Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this investigation was to describe the renal outcome and to identify risk factors for acute kidney injury (AKI), as defined by the Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN), during aortic arch surgery (AAS) under deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA).
Methods
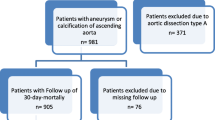
A retrospective and observational study has been performed. One hundred thirty-five patients requiring AAS under DHCA were studied.
Results
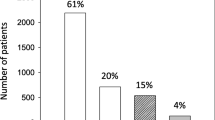
Seventy-one patients (52.6%) developed AKI during the postoperative period. A logistic regression analysis identified three independent risk factors for AKI: preoperative hypertension (HT), emergency surgery, and duration of DHCA. Renal replacement therapy (RRT) was required in four patients (3.0%). The postoperative mortality rate among the patients with AKI was 2.8%, which was not statistically different from the rate of 1.6% observed in the non-AKI group (P = 0.62).
Conclusions
A high incidence of AKI during AAS under DHCA was confirmed. Because AKI is highly associated with aortic surgery, novel approaches for protecting the kidneys other than deep hypothermia are needed. The logistic regression model identified HT, emergency surgery, and duration of DHCA as independent risk factors for AKI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Brien MM, Gonzales R, Shroyer AL, Grunwald GK, Daley J, Henderson WG, Khuri SF, Anderson RJ. Modest serum creatinine elevation affects adverse outcome after general surgery. Kidney Int. 2002;62:585–92.
Estrera AL, Miller CC 3rd, Huynh TT, Porat EE, Safi HJ. Replacement of the ascending and transverse aortic arch: determinants of long-term survival. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;74:1058–64.
Arnaoutakis GJ, Bihorac A, Martin TD, Hess PJ Jr, Klodell CT, Ejaz AA, Garvan C, Tribble CG, Beaver TM. RIFLE criteria for acute kidney injury in aortic arch surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;134:1554–60.
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A. Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2007;11:R31.
Griepp RB, Stinson EB, Hollingsworth JF, Buehler D. Prosthetic replacement of the aortic arch. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1975;70:1051–63.
Goldstein DJ, DeRosa CM, Mongero LB, Weinberg AD, Michler RE, Rose EA, Oz MC, Smith CR. Safety and efficacy of aprotinin under conditions of deep hypothermia and circulatory arrest. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995;110:1615–21.
Mora Mangano CT, Neville MJ, Hsu PH, Mignea I, King J, Miller DC. Aprotinin, blood loss, and renal dysfunction in deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. Circulation. 2001;104:I276–81.
Augoustides JG, Floyd TF, McGarvey ML, Ochroch EA, Pochettino A, Fulford S, Gambone AJ, Weiner J, Raman S, Savino JS, Bavaria JE, Jobes DR. Major clinical outcomes in adults undergoing thoracic aortic surgery requiring deep hypothermic circulatory arrest: quantification of organ-based perioperative outcome and detection of opportunities for perioperative intervention. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2005;19:446–52.
Augoustides JG, Pochettino A, Ochroch EA, Cowie D, Weiner J, Gambone AJ, Pinchasik D, Bavaria JE, Jobes DR. Renal dysfunction after thoracic aortic surgery requiring deep hypothermic circulatory arrest: definition, incidence, and clinical predictors. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2006;20:673–7.
Levy EM, Viscoli CM, Horwitz RI. The effect of acute renal failure on mortality. A cohort analysis. JAMA. 1996;275:1489–94.
Brezis M, Rosen S. Hypoxia of the renal medulla—its implications for disease. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:647–55.
Devarajan P. Update on mechanisms of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1503–20.
Sreeram GM, Grocott HP, White WD, Newman MF, Stafford-Smith M. Transcranial Doppler emboli count predicts rise in creatinine after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2004;18:548–51.
Black SA, Brooks MJ, Naidoo MN, Wolfe JH. Joint Vascular Research Group. Assessing the impact of renal impairment on outcome after arterial intervention: a prospective review of 1,559 patients. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2006;32:300–4.
Augoustides JG, Pochettino A, Ochroch EA, Cowie D, McGarvey ML, Weiner J, Gambone AJ, Pinchasik D, Cheung AT, Bavaria JE. Clinical predictors for prolonged intensive care unit stay in adults undergoing thoracic aortic surgery requiring deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2006;20:8–13.
Aronson S, Fontes ML, Miao Y, Mangano DT. Investigators of the Multicenter Study of Perioperative Ischemia Research Group; Ischemia Research and Education Foundation Risk index for perioperative renal dysfunction/failure: critical dependence on pulse pressure hypertension. Circulation. 2007;115:733–42.
Kumral E, Yüksel M, Büket S, Yagdi T, Atay Y, Güzelant A. Neurologic complications after deep hypothermic circulatory arrest: types, predictors, and timing. Tex Heart Inst J. 2001;28:83–8.
Mangano DT, Tudor IC, Dietzel C. Multicenter Study of Perioperative Ischemia Research Group; Ischemia Research and Education Foundation. The risk associated with aprotinin in cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:353–65.
Mangano DT, Miao Y, Vuylsteke A, Tudor IC, Juneja R, Filipescu D, Hoeft A, Fontes ML, Hillel Z, Ott E, Titov T, Dietzel C, Levin J. Investigators of the Multicenter Study of Perioperative Ischemia Research Group; Ischemia Research and Education Foundation. Mortality associated with aprotinin during 5 years following coronary artery bypass graft surgery. JAMA. 2007;297:471–9.
Fergusson DA, Hébert PC, Mazer CD, Fremes S, MacAdams C, Murkin JM, Teoh K, Duke PC, Arellano R, Blajchman MA, Bussières JS, Côté D, Karski J, Martineau R, Robblee JA, Rodger M, Wells G, Clinch J, Pretorius R. BART investigators. A comparison of aprotinin and lysine analogues in high-risk cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2319–31.
Halpenny M, Lakshmi S, O’Donnell A, O’Callaghan-Enright S, Shorten GD. Fenoldopam: renal and splanchnic effects in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. Anaesthesia. 2001;56:953–60.
Halpenny M, Rushe C, Breen P, Cunningham AJ, Boucher-Hayes D, Shorten GD. The effects of fenoldopam on renal function in patients undergoing elective aortic surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2002;19:32–9.
Roasio A, Lobreglio R, Santin A, Landoni G, Verdecchia C. Fenoldopam reduces the incidence of renal replacement therapy after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2008;22:23–6.
Swärd K, Valsson F, Odencrants P, Samuelsson O, Ricksten SE. Recombinant human atrial natriuretic peptide in ischemic acute renal failure: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:1310–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, Y., Sato, N., Kobayashi, Y. et al. Acute kidney injury during aortic arch surgery under deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. J Anesth 25, 799–804 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-011-1210-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-011-1210-8