Abstract
Background
Insufficient vascular supply is one of the main causes of anastomotic leak in colorectal surgery. Intraoperative indocyanine-green (ICG) angiography has been shown to provide information on tissue perfusion, identifying a well-perfused location for colonic and rectal transections, and thus possibly reducing the leak rate. Aim of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of intraoperative assessment of anastomotic perfusion using ICG angiography in patients undergoing left-sided colon or rectal resection with colorectal anastomosis.
Methods
This randomized trial involved 252 patients undergoing laparoscopic left-sided colon and rectal resection randomized 1:1 to intraoperative ICG or to subjective visual evaluation of the bowel perfusion without ICG. The primary aim was to assess whether ICG angiography could lead to a reduction in anastomotic leak rate. Secondary outcomes were possible changes in the surgical strategy and postoperative morbidity.
Results
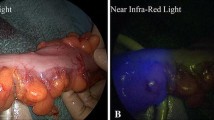
After randomization, 12 patients were excluded. Accordingly, 240 patients were included in the analysis; 118 were in the study group, and 122 in the control group. ICG angiography showed insufficient perfusion of the colic stump, which led to extended bowel resection in 13 cases (11%). An anastomotic leak developed in 11 patients (9%) in the control group and in 6 patients (5%) in the study group (p = n.s.).
Conclusions
Intraoperative ICG fluorescent angiography can effectively assess vascularization of the colic stump and anastomosis in patients undergoing colorectal resection. This method led to further proximal bowel resection in 13 cases, however, there was no statistically significant reduction of anastomotic leak rate in the ICG arm.
Clinical trial
ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02662946.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park JS1, Choi GS, Kim SH, Kim HR, Kim NK, Lee KY, Kang SB, Kim JY, Lee KY, Kim BC, Bae BN, Son GM, Lee SI, Kang H (2013) Multicenter analysis of risk factors for anastomotic leakage after laparoscopic rectal cancer excision: the Korean laparoscopic colorectal surgery study group. Ann Surg 257:665–671
Kang CY, Halabi WJ, Chaudhry OO, Nguyen V, Pigazzi A, Carmichael JC, Mills S, Stamos MJ (2013) Risk factors for anastomotic leakage after anterior resection for rectal cancer. JAMA Surg 148:65–71
Kingham TP1, Pachter HL (2009) Colonic anastomotic leak: risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. J Am Coll Surg 208:269–278
Buchs NC1, Gervaz P, Secic M, Bucher P, Mugnier-Konrad B, Morel P (2008) Incidence, consequences, and risk factors for anastomotic dehiscence after colorectal surgery: a prospective monocentric study. Int J Colorectal Dis 23:265–270
Mirnezami A, Mirnezami R, Chandrakumaran K, Sasapu K, Sagar P, Finan P (2011) Increased local recurrence and reduced survival from colorectal cancer following anastomotic leak: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 253:890–899
Vignali A, Gianotti L, Braga M, Radaelli G, Malvezzi L, Di Carlo V (2000) Altered microperfusion of the rectal stump is predictive for rectal anastomotic leak. Dis Colon Rectum 30:867–871
Urbanavičius L, Pattyn P, de Putte DV, Venskutonis D (2011) How to assess intestinal viability during surgery: A review of techniques. World J Gastrointest Surg 3:59–69
Luo S, Zhang E, Su Y, Cheng T, Shi C (2011) A review of NIR dyes in cancer targeting and imaging. Biomaterials 37:7127–7138
Gossedge G, Vallance A, Jayne D (2015) Diverse applications for near infra-red intraoperative imaging. Colorectal Dis 17(Suppl 3):7–11
Degett TH, Andersen HS, Gögenur I (2016) Indocyanine green fluorescence angiography for intraoperative assessment of gastrointestinal anastomotic perfusion: a systematic review of clinical trials. Langenbecks Arch Surg 401:767–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-016-1400-9
Dindo D, Clavien PA, Demartines N (2004) Classification of surgical complications. Ann Surg 240:205–213
Rahbari NN1, Weitz J, Hohenberger W, Heald RJ, Moran B, Ulrich A, Holm T, Wong WD, Tiret E, Moriya Y, Laurberg S, den Dulk M, van de Velde C, Büchler MW (2010) Definition and grading of anastomotic leakage following anterior resection of the rectum: a proposal by the International Study Group of Rectal Cancer. Surgery 147:339–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2009.10.012
Pommergaard HC, Gessler B, Burcharth J, Angenete E, Haglind E, Rosenberg J (2014) Preoperative risk factors for anastomotic leakage after resection for colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Colorectal Dis 16:662–671. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.12618
Guraieb-Trueba M, Frering T, Atallah S (2016) Combined endoscopic and laparoscopic real-time intra-operative evaluation of bowel perfusion using fluorescence angiography. Tech Coloproctol 20:883–884
Karliczek A, Harlaar NJ, Zeebregts CJ, Wiggers T, Baas PC, van Dam GM (2009) Surgeons lack predictive accuracy for anastomotic leakage in gastrointestinal surgery. Int J Colorectal Dis 24:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-009-0658-6
Cahill RA, Ris F, Mortensen NJ (2011) Near-infrared laparoscopy for real-time intra-operative arterial and lymphatic perfusion imaging. Colorectal Dis 13:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1318.2011.02772.x
Ris F, George B, Cahill RA, Mortensen NJ (2014) Near-infrared (NIR) perfusion angiography in minimally invasive colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc 28:2221–2226
Boni L, David G, Dionigi G, Rausei S, Cassinotti E, Fingerhut A (2016) Indocyanine green-enhanced fluorescence to assess bowel perfusion during laparoscopic colorectal resection. Surg Endosc 30:2736–2742
Kudszus S, Roesel C, Schachtrupp A, Höer JJ (2010) Intraoperative laser fluorescence angiography in colorectal surgery: a noninvasive analysis to reduce the rate of anastomotic leakage. Langenbecks Arch Surg 395:1025–1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-010-0699-x
Paun BC, Cassie S, MacLean AR, Dixon E, Buie WD (2010) Postoperative complications following surgery for rectal cancer. Ann Surg 251:807–818. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181dae4ed
Guillou PJ, Quirke P, Thorpe H et al (2005) Short-term endpoints of conventional versus laparoscopic-assisted surgery in patients with colorectal cancer (MRC CLASICC trial): multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 365:1718e1726
van der Pas MH, Haglind E, Cuesta MA, Fürst A, Lacy AM, Hop WCJ, Bonjer HJ, COLOR II Study Group (2013) Laparoscopic versus open surgery for rectal cancer (COLOR II): short-term outcomes of a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14:210–218
Braga M, Frasson M, Zuliani W, Vignali A, Pecorelli N, Di Carlo V (2010) Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic versus open left colonic resection. Br J Surg 97:1180–1186. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.7094
Parthasarathy M, Greensmith M, Bowers D, Groot-Wassink T (2017) Risk factors for anastomotic leakage after colorectal resection: a retrospective analysis of 17 518 patients. Colorectal Dis 19:288–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.13476
Alves A, Panis Y, Trancart D et al (2002) Factors associated with clinically significant anastomotic leakage after large bowel resection: multivariate analysis of 707 patients. World J Surg 26:499–502
Van den Bos J, Al-Taher M, Schols RM, van Kuijk S, Bouvy ND, Stassen LPS (2018) Near-infrared fluorescence imaging for real-time intraoperative guidance in anastomotic colorectal surgery: a systematic review of literature. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 28:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2017.0231
Foppa C, Denoya PI, Tarta C, Bergamaschi R (2014) Indocyanine green fluorescent dye during bowel surgery: are the blood supply “guessing days”. over? Techol Coloproctol 18:753–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10151-014-1130-3
Hellan M, Spinoglio G, Pigazzi A, Lagares-Garcia JA (2014) The influence of fluorescence imaging on the location of bowel transection during robotic left-sided colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc 28:1695–1702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3377-6
Jafari MD, Wexner SD, Martz JE, McLemore EC, Margolin DA, Sherwinter DA, Lee SW, Senagore AJ, Phelan MJ, Stamos MJ (2015) Perfusion assessment in laparoscopic left-sided/anterior resection (PILLAR II): a multi-institutional study. J Am Coll Surg 220:82–92.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2014.09.015
Boni L, Fingerhut A, Marzorati A, Rausei S, Dionigi G, Cassinotti E (2016) Indocyanine green fluorescence angiography during laparoscopic low anterior resection: results of a case-matched study. Surg Endosc 31:1836–1840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5181-6
Kin C, Vo H, Welton L, Welton M (2015) Equivocal effect of intraoperative fluorescence angiography on colorectal anastomotic leaks. Dis Colon Rectum 58:582–587. https://doi.org/10.1097/DCR.0000000000000320
Jafari MD, Lee KH, Halabi WJ, Mills SD, Carmichael JC, Stamos MJ, Pigazzi A (2013) The use of indocyanine green fluorescence to assess anastomotic perfusion during robotic assisted laparoscopic rectal surgery. Surg Endosc 27:3003–3008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2832-8
Hope-Ross M, Yannuzzi LA, Gragoudas ES, Guyer DR, Slakter JS, Sorenson JA, Krupsky S, Orlock DA, Puliafito CA (1994) Adverse reactions due to indocyanine green. Ophthalmology 101:529–533
Funding
No funding was received in support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
P. De Nardi, U. Elmore, G. Maggi, R. Maggiore, L. Boni, E. Cassinotti, U. Fumagalli, M. Gardani, S. De Pascale, P. Parise, A. Vignali, and R. Rosati have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Nardi, P., Elmore, U., Maggi, G. et al. Intraoperative angiography with indocyanine green to assess anastomosis perfusion in patients undergoing laparoscopic colorectal resection: results of a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc 34, 53–60 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06730-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06730-0