakai O, Ookawa A, Yamaura I (1991) Long-term roentgenographic and functional changes in patients who were treated with wide fenestration for central lumbar stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73(8):1184–1191
Palmer S, Turner R, Palmer R (2002) Bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis involving a unilateral approach with microscope and tubular retractor system. J Neurosurg 97(2 Suppl):213–217
Pinar R (2005) Reliability and construct validity of the SF-36 in Turkish cancer patients. Qual Life Res 14(1):259–264
Prestar FJ (1982) Morphology and function of the interspinal ligaments and the supraspinal ligament of the lumbar portion of the spine. Morphol Med 2:53–58
Postacchini F, Cinotti G, Perugia D, Gumina S (1993) The surgical treatment of central lumbar stenosis. Multiple laminotomy compared with total laminectomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75(3):386–392
See DH, Kraft GH (1975) Electromyography in paraspinal muscles following surgery for root compression. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 56(2):80–83
Sengupta DK, Herkowitz HN (2003) Lumbar spinal stenosis. Treatment strategies and indications for surgery. Orthop Clin North Am 34(2):281–295
Sihvonen T, Herno A, Paljarva L, Airaksinen O, Patanen J, Tapaninaho A (1993) Local denervation atrophy of paraspinal muscles in postoperative failed back syndrome. Spine 18(5):575–581
Silvers HR, Lewis PJ, Asch HL (1993) Decompressive lumbar laminectomy for spinal stenosis. J Neurosurg 78(5):695–701
Spetzger U, Bertalanffy H, Naujokat C, von Keyserlingk DG, Gilsbach JM (1997) Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. Part I: Anatomical and surgical considerations. Acta Neurochir 139(5):392–396
Spetzger U, Bertalanffy H, Reinges MH, Gilsbach JM (1997) Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. Part II: Clinical experiences. Acta Neurochir 139(5):397–403
Thomas NW, Rea GL, Pikul BK, Mervis LJ, Irsik R, McGregor JM (1997) Quantitative outcome and radiographic comparisons between laminectomy and laminotomy in the treatment of acquired lumbar stenosis. Neurosurgery 41(3):567–574 discussion 574–75
Thome C, Zevgaridis D, Leheta O, Bazner H, Pockler-Schoniger C, Wohrle J et al (2005) Outcome after less-invasive decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis: a randomized comparison of unilateral laminotomy, bilateral laminotomy, and laminectomy. J Neurosurg Spine 3(2):129–141
Tsai RY, Yang RS, Bray RS Jr (1998) Microscopic laminotomies for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 11(5):389–394
Tuite GF, Stern JD, Doran SE, Papadopoulos SM, McGillicuddy JE, Oyedijo DI et al (1994) Outcome after laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis: Part I: Clinical correlations. J Neurosurg 81(5):699–706
Tuite GF, Doran SE, Stern JD, McGillicuddy JE, Papadopoulos SM, Lundquist CA et al (1994) Outcome after laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis. Part II: Radiographic changes and clinical correlations. J Neurosurg 81(5):707–715
Turner JA, Ersek M, Herron L, Deyo R (1992) Surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Attempted meta-analysis of the literature. Spine 17(1):1–8
Wang JC, Bohlman HH, Riew KD (1998) Dural tears secondary to operations on the lumbar spine. Management and results after a two-year-minimum follow-up of eighty-eight patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80(12):1728–1732
Weiner BK, Walker M, Brower RS, McCulloch JA (1999) Microdecompression for lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine 24(21):2268–2272
White AA, Panjabi MM (1990) Clinical biomechanics of the spine, 2nd edn. JB Lippincott, Philadelphia
Yakut E, Duger T, Oksuz C, Yorukan S, Ureten K, Turan D, et al (2004) Validation of the Turkish version of the Oswestry Disability Index for patients with low back pain. Spine 29(5):581–585 discussion 585
Yone K, Sakou T (1999) Usefulness of Posner’s definition of spinal instability for selection of surgical treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 12(1):40–44
Young S, Veerapen R, O’Laoire SA (1988) Relief of lumbar canal stenosis using multilevel subarticular fenestrations as an alternative to wide laminectomy: preliminary report. Neurosurgery 23(5):628–633
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çavuşoğlu, H., Kaya, R.A., Türkmenoglu, O.N. et al. Midterm outcome after unilateral approach for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis: 5-year prospective study. Eur Spine J 16, 2133–2142 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-007-0471-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-007-0471-2