Abstract
Purpose
The dose and time course of propofol infusion required to induce rapid sedation without oversedation during spinal anesthesia were investigated.
Methods
Forty patients scheduled for spinal and epidural anesthesia were studied. After premedication with intramuscular midazolam 0.04 mg·kg−1, an epidural catheter was inserted, followed by spinal anersthesia at L4-L5 with 0.5% hyperbaric tetracaine with epinephrine. The infusion of propofol was started with 10 mg·kg−1·h−1 and was decreased to 5 mg·kg−1·h−1 at spontaneous eye closure. According to the increase or decrease of the sedation level, the infusion does was decreased or increased to half or twice the initial dose, respectively, to keep the Observer's Assessment of Alertness Sedation (OAAS) score at 3 or 4.
Results
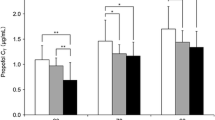
Eye closure was observed at 1.0 ± 0.4 min after the start of insusion. The maintenance insusion dose to keep the OAAS score at 3 or 4 was about 2.5 mg·kg−1·h−1.
Conclusion
Propofol infusion, starting with 10 mg·kg−1·h−1, decreasing to 5 mg·kg−1·h−1 after 1 minute, and then decreasing to 2.5 mg·kg−1·h−1 after another min induced rapid onset of sedation and kept the OAAS score at 3 or 4 during spinal anesthesia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E Wilson RN Mackenzie IS Grant (1988) ArticleTitleA comparison of propofol and midazolam by infusion to provide sedation in patients who receive spinal anaesthesia Anaesthesia 43 S91–94 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2044.1988.tb09084.x
MG Pratila ME Fischer R Alagesan R Alagesan RA Reinsel D Pratilas (1993) ArticleTitlePropofol versus midazolam for monitored sedation: a comparison of intraoperative and recovery parameters J Clin Anesth 5 268–274 Occurrence Handle8373602 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0952-8180(93)90117-W Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3szosVyntg%3D%3D
K Torigoe Y Sumiya N Shimizu Y Kobayashi R Shiratori S Ogawa (2000) ArticleTitleA new sedation technique with propofol during spinal anesthesia (in Japanese with English abstract) Masui (Jpn J Anesthesiol) 49 740–744 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvps12gtQ%3D%3D
M Nakagawa T Mammoto A Hazama T Kita T Akamatsu N Kambara T Sakai Y Kishi (2000) ArticleTitleMidazolam premedication reduces propofol requirements for sedation during regional anesthesia Can J Anaesth 47 47–49 Occurrence Handle10626718 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FptVWntg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF03020731
N Mackenzie IS Grant (1987) ArticleTitlePropofol for intravenous sedation Anaesthesia 42 3–6 Occurrence Handle3493711 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2044.1987.tb02936.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s7lsVamug%3D%3D
T Sasaki H Kato (2001) ArticleTitleThe effects of conscious sedation by propofol on respiration during abdominal hysterectomy under spinal anesthesia (in Japanese with English abstract) Masui (Jpn J Anesthesiol) 50 491–495 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzmtlKgtQ%3D%3D
AG Doufas M Bakhshandeh AR Bjorksten R Greif DI Sessler (2001) ArticleTitleAutomated responsiveness test (ART) predicts loss of consciousness and adverse physiologic responses during propofol conscious sedation Anesthesiology 94 585–592 Occurrence Handle11379677 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000542-200104000-00010 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtVyisb8%3D
IG Kestin PB Harvey C Nixon (1990) ArticleTitlePsychomotor recovery after three methods of sedation during spinal anaesthesia Br J Anaesth 64 675–681 Occurrence Handle2116156 Occurrence Handle10.1093/bja/64.6.675 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3czjsV2gtw%3D%3D
G Rosa G Conti P Orsi F D'Alessandro I La Rossa G Di Giugno A Gasparetto (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of low-dose propofol administration on central respiratory drive, gas exchanges and respiratory pattern Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 36 128–131 Occurrence Handle1549931 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK387pslamsg%3D%3D
SM Geddes WM Gray AJ Asbury (1994) ArticleTitleSkin conductance responses in patients sedated with midazolam or propofol Br J Anaesth 73 345–349 Occurrence Handle7946862 Occurrence Handle10.1093/bja/73.3.345 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M%2FjtlyjtQ%3D%3D
VLBO Lim M White CJ Kalkman FHM Engbers PC Makkes (1998) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetics of propofol during conscious sedation using target-controlled infusion in anxious patients undergoing dental treatment Br J Anaesth 80 324–331
A de Roode JMA van Gerven RC Schoemaker FHM Engbers W Olieman JR Kroon AF Cohen JG Bovill (2000) ArticleTitleA comparison of the effects of propofol and midazolam on memory during two levels of sedation by using target-controlled infusion Anesth Analg 91 1056–1061 Occurrence Handle11049883 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000539-200011000-00003 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXot1Sltb8%3D
IG Skipsey JR Colvin N Mackenzie GNC Kenny (1993) ArticleTitleSedation with propofol during surgery under local blockade. Assessment of a target-controlled infusion system Anaesthesia 48 210–213 Occurrence Handle8460797 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2044.1993.tb06903.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s3ht12ntg%3D%3D
PH Manninen ASH Chan D Papworth (1997) ArticleTitleConscious sedation for interventional neuroradiology: a comparison of midazolam and propofol infusion Can J Anaesth 44 26–30 Occurrence Handle8988820 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s7kt1Oqug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF03014320
C Newson GP Joshi R Victory PF White (1995) ArticleTitleComparison of propofol administration technique for sedation during monitored anesthesia care Anesth Analg 81 486–491 Occurrence Handle7653809 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000539-199509000-00010 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXos1Gmtb4%3D
L Smith TG Monk PF White Y Ding (1994) ArticleTitlePropofol infusion during regional anesthesia: sedative, amnesic, and anxiolytic properties Anesth Analg 79 313–319 Occurrence Handle7639371 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2Mzms1KjtQ%3D%3D
RA Veselis RA Reinsel M Wronski P Marino WP Tong RF Bedford (1992) ArticleTitleEEG and memory effects of low-dose infusions of propofol Br J Anaesth 69 246–254 Occurrence Handle1389841 Occurrence Handle10.1093/bja/69.3.246 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XmsVGntr8%3D
T Nishiyama T Yokoyama K Hanaoka (2004) ArticleTitleSedation guidelines for midazolam infusion during combined spinal and epidural anesthesia J Clin Anesth 16 568–572 Occurrence Handle15610836 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jclinane.2004.02.004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhtVyqsLzK
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Nishiyama, T. Propofol infusion for sedation during spinal anesthesia. J Anesth 21, 265–269 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-006-0489-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-006-0489-3