Abstract
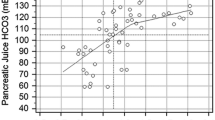
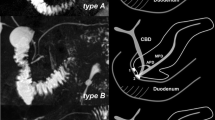
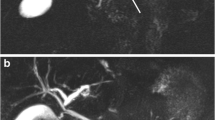
A diagnostic means of detecting chronic pancreatitis at an early stage, when the disease is still reversible, needs to be developed. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) has recently been evolving as an important tool for the evaluation of chronic pancreatitis. In patients with moderate chronic pancreatitis, the pancreatic parenchyma displays an abnormal enhancement pattern on T1-weighted sequences after gadolinium administration. The presence of a signal intensity ratio of <1.7 in the arterial phase and/or delayed peak enhancement after contrast administration has a sensitivity of 92% and a specificity of 75% for the demonstration of early chronic pancreatitis. The secretin-induced pancreatic T2 signal intensity changes are significantly reduced in patients with a mild exocrine pancreatic insufficiency as compared with healthy volunteers. MRCP visualizes fluid in the pancreatic and biliary ducts as high signal intensity on heavily T2-weighted sequences. However, visualization of normal or minimally dilated pancreatic ducts by MRCP is more challenging because of their small size. Secretin administration stimulates fluid and bicarbonate secretion by the exocrine pancreas; consequently, it improves the pancreatic duct and side-branch delineation and allows an evaluation of the exocrine pancreatic function. Side-branch ectasia, mild ductal dilatation with loss of the normal gentle taper, and mural irregularities are the pathognomonic MRCP features of early-stage chronic pancreatitis. Through measurement of the duodenal filling, secretin-MRCP allows quantitative assessment of the exocrine pancreatic function, even in patients with a mild exocrine insufficiency. The morphology of the pancreatic ducts, particularly in the early stages, does not always correlate with the functional status. MRCP permits visualization of the ductal changes and furnishes functional information on the pancreas; this combination may enhance its diagnostic accuracy so that MRCP can become a valuable diagnostic means in early-stage chronic pancreatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Otsuki (2004) ArticleTitleChronic pancreatitis. The problems of diagnostic criteria Pancreatology 4 28–41 Occurrence Handle14988656 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000077066
B Etemad DC Whitcomb (2001) ArticleTitleChronic pancreatitis: diagnosis, classification, and new genetic developments Gastroenterology 120 682–707 Occurrence Handle11179244 Occurrence Handle10.1053/gast.2001.22586 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7lvV2mtw%3D%3D
ML Steer I Waxman S Freedman (1995) ArticleTitleChronic pancreatitis N Eng J Med 332 1482–90 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199506013322206 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M3lvVSqtQ%3D%3D
S Kahl B Glasbrenner A Leodolter M Pross HU Schulz P Malfertheiner (2002) ArticleTitleEUS in the diagnosis of early chronic pancreatitis: a prospective follow-up study Gastrointest Endosc 55 507–11 Occurrence Handle11923762 Occurrence Handle10.1067/mge.2002.122610
MB Wallace RH Hawes (2001) ArticleTitleEndoscopic ultrasound in the evaluation and treatment of chronic pancreatitis Pancreas 23 26–35 Occurrence Handle11451144 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006676-200107000-00004 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FitVCktQ%3D%3D
R Tamura T Ishibashi S Takahashi (2006) ArticleTitleChronic pancreatitis: MRCP versus ERCP for quantitative caliber measurement and qualitative evaluation Radiology 238 920–8 Occurrence Handle16424235
FV Coakley LH Schwartz (1999) ArticleTitleMagnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography J Magn Reson Imaging 9 157–62 Occurrence Handle10077008 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1522-2586(199902)9:2<157::AID-JMRI2>3.0.CO;2-N Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7nsVKhtA%3D%3D
Y Takehara (1998) ArticleTitleCan MRCP replace ERCP? J Magn Reson Imaging 8 517–34 Occurrence Handle9626864 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3ovVGmsQ%3D%3D
C Villalba-Martin E Dominquez-Munoz (2005) Role of imaging methods in diagnosing, staging and detecting complications of chronic pancreatitis in clinical practice: should MRCP and MRI replace ERCP and CT? E Dominquez-Munoz (Eds) Clinical pancreatology EditionNumber1st ed Blackwell Oxford 236–45
AL Keppke FH Miller (2005) ArticleTitleMagnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas: the future is now Semin Ultrasound CT MR 26 IssueID3 132–52 Occurrence Handle15987063 Occurrence Handle10.1053/j.sult.2005.02.010
E Pamuklar RC Semelka (2005) ArticleTitleMR imaging of the pancreas Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 13 313–30 Occurrence Handle15935314 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.mric.2005.03.012
Zhang Xm H Shi L Parker M Dohke GA Holland DG Mitchell (2003) ArticleTitleSuspected early or mild chronic pancreatitis: enhancement patterns on gadolinium chelate dynamic MRI J Magn Reson Imaging 17 86–94 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jmri.10218
L Czakó J Endes T Takács K Boda J Lonovics (2001) ArticleTitleEvaluation of pancreatic exocrine function by means of secretin-enhanced MR cholangiopancreatography Pancreas 23 323–8 Occurrence Handle11590330 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006676-200110000-00015
KJ Hellerhoff H Helmberger Suffix3rd T Rosch MR Settles TM Link EJ Rummeny (2002) ArticleTitleDynamic MR pancreatography after secretin administration: image quality and diagnostic accuracy AJR Am J Roentgenol 179 121–9 Occurrence Handle12076919
R Manfredi G Costamagna MG Brizi G Maresca A Vecchioli C Colagrande et al. (2000) ArticleTitleSevere chronic pancreatitis versus suspected pancreatic disease: dynamic MR cholangiopancreatography after secretin stimulation Radiology 214 849–55 Occurrence Handle10715057 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7osV2ntA%3D%3D
JE Clain RK Pearson (1999) ArticleTitleDiagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. Is a gold standard necessary? Surg Clin North Am 79 829–45 Occurrence Handle10470330 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0039-6109(05)70046-3 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzpvFentw%3D%3D
PG Lankisch F Seidensticker J Otto H Lubbers R Mahlke F Stockmann et al. (1996) ArticleTitleSecretin-pancreozymin test (SPT) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): both are necessary for diagnosing or excluding chronic pancreatitis Pancreas 12 149–52 Occurrence Handle8720661 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28zkt12htg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006676-199603000-00007
P Malfertheiner M Büchler (1989) ArticleTitleCorrelation of imaging and function in chronic pancreatitis Radiol Clin North Am 27 51–64 Occurrence Handle2642276 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1M%2FlvVWjsQ%3D%3D
O Cappeliez M Delhaye J Deviére O Le Moine T Metens N Nicaise et al. (2000) ArticleTitleChronic pancreatitis: evaluation of pancreatic exocrine function with MR pancreatography after secretin stimulation Radiology 215 358–64 Occurrence Handle10796908 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3ls12ktg%3D%3D
MA Bali A Sztantics T Metens M Arvanitakis M Delhaye J Deviére et al. (2005) ArticleTitleQuantification of pancreatic exocrine function with secretin-enhanced magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: normal values and short-term effects of pancreatic duct drainage procedures in chronic pancreatitis Eur Radiol 15 2110–21 Occurrence Handle15991016 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00330-005-2819-5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2MvpslWltQ%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Czakó, L. Diagnosis of early-stage chronic pancreatitis by secretin-enhanced magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. J Gastroenterol 42 (Suppl 17), 113–117 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-006-1919-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-006-1919-6